Abstract
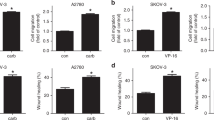
IFNγ is a pleiotropic cytokine that has both antitumor functions and pro-tumorigenic effects. Recent studies have shown that IFNγ induces expression of the immune checkpoint PD-L1 in ovarian cancer (OC) cells, resulting in their increased proliferation and tumor growth. Here, we tested the hypothesis that IFNγ induces migration of OC cells. Using the scratch wound healing assay, our results demonstrate that IFNγ promotes OC cell migration, thus adding to the complexities of IFNγ pro-tumorigenic mechanisms. This chapter describes analysis of the IFNγ-induced migration of OC cells by the wound healing assay followed by quantification of the obtained images using ImageJ software.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ikeda H, Old LJ, Schreiber RD (2002) The roles of IFN gamma in protection against tumor development and cancer immunoediting. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 13:95–109
Zaidi MR, Merlino G (2011) The two faces of interferon-γ in cancer. Clin Cancer Res 17:6118–6124
Mandai M, Hamanishi J, Abiko K et al (2016) Dual faces of IFNγ in cancer progression: a role of PD-L1 induction in the determination of pro- and antitumor immunity. Clin Cancer Res 22:2329–2334
Mojic M, Takeda K, Hayakawa Y (2017) The dark side of IFN-γ: its role in promoting cancer immunoevasion. Int J Mol Sci 19(1):E89. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19010089
Castro F, Cardoso AP, Gonçalves RM et al (2018) Interferon-gamma at the crossroads of tumor immune surveillance or evasion. Front Immunol 9:847
Zaidi MR (2019) The interferon-gamma paradox in cancer. J Interf Cytokine Res 9:30–38
Iwai Y, Ishida M, Tanaka Y et al (2002) Involvement of PD-L1 on tumor cells in the escape from host immune system and tumor immunotherapy by PD-L1 blockade. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99:12293–12297
Loke P, Allison JP (2003) PD-L1 and PD-L2 are differentially regulated by Th1 and Th2 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100:5336–5341
Chinai JM, Janakiram M, Chen F et al (2015) New immunotherapies targeting the PD-1 pathway. Trends Pharmacol Sci 36:587–595
Boussiotis VA (2016) Molecular and biochemical aspects of the PD-1 checkpoint pathway. N Engl J Med 375:1767–1778
Azuma T, Yao S, Zhu G et al (2008) B7-H1 is a ubiquitous antiapoptotic receptor on cancer cells. Blood 111:3635–3643
Chang CH, Qiu J, O’Sullivan D et al (2015) Metabolic competition in the tumor microenvironment is a driver of cancer progression. Cell 162:1229–1241
Clark CA, Gupta HB, Sareddy G et al (2016) Tumor-intrinsic PD-L1 signals regulate cell growth, pathogenesis, and autophagy in ovarian cancer and melanoma. Cancer Res 76:6964–6974
Abiko K, Mandai M, Hamanishi J et al (2013) PD-L1 on tumor cells is induced in ascites and promotes peritoneal dissemination of ovarian cancer through CTL dysfunction. Clin Cancer Res 19:1363–1374
Abiko K, Matsumura N, Hamanishi J et al (2015) IFN-gamma from lymphocytes induces PD-L1 expression and promotes progression of ovarian cancer. Br J Cancer 112:1501–1509
Zou Y, Uddin MM, Padmanabhan S et al (2018) The proto-oncogene Bcl3 induces immune checkpoint PD-L1 expression, mediating proliferation of ovarian cancer cells. J Biol Chem 293:15483–15496
Liang CC, Park AY, Guan JL (2007) In vitro scratch assay: a convenient and inexpensive method for analysis of cell migration in vitro. Nat Protoc 2:329–333
Cory G (2011) Scratch-wound assay. Methods Mol Biol 769:25–30
Kramer N, Walzl A, Unger C et al (2013) In vitro cell migration and invasion assays. Mutat Res 752:10–24
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by NIH grant CA202775 to I. Vancurova.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Gaire, B., Uddin, M.M., Zou, Y., Vancurova, I. (2020). Analysis of IFNγ-Induced Migration of Ovarian Cancer Cells. In: Vancurova, I., Zhu, Y. (eds) Immune Mediators in Cancer. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 2108. Humana, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-0247-8_8
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-0247-8_8
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-0716-0246-1
Online ISBN: 978-1-0716-0247-8
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols