Abstract
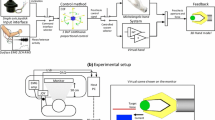
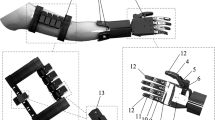
This chapter describes the implementation of a neural network-based predictive control system for driving a prosthetic hand. Nonlinearities associated with the electromechanical aspects of prosthetic devices present great challenges for precise control of this type of device. Model-based controllers may overcome this issue. Moreover, given the complexity of these kinds of electromechanical systems, neural network-based modeling arises as a good fit for modeling the fingers’ dynamics. The results of simulations mimicking potential situations encountered during activities of daily living demonstrate the feasibility of this technique.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Smith RJ, Tenore F, Huberdeau D et al (2008) Continuous decoding of finger position from surface EMG signals for the control of powered prostheses. 30th Annual international conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, 20–25 Aug 2008, pp 197–200
Matrone G, Cipriani C, Secco EL et al (2009) Bio-inspired controller for a dexterous prosthetic hand based on principal components analysis. Annual international conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, 3–6 Sep 2009, pp 5022–5025
Jingdong Z, Li J, Shicai S et al (2006) A five-fingered underactuated prosthetic hand system. Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on mechatronics and automation, 25–28 Jun 2006, pp 1453–1458
Jingdong Z, Zongwu X, Li J et al (2005) Levenberg-Marquardt based neural network control for a five-fingered prosthetic hand. Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on robotics and automation, 18–22 Apr 2005, pp 4482–4487
Zajdlik J (2006) The preliminary design and motion control of a five-fingered prosthetic hand. Proceedings of the international conference on intelligent engineering systems, 0-0 0, pp 202–206
Dapeng Y, Jingdong Z, Yikun G et al (2009) EMG pattern recognition and grasping force estimation: improvement to the myocontrol of multi-DOF prosthetic hands. IEEE/RSJ international conference on intelligent robots and systems, 10–15 Oct 2009, pp 516–521
Tsujiuchi N, Takayuki K, Yoneda M (2004) Manipulation of a robot by EMG signals using linear multiple regression model. Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ international conference on intelligent robots and systems, vol 1992, 28 Sep–2 Oct 2004, pp 1991–1996
Jingdong Z, Zongwu X, Li J et al (2006) EMG control for a five-fingered underactuated prosthetic hand based on wavelet transform and sample entropy. International conference on intelligent robots and systems, 9–15 Oct 2006, pp 3215–3220
Weir RF, Ajiboye AB (2003) A multifunction prosthesis controller based on fuzzy-logic techniques. Proceedings of the 25th annual international conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, vol 1672, 17–21 Sep 2003, pp 1678–1681
Pylatiuk C, Mounier S, Kargov A et al (2004) Progress in the development of a multifunctional hand prosthesis. 26th Annual international conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, 1–5 Sep 2004, pp 4260–4263
Cipriani C, Antfolk C, Balkenius C et al (2009) A novel concept for a prosthetic hand with a bidirectional interface: a feasibility study. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 56(11):2739–2743. doi:10.1109/TBME.2009.2031242
Panarese A, Edin BB, Vecchi F et al (2009) Humans can integrate force feedback to toes in their sensorimotor control of a robotic hand. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng 17(6):560–567. doi:10.1109/TNSRE.2009.2021689
Rodriguez-Cheu LE, Casals A (2006) Sensing and control of a prosthetic hand with myoelectric feedback. The first IEEE/RAS-EMBS international conference on biomedical robotics and biomechatronics, 20–22 Feb 2006, pp 607–612
Dhillon GS, Horch KW (2005) Direct neural sensory feedback and control of a prosthetic arm. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng 13(4):468–472. doi:10.1109/TNSRE.2005.856072
Lundborg G, Rosén B (2001) Sensory substitution in prosthetics. Hand Clin 17(3):481–488
Mangieri E, Ahmadi A, Maharatna K et al (2008) A novel analogue circuit for controlling prosthetic hands. IEEE biomedical circuits and systems conference, 20–22 Nov 2008, pp 81–84
Wettels N, Parnandi AR, Moon JH et al (2009) Grip control using biomimetic tactile sensing systems. IEEE/ASME Trans Mechatron 14(6):718–723
Tura A, Lamberti C, Davalli A et al (1998) Experimental development of a sensory control system for an upper limb myoelectric prosthesis with cosmetic covering. J Rehabil Res Dev 35(1):14–26
Engeberg ED, Meek SG (2008) Adaptive object slip prevention for prosthetic hands through proportional-derivative shear force feedback. IEEE/RSJ International conference on intelligent robots and systems, 22–26 Sep 2008, pp 1940–1945
Engeberg ED, Meek S (2008) Improved grasp force sensitivity for prosthetic hands through force-derivative feedback. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 55(2):817–821
Engeberg ED, Meek SG, Minor MA (2008) Hybrid force-velocity sliding mode control of a prosthetic hand. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 55(5):1572–1581
Zhao DW, Jiang L, Huang H et al (2006) Development of a multi-DOF anthropomorphic prosthetic hand. International conference on robotics and biomimetics, 17–20 Dec 2006, pp 878–883
Cipriani C, Zaccone F, Stellin G et al (2006) Closed-loop controller for a bio-inspired multi-fingered underactuated prosthesis. Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on robotics and automation, 15–19 May 2006, pp 2111–2116
Carrozza MC, Cappiello G, Micera S et al (2006) Design of a cybernetic hand for perception and action. Biol Cybern 95(6):629–644
Light CM, Chappell PH, Hudgins B et al (2002) Intelligent multifunction myoelectric control of hand prostheses. J Med Eng Technol 26(4):139–146
Connolly C (2008) Prosthetic hands from Touch Bionics. Ind Rob 35(4):290–293
Engeberg ED, Meek SG (2013) Adaptive sliding mode control for prosthetic hands to simultaneously prevent slip and minimize deformation of grasped objects. IEEE/ASME Trans Mechatron 18(1):376–385. doi:10.1109/TMECH.2011.2179061
Andrecioli R, Engeberg ED (2013) Adaptive sliding manifold slope via grasped object stiffness detection with a prosthetic hand. Mechatronics 23(8):1171–1179
Peerdeman B, Fabrizi U, Palli G et al (2012) Development of prosthesis grasp control systems on a robotic testbed. 4th IEEE RAS & EMBS international conference on biomedical robotics and biomechatronics, 24–27 Jun 2012, pp 1110–1115
Luo Z-z, Wang F, Wang R-c (2006) Study of multi-freedom myoelectric prostheses with tactile sense. 27th Annual international conference of the Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, 17–18 Jan 2006, pp 3004–3007
Cipriani C, Zaccone F, Micera S et al (2008) On the shared control of an EMG-controlled prosthetic hand: analysis of user-prosthesis interaction. IEEE Transactions on Robotics 24(1):170–184. doi:10.1109/TRO.2007.910708
Cipriani C, Controzzi M, Vecchi F et al (2008) Embedded hardware architecture based on microcontrollers for the action and perception of a transradial prosthesis. 2nd IEEE RAS & EMBS International conference on biomedical robotics and biomechatronics, 19–22 Oct 2008, pp 848–853
Rodriguez-Cheu LE, Gonzalez D, Rodriguez M () Result of a perceptual feedback of the grasping forces to prosthetic hand users. 2nd IEEE RAS & EMBS international conference on biomedical robotics and biomechatronics, 19–22 Oct 2008, pp 901–906
Pasluosta CF (2010) Nonlinear control strategy for a cost effective myoelectric prosthetic hand. Dissertation, Lousiana Tech University, Ruston, Lousiana, USA
Pasluosta CF, Chiu AWL (2012) Evaluation of a neural network-based control strategy for a cost-effective externally-powered prosthesis. Assist Technol 24(3):196–208
Norgaard M, Ravn O, Poulsen NK, Hansen LK (2000) Neural networks for modelling and control of dynamic systems: a practitioner’s handbook. Advanced textbooks in control and signal processing. Springer, Great Britain
Hornik K, Stinchcombe M, White H (1989) Multilayer feedforward networks are universal approximators. Neural Netw 2(5):359–366
Dahunsi OA, Pedro JO, Nyandoro OT (2009) Neural network-based model predictive control of a servo-hydraulic vehicle suspension system. AFRICON ‘09, 23–25 Sep 2009, pp 1–6
Haichen Y, Zhijun Z (2006) Predictive control based on neural networks of the chemical process. Chinese Control Conference, 7–11 Aug 2006, pp 1143–1147
Bandyopadhyay B (2005) Neural network based predictive controller (NNPC): an investigation into its application in Textiles. International conference on computational intelligence for modelling, control and automation and international conference on intelligent agents, web technologies and internet commerce, 28–30 Nov 2005, pp 963–967
Jianbin H, Shaohua T, Vandewalle J (1993) One step ahead predictive control of nonlinear systems by neural networks. Proceedings of international joint conference on neural networks, vol 2763, 25–29 Oct 1993, pp 2761–2764
Soloway D, Haley P (2001) Aircraft reconfiguration using neural generalized predictive control. Proceedings of the 2001 American Control Conference, 2001, vol 2924, pp 2924–2929
Qiang S, Fang L, Findlay RD (2006) Generalized predictive control for a pneumatic system based on an optimized ARMAX model with an artificial neural network. International conference on computational intelligence for modelling, control and automation and international conference on intelligent agents, web technologies and internet commerce, Nov 28–Dec 1 2006, pp 223–223
Haley P, Soloway D, Gold B (1999) Real-time adaptive control using neural generalized predictive control. Proceedings of the American Control Conference, vol 4276, 1999, pp 4278–4282
Noriega JR, Wang H (1998) A direct adaptive neural-network control for unknown nonlinear systems and its application. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 9(1):27–34
Norgaard M, Ravn O, Poulsen NK (2001) NNSYSID and NNCTRL tools for system identification and control with neural networks. Computing and Control Engineering Journal 12(1):29–36
Gunji D, Mizoguchi Y, Teshigawara S et al (2008) Grasping force control of multi-fingered robot hand based on slip detection using tactile sensor. IEEE international conference on robotics and automation, 19–23 May 2008, pp 2605–2610
Schuurmans J, Van Der Linde RQ, Plettenburg DH et al (2007) Grasp force optimization in the design of an underactuated robotic hand. IEEE 10th international conference on rehabilitation robotics, 13–15 Jun 2007, pp 776–782
Kamikawa Y, Maeno T (2008) Underactuated five-finger prosthetic hand inspired by grasping force distribution of humans. IEEE/RSJ international conference on intelligent robots and systems, 22–26 Sep 2008, pp 717–722
Acknowledgement
This work was supported by the NIH NCRR INBRE grant P20RR016456, and the Louisiana Board of Regents RCS LEQSF(2007-10)-RD-A-20.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2015 Springer Science+Business Media New York
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Pasluosta, C.F., Chiu, A.W.L. (2015). Modulation of Grasping Force in Prosthetic Hands Using Neural Network-Based Predictive Control. In: Cartwright, H. (eds) Artificial Neural Networks. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 1260. Springer, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-2239-0_11
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-2239-0_11
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-4939-2238-3
Online ISBN: 978-1-4939-2239-0
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols