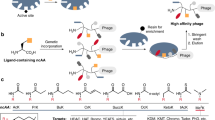
Abstract
Protein kinases are implicated in diverse signaling cascades and have been targeted with small molecules that typically bind the conserved ATP-binding active site. These inhibitors are often promiscuous and target multiple protein kinases, which has led to the development of alternate strategies to discover selective ligands. We have recently described a fragment-based selection approach, where a small-molecule warhead can be non-covalently tethered to a phage-displayed library of cyclic peptides. This approach led to the conversion of the promiscuous kinase inhibitor, staurosporine, into a selective bivalent inhibitor.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hunter T, Cooper JA (1985) Protein-tyrosine kinases. Annu Rev Biochem 54:897–930
Levitzki A, Gazit A (1995) Tyrosine kinase inhibition—an approach to drug development. Science 267:1782–1788
Kyriakis JM, Avruch J (2012) Mammalian Mapk signal transduction pathways activated by stress and inflammation: a 10-year update. Physiol Rev 92:689–737
Karaman MW, Herrgard S, Treiber DK, Gallant P, Atteridge CE, Campbell BT, Chan KW, Ciceri P, Davis MI, Edeen PT, Faraoni R, Floyd M, Hunt JP, Lockhart DJ, Milanov ZV, Morrison MJ, Pallares G, Patel HK, Pritchard S, Wodicka LM, Zarrinkar PP (2008) A quantitative analysis of kinase inhibitor selectivity. Nat Biotechnol 26:127–132
Bishop AC, Ubersax JA, Petsch DT, Matheos DP, Gray NS, Blethrow J, Shimizu E, Tsien JZ, Schultz PG, Rose MD, Wood JL, Morgan DO, Shokat KM (2000) A chemical switch for inhibitor-sensitive alleles of any protein kinase. Nature 407:395–401
Zhang JM, Adrian FJ, Jahnke W, Cowan-Jacob SW, Li AG, Iacob RE, Sim T, Powers J, Dierks C, Sun FX, Guo GR, Ding Q, Okram B, Choi Y, Wojciechowski A, Deng XM, Liu GX, Fendrich G, Strauss A, Vajpai N, Grzesiek S, Tuntland T, Liu Y, Bursulaya B, Azam M, Manley PW, Engen JR, Daley GQ, Warmuth M, Gray NS (2010) Targeting Bcr-Abl by combining allosteric with ATP-binding-site inhibitors. Nature 463:501–506
Lamba V, Ghosh I (2012) New directions in targeting protein kinases: focusing upon true allosteric and bivalent inhibitors. Curr Pharm Des 18:2936–2945
Jencks WP (1981) On the attribution and additivity of binding-energies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 78:4046–4050
Chen JH, Zhang ZM, Stebbins JL, Zhang XY, Hoffman R, Moore A, Pellecchia M (2007) A fragment-based approach for the discovery of isoform-specific p38alpha inhibitors. ACS Chem Biol 2:329–336
Hill ZB, Perera BGK, Maly DJ (2009) A chemical genetic method for generating bivalent inhibitors of protein kinases. J Am Chem Soc 131:6686
Hill ZB, Perera BGK, Andrews SS, Maly DJ (2012) Targeting diverse signaling interaction sites allows the rapid generation of bivalent kinase inhibitors. ACS Chem Biol 7:487–495
Ricouart A, Gesquiere JC, Tartar A, Sergheraert C (1991) Design of potent protein-kinase inhibitors using the bisubstrate approach. J Med Chem 34:73–78
Parang K, Till JH, Ablooglu AJ, Kohanski RA, Hubbard SR, Cole PA (2001) Mechanism-based design of a protein kinase inhibitor. Nat Struct Biol 8:37–41
Erlanson DA, Braisted AC, Raphael DR, Randal M, Stroud RM, Gordon EM, Wells JA (2000) Site-directed ligand discovery. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97:9367–9372
Smith GP (1985) Filamentous fusion phage—novel expression vectors that display cloned antigens on the virion surface. Science 228:1315–1317
Smith GP, Petrenko VA (1997) Phage display. Chem Rev 97:391–410
Meyer SC, Shomin CD, Gaj T, Ghosh I (2007) Tethering small molecules to a phage display library: discovery of a selective bivalent inhibitor of protein kinase A. J Am Chem Soc 129:13812
Shomin CD, Restituyo E, Cox KJ, Ghosh I (2011) Selection of cyclic-peptide inhibitors targeting Aurora kinase A: problems and solutions. Bioorg Med Chem 19:6743–6749
Merrifield RB (1963) Solid phase peptide synthesis. 1. The synthesis of a tetrapeptide. J Am Chem Soc 85:2149–2154
Shomin CD, Meyer SC, Ghosh I (2009) Staurosporine tethered peptide ligands that target cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA): optimization and selectivity profiling. Bioorg Med Chem 17:6196–6202
King DS, Fields CG, Fields GB (1990) A cleavage method which minimizes side reactions following Fmoc solid-phase peptide-synthesis. Int J Pept Protein Res 36:255–266
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2015 Springer Science+Business Media New York
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Restituyo, E., Camacho-Soto, K., Ghosh, I. (2015). A Fragment-Based Selection Approach for the Discovery of Peptide Macrocycles Targeting Protein Kinases. In: Derda, R. (eds) Peptide Libraries. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 1248. Humana Press, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-2020-4_7
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-2020-4_7
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana Press, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-4939-2019-8
Online ISBN: 978-1-4939-2020-4
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols