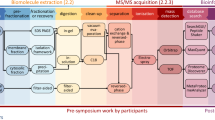
Abstract
Metaproteomics is the analysis of the proteome of environmental samples. While proteomics has been established as a robust and reliable technique, the meta aspect of this omic approach is still in its infancy and subject to methodological and data analysis improvements over the next years. The need to define correct methods for such analyses is essential before hypothesis-driven projects can be addressed. Here we discuss the current state of metaproteomics and propose a protocol covering the three main steps to be implemented in any metaproteomics pipeline: (1) sample preparation, (2) high-throughput mass spectrometry analysis and (3) data search. We also detail current bottlenecks and alternatives to such pipeline.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cox J, Mann M (2011) Quantitative, high-resolution proteomics for data-driven systems biology. Annu Rev Biochem 80:273–299
Armengaud J, Christie-Oleza JA, Clair G, Malard V, Duport C (2012) Exoproteomics: exploring the world around biological systems. Expert Rev Proteomics 9:561–575
Christie-Oleza JA, Fernandez B, Nogales B, Bosch R, Armengaud J (2012) Proteomic insights into the lifestyle of an environmentally relevant marine bacterium. ISME J 6:124–135
Hettich RL, Sharma R, Chourey K, Giannone RJ (2012) Microbial metaproteomics: identifying the repertoire of proteins that microorganisms use to compete and cooperate in complex environmental communities. Curr Opin Microbiol 15:373–380
Seifert J, Herbst FA, Halkjaer Nielsen P, Planes FJ, Jehmlich N, Ferrer M et al (2013) Bioinformatic progress and applications in metaproteogenomics for bridging the gap between genomic sequences and metabolic functions in microbial communities. Proteomics 13:2786–2804
Muth T, Kolmeder CA, Salojarvi J, Keskitalo S, Varjosalo M, Verdam FJ et al (2015) Navigating through metaproteomics data: a logbook of database searching. Proteomics. doi: 10.1002/pmic.201400560
Bork P, Bowler C, de Vargas C, Gorsky G, Karsenti E, Wincker P (2015) Tara Oceans studies plankton at planetary scale. Introduction. Science 348:873
Kashtan N, Roggensack SE, Rodrigue S, Thompson JW, Biller SJ, Coe A et al (2014) Single-cell genomics reveals hundreds of coexisting subpopulations in wild Prochlorococcus. Science 344:416–420
Christie-Oleza JA, Armengaud J, Guerin P, Scanlan DJ (2015) Functional distinctness in the exoproteomes of marine Synechococcus. Environ Microbiol. doi: 10.1111/1462-2920.12822
Christie-Oleza JA, Scanlan DJ, Armengaud J (2015) “You produce while I clean up”, a strategy revealed by exoproteomics during Synechococcus-Roseobacter interactions. Proteomics. doi: 10.1002/pmic.201400562
Moormann SM, Hampton-Marcell JT, Owens SM, Gilbert JA (2015) Protocols for metagenomic library generation and analysis in petroleum hydrocarbon microbe systems. In: McGenity TJ, Timmis KN, Nogales B (eds) Hydrocarbon and lipid microbiology protocols. Springer protocols handbooks. doi: 10.1007/8623_2014_37
Hartmann EM, Gaillard J-C, Armengaud J (2015) Shotgun proteomics for hydrocarbon microbiology. In: McGenity TJ, Timmis KN, Nogales B (eds) Hydrocarbon and lipid microbiology protocols. Springer protocols handbooks. doi: 10.1007/8623_2014_18
Allmer J (2011) Algorithms for the de novo sequencing of peptides from tandem mass spectra. Expert Rev Proteomics 8:645–657
Shteynberg D, Nesvizhskii AI, Moritz RL, Deutsch EW (2013) Combining results of multiple search engines in proteomics. Mol Cell Proteomics 12:2383–2393
Jagtap P, Goslinga J, Kooren JA, McGowan T, Wroblewski MS, Seymour SL, Griffin TJ (2013) A two-step database search method improves sensitivity in peptide sequence matches for metaproteomics and proteogenomics studies. Proteomics 13:1352–1357
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2015 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Christie-Oleza, J.A., Sousoni, D., Armengaud, J., Wellington, E.M., Jones, A.M.E. (2015). Defining a Pipeline for Metaproteomic Analyses. In: McGenity, T., Timmis, K., Nogales , B. (eds) Hydrocarbon and Lipid Microbiology Protocols. Springer Protocols Handbooks. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/8623_2015_130
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/8623_2015_130
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-662-50449-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-662-50450-5
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols