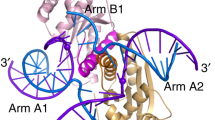
Abstract
The left-handed Z-DNA is surrounded by right-handed canonical B-DNA, and thus the junction between B- and Z-DNA has been occurred during temporal Z-DNA formation in the genome. The base extrusion structure of the BZ junction may help detect Z-DNA formation in DNAs. Here we describe the BZ junction structural detection by using 2-aminopurine (2AP) fluorescent probe. BZ junction formation can be measured in solution by this method.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang AH, Quigley GJ, Kolpak FJ, Crawford JL, van Boom JH, van der Marel G, Rich A (1979) Molecular structure of a left-handed double helical DNA fragment at atomic resolution. Nature 282(5740):680–686. https://doi.org/10.1038/282680a0
Schwartz T, Behlke J, Lowenhaupt K, Heinemann U, Rich A (2001) Structure of the DLM-1-Z-DNA complex reveals a conserved family of Z-DNA-binding proteins. Nat Struct Biol 8(9):761–765. https://doi.org/10.1038/nsb0901-761
Ha SC, Lokanath NK, Van Quyen D, Wu CA, Lowenhaupt K, Rich A, Kim YG, Kim KK (2004) A poxvirus protein forms a complex with left-handed Z-DNA: crystal structure of a Yatapoxvirus Zalpha bound to DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101(40):14367–14372. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0405586101
Kim D, Hur J, Park K, Bae S, Shin D, Ha SC, Hwang HY, Hohng S, Lee JH, Lee S, Kim YG, Kim KK (2014) Distinct Z-DNA binding mode of a PKR-like protein kinase containing a Z-DNA binding domain (PKZ). Nucleic Acids Res 42(9):5937–5948. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gku189
Schwartz T, Rould MA, Lowenhaupt K, Herbert A, Rich A (1999) Crystal structure of the Zalpha domain of the human editing enzyme ADAR1 bound to left-handed Z-DNA. Science 284(5421):1841–1845. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.284.5421.1841
Wittig B, Dorbic T, Rich A (1991) Transcription is associated with Z-DNA formation in metabolically active permeabilized mammalian cell nuclei. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 88(6):2259–2263. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.88.6.2259
Kim D, Lee YH, Hwang HY, Kim KK, Park HJ (2010) Z-DNA binding proteins as targets for structure-based virtual screening. Curr Drug Targets 11(3):335–344. https://doi.org/10.2174/138945010790711905
Wang G, Christensen LA, Vasquez KM (2006) Z-DNA-forming sequences generate large-scale deletions in mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103(8):2677–2682. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0511084103
Herbert A (2019) Z-DNA and Z-RNA in human disease. Commun Biol 2:7. https://doi.org/10.1038/s42003-018-0237-x
Beknazarov N, Jin S, Poptsova M (2020) Deep learning approach for predicting functional Z-DNA regions using omics data. Sci Rep 10(1):19134. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-76203-1
Vongsutilers V, Gannett PM (2018) C8-Guanine modifications: effect on Z-DNA formation and its role in cancer. Org Biomol Chem 16(13):2198–2209. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8ob00030a
Zhabinskaya D, Benham CJ (2011) Theoretical analysis of the stress induced B-Z transition in superhelical DNA. PLoS Comput Biol 7(1):e1001051. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1001051
Schroth GP, Chou PJ, Ho PS (1992) Mapping Z-DNA in the human genome. Computer-aided mapping reveals a nonrandom distribution of potential Z-DNA-forming sequences in human genes. J Biol Chem 267(17):11846–11855
Ha SC, Lowenhaupt K, Rich A, Kim YG, Kim KK (2005) Crystal structure of a junction between B-DNA and Z-DNA reveals two extruded bases. Nature 437(7062):1183–1186. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature04088
Kim D, Hur J, Han JH, Ha SC, Shin D, Lee S, Park S, Sugiyama H, Kim KK (2018) Sequence preference and structural heterogeneity of BZ junctions. Nucleic Acids Res 46(19):10504–10513. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gky784
Larsen OF, van Stokkum IH, Gobets B, van Grondelle R, van Amerongen H (2001) Probing the structure and dynamics of a DNA hairpin by ultrafast quenching and fluorescence depolarization. Biophys J 81(2):1115–1126. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0006-3495(01)75768-2
Holz B, Klimasauskas S, Serva S, Weinhold E (1998) 2-aminopurine as a fluorescent probe for DNA base flipping by methyltransferases. Nucleic Acids Res 26(4):1076–1083. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/26.4.1076
Kim D, Reddy S, Kim DY, Rich A, Lee S, Kim KK, Kim YG (2009) Base extrusion is found at helical junctions between right- and left-handed forms of DNA and RNA. Nucleic Acids Res 37(13):4353–4359. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkp364
Subramani VK, Ravichandran S, Bansal V, Kim KK (2019) Chemical-induced formation of BZ-junction with base extrusion. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 508(4):1215–1220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.12.045
Subramani VK, Kim D, Yun K, Kim KK (2016) Structural and functional studies of a large winged Z-DNA-binding domain of Danio rerio protein kinase PKZ. FEBS Lett 590(14):2275–2285. https://doi.org/10.1002/1873-3468.12238
Ho PS, Ellison MJ, Quigley GJ, Rich A (1986) A computer aided thermodynamic approach for predicting the formation of Z-DNA in naturally occurring sequences. EMBO J 5(10):2737–2744
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Ministry of Education, Science, and Technology (MSIT) of the Korean government (2020RC1C1C1007371 to D.K.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Kang, M., Kim, D. (2023). BZ Junctions and Its Application as Probe (2AP) to Detect Z-DNA Formation and Its Effector. In: Kim, K.K., Subramani, V.K. (eds) Z-DNA. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 2651. Humana, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-3084-6_7
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-3084-6_7
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-0716-3083-9
Online ISBN: 978-1-0716-3084-6
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols