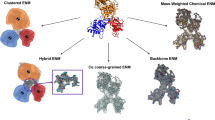
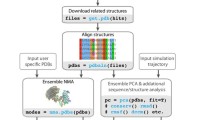
Abstract
Over the past decade, concepts of network theory in combination with dynamical information from conformational ensembles have been widely applied to gain insights in understanding allosteric regulation in biomolecules. In this chapter, we introduce the basic theories and protocols used in protein dynamics network analysis through a series of interactive python Jupyter notebook scripts. While various network analysis methods exist in the literature, here we focus on the two popular methods based on correlated atomic motions and pairwise interaction energies. While the tutorial is based on a small prototypic protein, the workflow and protocol introduced here are optimized to handle large membrane proteins.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stone J, Eargle J, Sethi A, Li L, Luthey-Schulten Z (2012) University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Luthey-Schulten Group. NIH Resource for Macromolecular Modeling and Bioinformatics, Citeseer
Koukos PI, Glykos NM (2013) Grcarma: a fully automated task-oriented interface for the analysis of molecular dynamics trajectories. J Comput Chem 34(26):2310–2312
Viloria JS, Allega MF, Lambrughi M, Papaleo E (2017) An optimal distance cutoff for contact-based protein structure networks using side-chain centers of mass. Sci Rep 7(1):1–11
Roe DR, Cheatham TE (2013) PTRAJ and CPPTRAJ: software for processing and analysis of molecular dynamics trajectory data. J Chem Theory Comput 9(7):3084–3095
Humphrey W, Dalke A, Schulten K (1996) VMD: visual molecular dynamics. J Mol Graph 14(1):33–38
Gowers R, Linke M, Barnoud J, Reddy T, Melo M, Seyler S et al (eds) (2016) MDAnalysis: a python package for the rapid analysis of molecular dynamics simulations. Python in science conference; 2016. Texas, Austin
Michaud-Agrawal N, Denning EJ, Woolf TB, Beckstein O (2011) MDAnalysis: a toolkit for the analysis of molecular dynamics simulations. J Comput Chem 32(10):2319–2327
Lindahl E, Hess B, van der Spoel D (2001) GROMACS 3.0: a package for molecular simulation and trajectory analysis. J Mol Model 7(8):306–317
Hess B, Kutzner C, van der Spoel D, Lindahl E (2008) GROMACS 4: algorithms for highly efficient, load-balanced, and scalable molecular simulation. J Chem Theory Comput 4(3):435–447
Pronk S, Páll S, Schulz R, Larsson P, Bjelkmar P, Apostolov R et al (2013) GROMACS 4.5: a high-throughput and highly parallel open source molecular simulation toolkit. Bioinformatics 29(7):845–854
Berendsen HJC, van der Spoel D, van Drunen R (1995) GROMACS: a message-passing parallel molecular dynamics implementation. Comput Phys Commun 91(1-3):43–56
Van Der Spoel D, Lindahl E, Hess B, Groenhof G, Mark AE, Berendsen HJC (2005) GROMACS: fast, flexible, and free. J Comput Chem 26(16):1701–1718
Abraham MJ, Murtola T, Schulz R, Páll S, Smith JC, Hess B et al (2015) GROMACS: high performance molecular simulations through multi-level parallelism from laptops to supercomputers. SoftwareX 1-2:19–25
Grant BJ, Rodrigues APC, ElSawy KM, McCammon JA, Caves LSD (2006) Bio3D: an R package for the comparative analysis of protein structures. Bioinformatics 22:2695–2696
Botello-Smith WM, Luo Y (2019) Robust determination of protein allosteric signaling pathways. J Chem Theory Comput 15(4):2116–2126
VanWart AT, Eargle J, Luthey-Schulten Z, Amaro RE (2012) Exploring residue component contributions to dynamical network models of Allostery. J Chem Theory Comput 8(8):2949–2961
Van Wart AT, Durrant J, Votapka L, Amaro RE (2014) Weighted implementation of suboptimal paths (WISP): an optimized algorithm and tool for dynamical network analysis. J Chem Theory Comput 10(2):511–517
Salomon-Ferrer R, Case DA, Walker RC (2013) An overview of the Amber biomolecular simulation package. WIRES Comput Mol Sci 3(2):198–210
Miller BR, TD MG, Swails JM, Homeyer N, Gohlke H, Roitberg AE (2012) MMPBSA.py: an efficient program for end-state free energy calculations. J Chem Theory Comput 8(9):3314–3321
Lange OF, Grubmüller H (2005) Generalized correlation for biomolecular dynamics. Proteins 62(4):1053–1061
Ribeiro AAST, Ortiz V (2014) Determination of signaling pathways in proteins through network theory: importance of the topology. J Chem Theory Comput 10(4):1762–1769
Yen JY (1970) An algorithm for finding shortest routes from all source nodes to a given destination in general networks. Q Appl Math 27(4):526–530
Hagberg AA, Schult DA, Swart PJ (eds) (2008) Exploring network structure, dynamics, and function using NetworkX2008. Pasadena, CA USA
Csardi G, Nepusz T (2005) The igraph software package for complex network research. Int J Complex Syst 1695:1–9
Brandes U, Fleischer D (2005) Centrality Measures Based on Current Flow. STACS; 2005. Springer, New York
Stephenson K, Zelen M (1989) Rethinking centrality: methods and examples. Soc Networks 11(1):1–37
Newman MEJ (2005) A measure of betweenness centrality based on random walks. Soc Networks 27(1):39–54
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by NIH Grant R01-GM130834. Computational resources were provided via the Extreme Science and Engineering Discovery Environment (XSEDE) allocation TG-MCB160119, which is supported by NSF grant number ACI-154862.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Botello-Smith, W.M., Luo, Y.L. (2021). Concepts, Practices, and Interactive Tutorial for Allosteric Network Analysis of Molecular Dynamics Simulations. In: Schmidt-Krey, I., Gumbart, J.C. (eds) Structure and Function of Membrane Proteins. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 2302. Humana, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-1394-8_17
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-1394-8_17
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-0716-1393-1
Online ISBN: 978-1-0716-1394-8
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols