Abstract
Objective
To investigate anti-infective treatments in HIV-infected surgical patients during the perioperative period.
Methods
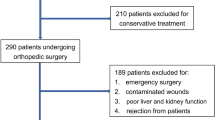
A retrospective study of sepsis and surgical site infections (SSIs) was conducted in 266 HIV-infected patients. The patients were divided into 3 groups based on CD4+ T cells counts in the preoperative period: group A (0–199 cell/ul), group B (200–349 cell/ul) and group C ([greater than or equal to] 350 cell/ul). When the CD4 count was below 350 cells/uL, anti-retrovirus therapy was started. For patients whose preoperative CD4 counts were [less than or equal to] 200 cells/uL, preoperative antibiotic medication was started.
Results
Patients in group A were more likely to get sepsis than patients in the other two groups (p0.01). Among 82 patients with clean wounds, only one patient got SSIs. All patients with dirty wounds had acquired SSIs after surgery. There were only 6 patients dead at 30 days after surgery, a death rate of 2.3%. Sepsis appeared in 110 patients (41%).
Conclusions
Complete evaluation of surgical risk and suitable perioperative anti-infective treatment may lead to better outcome for HIV-infected surgical patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
The patient who undergoes surgical treatment may experience postoperative infection. According to wound class and immune status, the postoperative infection rates are different. Based on the National Nosocomial Infections Surveillance (NNIS) system, surgical site infections (SSIs) are the third most frequently reported nosocomial infection, and the most common on surgical wards[1]. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) estimates that 22% of all health-care-associated infections are SSIs, with an increasing percentage over the last decade[1, 2]. SSIs increase morbidity as well as mortality, double the length of hospital stay[3–6] and increase the cost of surgery two- to five-fold[7].
The progressive failure of the immune system caused by HIV can increase the possibility of developing postoperative infection. In recent years, the number of HIV-infected patients is progressively increasing. The introduction of antiretroviral therapy (ART) has significantly improved the life expectancy of patients infected with HIV and those diagnosed with AIDS[8–13]. The demand for surgical treatment in HIV-infected patients is increasing and so is the frequency of resultant surgical disease[14, 15].
There are few reported data on the efficacy of anti-infective treatment in HIV-infected patients during the perioperative period. Since our institution is a designated tertiary care university hospital for treatment of HIV-infected patients we had the opportunity to investigate the efficacy of anti-infective treatments in HIV-infected patients during the perioperative period.
Patients and methods
Definitions
We defined the wound class at the surgical site of infection (SSI) using the definitions provided by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). An instance of surgical site infection was defined as an infection occurring within 30 days of the operative procedure, when the patient had one or more of the following: (1) organisms isolated from an aseptically obtained culture of fluid or tissue from the surgical incision; (2) purulent drainage from the surgical incision; (3) at least one of the following: pain or tenderness, localized swelling, redness, or heat. SSIs were classified as being incisional, deep incisional or organ/space. Surgical procedures were classified as clean, contaminated or dirty. Sepsis was defined as the infection in association with systemic inflammatory response syndrome.
Data collection
Clinical data of HIV-infected patients undergoing surgery from January 2009 to December 2011 were retrieved using our computerized patient record system. Inclusion criteria: HIV-infected patients were identified and diagnosed by local Centers for the Disease Prevention and Control in different locations in China. All selected patients had records that contained thorough disease histories, including physical examinations, preoperative and postoperative routine examinations, and immune function tests.
Patient group and study methods
We stratified and compared the incidence of SSIs and sepsis according to both wound class and preoperative CD4 counts with breakpoint values of 200 and 350 cell/μL. Demographic and clinical information was entered into a database that included: type of surgical procedure, age, peripheral blood cell counts, plasma albumin, CD4 counts, and CD4/CD8 ratios.
Statistical analysis
Date were analyzed using SPSS 16.0 statistical software (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL). Results of all continuous data are presented here as mean ± standard deviation. Continuous variables were compared by independent t-test. Univariate analysis of the categorical outcome was carried out using Chi-squared tests. P<0.05 indicates statistical significance.
Results
Two hundred and sixty-six HIV-infected patients were included in this study. Their mean (±SD) age was 42.3 (±13.1) years, and 237 (89.1%) were male. There were six deaths in the study population, five of whom had organ/space SSI and developed sepsis. The SSI cumulative incidence rate was 46.6% (124 of 266). The incidence of incisional SSI was 37.6%, deep incisional SSI was 5.3%, and organ/space SSI was 3.8%. Baseline characteristics of patients shown in (Table1).
Univariate analysis revealed that the following variables were associated with the occurrence of sepsis: preoperative WBC, hemoglobin, CD4, CD8 and CD4/CD8 (Table2).
At multivariate analysis, only preoperative WBC, hemoglobin and CD4 remained significantly (P<0.05) associated with sepsis, (Table3).
Comparisons of the incidence of sepsis according to preoperative CD4 counts shown in Table4.
Patients with lower preoperative CD4 counts undergoing surgery were more likely to develop sepsis. Surgical procedures were classified as clean (N = 82; 30.8%), contaminated (N = 171; 64.3%) and dirty (N = 13; 4.9%). The incidence of SSI differed significantly depending on wound class, and increased from 1.2% in patients with clean wounds to 100% in patients with dirty wound (Table5).
Our data show that SSIs were frequent and differed widely by wound class. Patients with SSIs were more likely to develop postoperative sepsis than non-SSIs patients (Table6).
Discussion
Anti-infective treatment in the perioperative period
HIV mainly invades and destroys CD4 T lymphocytes, causing CD4 counts to gradually decrease. In consequence of their significantly impaired immune function when the,CD4 count is below 350 cell/μL, HIV-infected patients are likely to get opportunistic infections and cancers and their mortality is then usually high[16]. At this stage ART is used, and usually includes two kinds of nucleosides and one kind of protease inhibitor. Patients using ART who undergo surgery need to continue ART use during the perioperative period[17]. Even if patients are undergoing gastrointestinal surgery and need to fast, they can take antiviral drugs. When a patient's, CD4 count is below 200 cell/μL, there is an additional high risk of acquiring fungal infections such as Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia which bring a marked increase in mortality[18, 19]. Therefore SMZ and fluconazole are conventionally added to ART during the perioperative period to prevent P. carinii pneumonia and other fungal infections. If tuberculosis, cryptococcosis, candidiasis or similar infections have been found before surgery, anti-TB or antifungal treatments are clearly required to control the disease. In summary, HIV patients undergoing emergency surgery need prophylactic anti-infective drugs based on doctor/clinical experience, and effective anti-infective treatments are to be applied according to the results of resection of lesions and blood culture[20, 21].
Prophylactic antibiotics
To reduce the incidence of surgical site infection, prophylactic antibiotics are generally used during the perioperative period. Because of the weakened immune function, HIV-infected patients are even more likely to need prophylactic antibiotics[22]. However, there are no reports specifically about how to use antibiotic in surgical patients who are HIV infected. We found that preoperative CD4 lymphocytes, WBC and hemoglobin are independent risk factors for sepsis. CD4 counts cannot be implied from white blood cell counts. Decline in CD4 T lymphocyte counts is often accompanied by decline in hemoglobin. Our principle in using prophylactic antibiotics was to use those antibiotics which can cover the most common infections according to surgical incision site and type of surgery. We took into account the likelihood of Gram-negative bacilli (enteric bacteria), gram-positive cocci (Staphylococcus aureus) and anaerobic bacteria, and chose between two kinds of antibiotic combinations. We usually selected first-generation cephalosporins on clean wound surgery. For nine patients who were undergoing excision of thyroid tumor or breast tumor, we did not use any antibiotics and no SSI arose. In all, 82 patients underwent clean wound surgery and 81 had healing wounds. In future we may try not using any antibiotic for classIminor incisions. For giant splenectomy with cirrhosis and for internal fixation of femoral fractures, we still need prophylactic antibiotics, and they should be used longer than for normal surgery. We generally use antibiotics until wound have healed. The first-generation cephalosporins have a strong bactericidal activity for Gram-positive S. aureus, but for Gram-positive intestinal bacteria its bactericidal activity is less than second- and third-generation cephalosporins (ceftriaxone, etc.). Second-generation cephalosporins have advantages in the prevention of wound infection for class-IIincisions and gastrointestinal tract surgery, but its bactericidal activity is less than third-generation cephalosporins in the prevention of intra-abdominal infection. Prophylactic antibiotics should also cover common anaerobic bacteria for lower gastrointestinal surgery where there is significant pollution. Antibiotics such as piperacillin, cefoxitin, cefotetan, etc., can cover gram-negative enteric bacilli as well as anaerobic bacteria. Metronidazole and clindamycin should be included when other antibiotics do not have activity against anaerobic bacteria.
Antibiotics for therapy
Therapeutic drugs should be used for intra or postoperative infections. According to our statistical analysis of the clinical data, the lower the preoperative CD4 counts, the higher the incidence of sepsis. Our data also show that SSIs were frequent and differed widely by wound class. The incidence of SSIs is high for Class II incisions because our study included many anal warts excision patients and these usually develop SSIs after surgery. Clearly, we should maintain clean wounds for superficial surgical site infections to reduce sepsis; our data show that the incidence of sepsis in the SSIs group was significantly higher than in the non-SSIs group. Therefore effective treatment should also be used for surgical site infection. Effective anti-infection treatment involves a multi-disciplinary knowledge for HIV-infected patients who may have tuberculosis, fungal infections and surgical site infections.
Surgical risk and prognosis
HIV-infected patients have a higher incidence of surgical complication and mortality than normal patients. Jeremiah L et al.[23] reported that the incidence of postoperative infectious complications was 55% and the 30-day mortality rate after surgery was 30% for HIV-infected patients. Our institution is a designated tertiary care university hospital for treatment of HIV-infected patients, so we have accumulated much perioperative anti-infection treatment experience. The mortality of HIV-infected patients undergoing abdominal surgery in our hospital was 7.7% which is significantly lower than previously reported data. Surgeons should pay attention to occupational exposure and aseptic technique in order to reduce SSIs and surgical trauma.
Limitations of the study
One of the limitations of the study was possible information biases due to the retrospective nature of the study design. Another was that the study did not control for possible confounders other than those investigated.
In conclusion, in order to reduce the incidence of infection complications and mortality, surgeons should combine multidisciplinary knowledge and carry out reasonable anti-infection treatments.
Ethical approval
The study was approved by the Ethical Committee of Shanghai Public Health Clinical Center, Fudan University, Shanghai, China. (International index IORG0006364).
References
Mangram A, Horan T, Pearson M: Guideline for prevention of surgical site infection, 1999 [J]. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 1999, 20: 250-278. 10.1086/501620
Evans RP: Surgical site infection prevention and control: an emerging paradigm. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2009, 91 (Suppl 6): 2-9.
Kirkland K, Briggs J, Trivette S: The impact of surgical site infections in the 1990s: attributable mortality, excess length of hospitalization, and extra costs [J]. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 1999, 20: 725-730. 10.1086/501572
McGarry S, Engemann J, Schmader K: Surgical site infection due to Staphylococcus aureus among elderly patients: mortality, duration of hospitalization, and cost [J]. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2004, 25: 461-479. 10.1086/502422
Palmer S, Parker M, Hollingworth W: The cost and implications of reoperation after surgery for fracture of the hip [J]. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2000, 82: 864-875. 10.1302/0301-620X.82B6.9974
Pollard T, Newman J, Barlow N: Deep wound infection after proximal femoral fracture: consequences and costs [J]. J Hosp Infect. 2006, 63: 133-143. 10.1016/j.jhin.2006.01.015
Edwards P, Lipp A, Holmes A: Preoperative skin antiseptics for preventing surgical wound infections after clean surgery. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2004, CD003949-3 10.1016/CD003949-3
Ruiz-Perez I, Olry de Labry-Lima A A, López-Ruz MA: Clinical status, adherence to HAART and quality of life in HIV-infected patients receiving antiretroviral treatment [J]. Enferm Infecc Microbiol Clin. 2005, 23: 581-590. 10.1157/13081565
Mocroft A, Vella S, Benfield TL: Changing patterns of mortality across Europe in patients infected with HIV-1. EuroSIDA Study Group [J]. Lancet. 1998, 352: 1725-1739. 10.1016/S0140-6736(98)03201-2
Palella FJ, Delaney KM, Moorman AC: Declining morbidity and mortality among patients with advanced human immunodeficiency virus infection. HIV Outpatient Study Investigators [J]. N Engl J Med. 1998, 338: 853-864. 10.1056/NEJM199803263381301
Needham DM, Hogg RS, Yip B: The impact of antiretroviral therapy on AIDS survival observed in a province-wide drug treatment program [J]. Int J STD AIDS. 1998, 9: 370-384.
Teng T, Shao Y: Scientific approaches to AIDS prevention and control in china [J]. Adv Dent Res. 2011, 23: 10-21. 10.1177/0022034511398871
Broder S: The development of antiretroviral therapy and its impact on the HIV-1/AIDS pandemic [J]. Antiviral Res. 2010, 85: 1-14. 10.1016/j.antiviral.2009.10.002
Grulich AE, van Leeuwen MT, Falster MO: Incidence of cancers in people with HIV/AIDS compared with immunosuppressed transplant recipients: A meta-analysis [J]. Lancet. 2007, 370: 59-72. 10.1016/S0140-6736(07)61050-2
Slaven EM, Lopez F, Weintraub SL: The AIDS patient with abdominal pain: A new challenge for the emergency physician [J]. Emerg Med Clin North Am. 2003, 21: 987-996. 10.1016/S0733-8627(03)00070-1
LaRaja RD, Rothenberg RE, Odom JW: The incidence of intro-abdominal surgery in acquired immunodeficiency syndrome: a statistical review of 904 patients. Surgery. 1989, 105 (2): 175-179.
Foschi D, Cellerino P, Corsi F: Impact of highly active antiretroviral therapy on outcome of cholecystectomy in patients with human immunodeficiency virus infection. Br J Surg. 2006, 93 (11): 1383-1389. 10.1002/bjs.5527
Albaran RG, Webber J, Steffes CP: CD4 cell counts as a prognostic factor of major abdominal surgery in patients infected with the human immunodeficiency virus [J]. Arch Surg. 1998, 133 (6): 626-631. 10.1001/archsurg.133.6.626
Emparan C, Iturburu IM, Ortiz J, Mendez JJ: Infective complications after abdominal surgery in patients infected with human immunodeficiency virus: role of CD4 + lymphocytes in prognosis [J]. Word J Surg. 1988, 22 (8): 778-782.
Delling RP, Leve MM, Carlet JM: Surviving sepsis Campaign:International guidelines for management of severe sepsis and septic shock;2008[J]. Crit Care Med. 2008, 36 (1): 296-327. 10.1097/01.CCM.0000298158.12101.41
Samuel B: The development of antiretroviral therapy and its impact on the HIV-1/AIDS pandemic [J]. Antiviral Res. 2010, 85: 1-18. 10.1016/j.antiviral.2009.10.002
Drapeau CM, Pan A, Bellacosa C: Surgical site infections in HIV-infected patients: results from an Italian prospective multicenter observational study[J]. Infection. 2009, 37 (5): 455-460. 10.1007/s15010-009-8225-1
Jeremiah L, Jessics G, Deneve : CD4 count is predictive of outcome in HIV-positive patients undergoing abdominal operations[J]. Am J Surg. 2010, 200 (6): 694-700. 10.1016/j.amjsurg.2010.07.030
Acknowledgements
Authors acknowledge Dr. W. Zhang, Dr. Y. Cao and Prof. Douglas in Shanghai Public Health Clinical Center affiliated to Fudan University for their critical comments and assistance to review and edit the manuscripts.
Funding
The study was supported by Research Foundation of Shanghai Public Health Clinical Center (RCJJP8).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interests
The authors have no financial or other conflicts of interest regarding this article.
Authors’ contributors
BL, LZ and GZ conceived of the study, participated in its design and draft the manuscript. LL and JS participated in data collection. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Rights and permissions
This article is published under license to BioMed Central Ltd. This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, B., Zhang, L., Guo, R. et al. Anti-infective treatment in HIV-infected patients during perioperative period. AIDS Res Ther 9, 36 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1186/1742-6405-9-36
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/1742-6405-9-36