Abstract
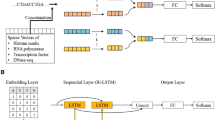
Here we describe an approach that uses deep learning neural networks such as CNN and RNN to aggregate information from DNA sequence; physical, chemical, and structural properties of nucleotides; and omics data on histone modifications, methylation, chromatin accessibility, and transcription factor binding sites and data from other available NGS experiments. We explain how with the trained model one can perform whole-genome annotation of Z-DNA regions and feature importance analysis in order to define key determinants for functional Z-DNA regions.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li H, Xiao J, Li J, Lu L, Feng S, Droge P (2009) Human genomic Z-DNA segments probed by the Z alpha domain of ADAR1. Nucleic Acids Res 37(8):2737–2746. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkp124
Herbert A (2020) ALU non-B-DNA conformations, flipons, binary codes and evolution. R Soc Open Sci 7(6):200222. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsos.200222
Herbert A, Alfken J, Kim YG, Mian IS, Nishikura K, Rich A (1997) A Z-DNA binding domain present in the human editing enzyme, double-stranded RNA adenosine deaminase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 94(16):8421–8426. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.94.16.8421
Shin SI, Ham S, Park J, Seo SH, Lim CH, Jeon H, Huh J, Roh TY (2016) Z-DNA-forming sites identified by ChIP-Seq are associated with actively transcribed regions in the human genome. DNA Res 23:477. https://doi.org/10.1093/dnares/dsw031
Singh R, Lanchantin J, Robins G, Qi Y (2016) DeepChrome: deep-learning for predicting gene expression from histone modifications. Bioinformatics 32(17):i639–i648. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btw427
Sekhon A, Singh R, Qi Y (2018) DeepDiff: DEEP-learning for predicting DIFFerential gene expression from histone modifications. Bioinformatics 34(17):i891–i900. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bty612
Yin Q, Wu M, Liu Q, Lv H, Jiang R (2019) DeepHistone: a deep learning approach to predicting histone modifications. BMC Genomics 20(Suppl 2):193. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-019-5489-4
Ben-Bassat I, Chor B, Orenstein Y (2018) A deep neural network approach for learning intrinsic protein-RNA binding preferences. Bioinformatics 34(17):i638–i646. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bty600
Li Y, Shi W, Wasserman WW (2018) Genome-wide prediction of cis-regulatory regions using supervised deep learning methods. BMC Bioinform 19(1):202. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12859-018-2187-1
Beknazarov N, Jin S, Poptsova M (2020) Deep learning approach for predicting functional Z-DNA regions using omics data. Sci Rep 10(1):19134. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-76203-1
Wu T, Lyu R, You Q, He C (2020) Kethoxal-assisted single-stranded DNA sequencing captures global transcription dynamics and enhancer activity in situ. Nat Methods 17(5):515–523. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41592-020-0797-9
Kouzine F, Wojtowicz D, Baranello L, Yamane A, Nelson S, Resch W, Kieffer-Kwon KR, Benham CJ, Casellas R, Przytycka TM, Levens D (2017) Permanganate/S1 nuclease footprinting reveals non-B DNA structures with regulatory potential across a mammalian genome. Cell Syst 4(3):344–356. e347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cels.2017.01.013
Amemiya HM, Kundaje A, Boyle AP (2019) The ENCODE blacklist: identification of problematic regions of the genome. Sci Rep 9(1):9354. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-45839-z
Ho PS, Ellison MJ, Quigley GJ, Rich A (1986) A computer aided thermodynamic approach for predicting the formation of Z-DNA in naturally occurring sequences. EMBO J 5(10):2737–2744
Gao Y, Li L, Yuan P, Zhai F, Ren Y, Yan L, Li R, Lian Y, Zhu X, Wu X, Kee K, Wen L, Qiao J, Tang F (2020) 5-Formylcytosine landscapes of human preimplantation embryos at single-cell resolution. PLoS Biol 18(7):e3000799. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.3000799
Alipanahi B, Delong A, Weirauch MT, Frey BJ (2015) Predicting the sequence specificities of DNA- and RNA-binding proteins by deep learning. Nat Biotechnol 33(8):831–838. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.3300
Kalkatawi M, Magana-Mora A, Jankovic B, Bajic VB (2019) DeepGSR: an optimized deep-learning structure for the recognition of genomic signals and regions. Bioinformatics 35(7):1125–1132. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bty752
Simonyan K, Vedaldi A, Zisserman A (2013) Deep inside convolutional networks: visualising image classification models and saliency maps. arXiv preprint arXiv:13126034
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Beknazarov, N., Poptsova, M. (2023). DeepZ: A Deep Learning Approach for Z-DNA Prediction. In: Kim, K.K., Subramani, V.K. (eds) Z-DNA. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 2651. Humana, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-3084-6_15
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-3084-6_15
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-0716-3083-9
Online ISBN: 978-1-0716-3084-6
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols