Abstract
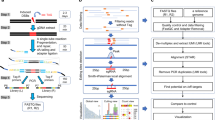
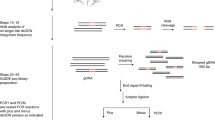
The clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats (CRISPR)-Caspase9 (Cas9) system provides a programmable technology that may be used to edit the eukaryotic genome and epigenome. CRISPR/Cas9 includes a guide RNA targeted to a gene of interest which hybridizes to a nucleotide sequence next to a protospacer-adjacent motif (PAM) which guides the Cas9 endonucleases to the target site for cleavage via double-strand breaks. A caveat of the CRISPR/Cas9 system is the creation of off-target double-strand breaks (DSBs) which may result in anomalous insertions, deletions, and translocations. Thus, assays for the sensitive detection and analysis of off-target editing are critical. Here, we describe currently available CRISPR technologies, CRISPR applications, and current analysis platforms to detect off-target effects including genome-wide, unbiased identification of DSBs enabled by sequencing (GUIDE-Seq), high-throughput genomic translocation sequencing (HTGTS), breaks labeling, enrichments on streptavidin and next-generation sequencing (BLESS), and in vitro nuclease-digested genome sequencing (Digenome-seq).
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jinek M et al (2012) A programmable dual-RNA-guided DNA endonuclease in adaptive bacterial immunity. Science 337(6096):816–821
Sander JD, Joung JK (2014) CRISPR-Cas systems for editing, regulating and targeting genomes. Nat Biotechnol 32(4):347–355
Hsu PD et al (2013) DNA targeting specificity of RNA-guided Cas9 nucleases. Nat Biotechnol 31(9):827–832
Koo T, Lee J, Kim JS (2015) Measuring and reducing off-target activities of programmable nucleases including CRISPR-Cas9. Mol Cells 38(6):475–481
Cho SW et al (2014) Analysis of off-target effects of CRISPR/Cas-derived RNA-guided endonucleases and nickases. Genome Res 24(1):132–141
Urnov FD et al (2005) Highly efficient endogenous human gene correction using designed zinc-finger nucleases. Nature 435(7042):646–651
Kim D et al (2015) Digenome-seq: genome-wide profiling of CRISPR-Cas9 off-target effects in human cells. Nat Methods 12(3):237–243. 1 p following 243
Chiarle R et al (2011) Genome-wide translocation sequencing reveals mechanisms of chromosome breaks and rearrangements in B cells. Cell 147(1):107–119
Frock RL et al (2015) Genome-wide detection of DNA double-stranded breaks induced by engineered nucleases. Nat Biotechnol 33(2):179–186
Martin F et al (2016) Biased and unbiased methods for the detection of off-target cleavage by CRISPR/Cas9: an overview. Int J Mol Sci 17(9):1507
Tsai SQ et al (2015) GUIDE-seq enables genome-wide profiling of off-target cleavage by CRISPR-Cas nucleases. Nat Biotechnol 33(2):187–197
Crosetto N et al (2013) Nucleotide-resolution DNA double-strand break mapping by next-generation sequencing. Nat Methods 10(4):361–365
Zhang XH et al (2015) Off-target effects in CRISPR/Cas9-mediated genome engineering. Mol Ther Nucl Acids 4:e264
Zischewski J, Fischer R, Bortesi L (2017) Detection of on-target and off-target mutations generated by CRISPR/Cas9 and other sequence-specific nucleases. Biotechnol Adv 35(1):95–104
Kim E et al (2012) Precision genome engineering with programmable DNA-nicking enzymes. Genome Res 22(7):1327–1333
Ran FA et al (2013) Double nicking by RNA-guided CRISPR Cas9 for enhanced genome editing specificity. Cell 154(6):1380–1389
Mali P et al (2013) CAS9 transcriptional activators for target specificity screening and paired nickases for cooperative genome engineering. Nat Biotechnol 31(9):833–838
Kim S et al (2014) Highly efficient RNA-guided genome editing in human cells via delivery of purified Cas9 ribonucleoproteins. Genome Res 24(6):1012–1019
Zuris JA et al (2015) Cationic lipid-mediated delivery of proteins enables efficient protein-based genome editing in vitro and in vivo. Nat Biotechnol 33(1):73–80
Ramakrishna S et al (2014) Gene disruption by cell-penetrating peptide-mediated delivery of Cas9 protein and guide RNA. Genome Res 24(6):1020–1027
Waltz E (2018) With a free pass, CRISPR-edited plants reach market in record time. Nat Biotechnol 36(1):6–7
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Ethics declarations
Stephen H. Tsang receives financial support from Abeona Therapeutics, Inc and Emendo. He is also the founder of Rejuvitas and is on the scientific and clinical advisory board for Nanoscope Therapeutics.
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Xu, C.L., Ruan, M.Z., Ragi, S.D., Tsang, S.H. (2023). CRISPR Off-Target Analysis Platforms. In: Tsang, S.H., Quinn, P.M. (eds) Retinitis Pigmentosa. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 2560. Humana, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-2651-1_26
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-2651-1_26
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-0716-2650-4
Online ISBN: 978-1-0716-2651-1
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols