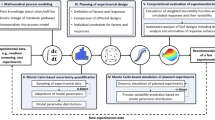
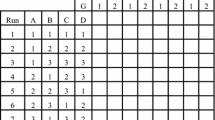
Abstract
Conventional design of experiments (DoE) methods require expert knowledge about the investigated factors and their boundary values and mostly lead to multiple rounds of time-consuming and costly experiments. The combination of DoE with mathematical process modeling in model-assisted DoE (mDoE) can be used to increase the mechanistic understanding of the process. Furthermore, it is aimed to optimize the processes with respect to a target (e.g., amount of cells, product titer), which also provides new insights into the process. In this chapter, the workflow of mDoE is explained stepwise including corresponding protocols. Firstly, a mathematical process model is adapted to cultivation data of first experimental data or existing knowledge. Secondly, model-assisted simulations are treated in the same way as experimentally derived data and included as responses in statistical DoEs. The DoEs are then evaluated based on the simulated data, and a constrained-based optimization of the experimental space can be conducted. This loop can be repeated several times and significantly reduces the number of experiments in process development.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Möller J, Pörtner R (2017) Model-based design of process strategies for cell culture bioprocesses: state of the art and new perspectives. In: Gowder S (ed) New insights in cell culture technology. InTech, London. ISBN: 978-953-51-3133-5
Sandadi S, Ensari S, Kearns B (2006) Application of fractional factorial designs to screen active factors for antibody production by Chinese hamster ovary cells. Biotechnol Prog 22:595–600. https://doi.org/10.1021/bp050300q
Kleppmann W (2013) Versuchsplanung. Produkte und Prozesse optimieren, 8th edn. Hanser, München, Wien. ISBN: 978-3446437524
Zhang H, Wang H, Liu M, Zhang T, Zhang J, Wang X, Xiang W (2013) Rational development of a serum-free medium and fed-batch process for a GS-CHO cell line expressing recombinant antibody. Cytotechnology 65:363–378. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10616-012-9488-4
Nasri NMR, Razavi SH (2010) Use of response surface methodology in a fed-batch process for optimization of tricarboxylic acid cycle intermediates to achieve high levels of canthaxan-thin from Dietzia natronolimnaea HS-1. J Biosci Bioeng 109:361–368. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiosc.2009.10.013
Siebertz K, Bebber DV, Hochkirchen T (2010) Statistische Versuchsplanung. In: Design of Experiments (DoE). Springer, Heidelberg, ISBN: 978-3-642-05493-8
Mandenius C, Graumann K, Schultz T, Premstaller A, Olsson M, Petiot E, Clemens C, Welin M (2009) Quality-by-design for biotechnology-related pharmaceuticals. Biotechnol J 4:600–609. https://doi.org/10.1002/biot.200800333
Möller J, Kuchemüller KB, Hernández Rodríguez T, Frahm B, Hass VC, Pörtner R (2018) Model-assisted design of process strategies for cell culture processes. Am Pharm Rev 21(3):39–41
Möller J, Kuchemüller K, Pörtner R (2018) Model-assisted DoE – A concept study for cell culture process development. Chemie Ingenieur Technik 90(9):1235–1235. https://doi.org/10.1002/cite.201855228
Abt V, Barz T, Cruz N, Herwig C, Kroll P, Möller J, Pörtner R, Schenkendorf R (2018) Model-based tools for optimal experiments in bioprocess engineering. Curr Opin Chem Eng 22:244–252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coche.2018.11.007
Möller J, Kuchemüller KB, Steinmetz T, Koopmann KS, Pörtner R (2019) Model-assisted design of experiments as a concept for knowledge-based bioprocess development. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 42(5):867–882. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-019-02089-7
Kern S, Platas-Barradas O, Pörtner R, Frahm B (2014) Model-based strategy for cell culture seed train layout verified at lab scale. Cytotechnology 68(4):1019–1032. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10616-015-9858-9
Frahm B, Lane P, Märkl H, Pörtner R (2003) Improvement of a mammalian cell culture process by adaptive, model-based dialysis fed-batch cultivation and suppression of apoptosis. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 26:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-003-0335-z
Mohler L, Bock A, Reichl U (2008) Segregated mathematical model for growth of anchorage-dependent MDCK cells in microcarrier culture. Biotechnol Prog 24:110–119. https://doi.org/10.1021/bp0701923
Ling WLW, Bai Y, Cheng C, Padawer I, Wu C (2015) Development and manufacturability assessment of chemically-defined medium for the production of protein therapeutics in CHO cells. Biotechnol Prog 31:1163–1171. https://doi.org/10.1002/btpr.2108
Liu C, Chang T (2006) Rational development of serum-free medium for Chinese hamster ovary cells. Process Biochem 41:2314–2319. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2006.06.008
Torkashvand F, Vaziri B, Maleknia S, Heydari A, Vossoughi M, Davami F, Mahboudi F (2015) Designed amino acid feed in improvement of production and quality targets of a therapeutic monoclonal antibody. PLoS One 10:e0140597. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0140597
Castro PML, Hayter PM, Ison AP, Bull AT (1992) Application of a statistical design to the optimization of culture medium for recombinant interferon-gamma production by Chinese hamster ovary cells. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 38(1):84–90. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00169424
Chun C, Heineken K, Szeto D, Ryll T, Chamow S, Chung JD (2003) Application of factorial design to accelerate identification of CHO growth factor requirements of CHO growth factor requirements. Biotechnol Prog 19:52–57. https://doi.org/10.1021/bp025575
Liu C, Chu I, Hwang S (2001) Factorial designs combined with the steepest ascent method to optimize serum-free media for CHO cells. Enzym Microb Technol 28:314–321. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0141-0229(00)00346-X
Alt W (2011) Nichtlineare Optimierung, Eine Einführung in Theorie, Verfahren und Anwendungen, 2nd edn. Vieweg+Teubner Verlag, Wiesbaden. ISBN: 978-3-8348-1558-3
Frahm B, Lane P, Atzert H, Munack A, Hoffmann M, Hass VC, Pörtner R (2002) Adaptive, Model-Based Control by the Open-Loop-Feedback-Optimal (OLFO) controller for the effective fed-batch cultivation of hybridoma cells. Biotechnol Prog 18:1095–1103. https://doi.org/10.1021/bp020035y
Cameron A, Windmeijer F (1997) An R-squared measure of goodness of fit for some common nonlinear regression models. J Econ 77:329–342. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-4076(96)01818-0
McHugh MJ (2005) Multi-model trends in East African rainfall associated with increased CO2. Geophys Res Lett 32:2068. https://doi.org/10.1029/2004GL021632
Deppe S, Kuchemüller KB, Hernández Rodríguez T, Pörtner R, Möller J, Frahm B (2019) Estimation of process model parameters. In: Pörtner R (ed) Methods in molecular biology – animal cell biotechnology, 4th edn. Springer, New York
Mandenius CF, Brundin A (2008) Bioprocess optimization using design-of-experiments methodology. Biotechnol Prog 24:1191–1203. https://doi.org/10.1002/btpr.67
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Kuchemüller, K.B., Pörtner, R., Möller, J. (2020). Efficient Optimization of Process Strategies with Model-Assisted Design of Experiments. In: Pörtner, R. (eds) Animal Cell Biotechnology. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 2095. Humana, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-0191-4_13
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-0191-4_13
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-0716-0190-7
Online ISBN: 978-1-0716-0191-4
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols