Abstract
Seamounts are hotspots for marine life, but to date, no bacteriophages have been reported. Here, a novel Bacillus podophage (named as Bacillus phage Gxv1) was isolated from deep-sea seamount sediments of the western Pacific Ocean (~ 5790 m). Phage Gxv1 has a hexameric head ~ 42–53 nm in diameter and a short tail of ~ 30 nm long, which is a typical feature of the Podoviridae family. One-step curve analysis showed that Gxv1 is a lytic phage that can initiate host lysis within 3.5 h post-infection, and has a relatively large burst size. The 21,781-bp genome contains 34 predicted genes, and the G + C content of phage Gxv1 is 39.69%. Whole-genome comparison of phage Gxv1 with known bacteriophages, using BlastN analysis against the IMG/VR database, revealed that phage Gxv1 is closely related to Bacillus phage phi29 that infects Bacillus subtilis, and their genome-wide similarity is 93.62%. Phylogenetic analysis based on DNA polymerase showed that phage Gxv1 belongs to the Salasvirus genus. Multiple genome alignment showed that phage Gxv1 shares a high level of sequence similarity and common gene order with Bacillus phage phi29. However, some sequences are unique to phage Gxv1, and this region contains genes encoding DNA packing protein, DNA replication protein, and unknown protein. These sequences exhibit low sequence similarity to known bacteriophages, highlighting an unknown origin of these sequences. This study will help improve our understanding of the Salasvirus genus and phage diversity in deep-sea seamounts.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Seamounts are isolated topographic elevations with summit depths at least 100 m above the seafloor (Hillier and Watts 2007). Seamounts are one of the most ubiquitous landforms on Earth but are unevenly distributed among ocean basins. As estimated, more than 100,000 seamounts reach a kilometer or more above the seafloor (Wessel et al. 2010), and only a few have been studied extensively. Seamounts are recognized as unique environments and hotspots of biodiversity and biomass (Morato et al. 2010). However, our knowledge of seamount biodiversity is limited. Previous studies have mainly investigated the biodiversity of seamount fauna (Forges et al. 2000; Gollner et al. 2017; Morato et al. 2010), and studies on seamount microorganisms are limited (Ana et al. 2012). In particular, there are only two studies that describe virioplankton abundance and distribution associated with seamounts, using fluorescent enumeration methods (Chiang and Quiñones 2007; Zhao et al. 2020). To our knowledge, no viruses from deep-sea seamounts have been isolated. Given the importance of viruses in structuring and regulating host communities and mediating element biogeochemical cycles, exploring viral diversity is essential for understanding the ecological function of seamounts (Jin et al. 2019; Rohwer and Thurber 2009; Suttle 2005).
The Seamount Endemicity Hypothesis, which is derived from fauna investigation, states that the geographical isolation, hydrological characteristics, and unique habitats of seamounts make seamount bio-segregation ecologically and evolutionarily isolated from other ecological environments in the deep sea, thus forming a higher proportion of endemic species (Koslow et al. 2001). Several studies suggested that the unique geographical and hydrological characteristics of seamounts affect patterns of distribution, abundances and community structure of planktonic microorganisms (Ana et al. 2012; Zhao et al. 2020). However, a number of studies suggest that seamounts possess levels of endemism commensurate with other deep-sea ecosystems (Rogers 2019; Rowden et al. 2010). In this context, isolating and characterizing bacteriophages from deep-sea seamounts may help elucidate the ongoing considerable debate on seamount endemicity.
The Salasvirus genus, also called Phi29likevirus, belongs to the Podoviridae family, and Bacillus phage phi29 is a characteristic phage of the genus. In addition to phi29, several other Phi29likevirus have been identified, such as phages PZA, f15, BS32, B103, M2Y (M2), Nf, and vB_BveP-Goe6 (Meijer et al. 2001; Schilling et al. 2018). Most of these phages infect Bacillus subtilis, but often they also infect other related species. The morphological features of these phages are similar, and their genomes consist of linear double-stranded DNA of approximately 20 kb. An interesting characteristic of Phi29-like phages is that they have terminal proteins as primers for DNA replication (Salas 1983). The DNA polymerase of phage phi29 has unique properties, such as continuous synthesis and high fidelity. Monomeric phage phi29 DNA polymerase has a relative molecular mass of 66 k, and the N terminus is the domain of the exonuclease (Salas 2007). Multiple displacement amplification (MDA) using Phi29 DNA polymerase and random primers is the most widely used method for single-cell whole genome amplification (WGA); this method is also used for single-cell transcriptome sequencing, virus detection (Hamidi et al. 2015), and miRNA detection (Chen et al. 2015). As close relatives, phages belonging to the Salasvirus may serve as a promising source of novel phi29-like DNA polymerase, which have possible superior properties and may be important in several industries, including precision medicine and molecular diagnosis.
Results and discussion
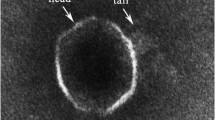
Morphology of phage Gxv1
We isolated Bacillus sp. WP4 from Western Pacific M2 seamount sediments (see “Methods”) and found plaques during the culture of bacteria. The 16S rRNA analysis showed that Bacillus sp. WP4 has high homology with Bacillus velezensis, and the similarity is 99.73%. The phage particles (named as phage Gxv1) were purified by polyethylene glycol method. Phage Gxv1 has head–tail morphology that is typical of Caudovirales, which comprises approximately 1% of all known phages (Ackermann 2001). The head of phage Gxv1 has a hexagonal outline with a flattened top and is ~ 53 nm wide and 42 nm long (Fig. 1). The tail is ~ 30 nm long. Thus, phage Gxv1 can be grouped based on its morphology into the Podoviridae family. Phage Gxv1 is the most homologous to Bacillus phage phi29 (see the below section for details) and has highly similar morphology to phage phi29, which has a hexameric head and top head that appears flattened in outline. The head of phage phi29 is ~ 31.5 nm wide and 41.5 nm long, and the tail of phage phi29 is ~ 32.5 nm long (Anderson et al. 1966).
Life cycle of phage Gxv1
To investigate the replication characteristics of phage Gxv1, we performed one-step growth curve analysis of Gxv1 (Fig. 2). The host cells were infected with purified Gxv1 virions at a MOI of 0.01 when the host bacteria reached the logarithmic phase (OD600 = 0.2). Phage Gxv1 began to replicate approximately 3–3.5 h post-infection and reached the growth plateau at 6.5 h post-infection (Fig. 2). Previous studies reported that the latent period of phage phi29 is 55 min and reaches the plateau phase at 120 min post-infection (Ito et al. 1973). The growth characteristics of phage Gxv1 and phage phi29 are quite different. Phage Gxv1 exhibited a longer latent period and higher burst size than phage phi29. The burst size of Caudovirales appeared to be highly variable. In addition to differences in the methods used to enumerate viral abundance, several factors affected the bacteriophage burst size. These factors include the characteristics of the phage and host, the bacterial and viral size, and the metabolic status of the host. Previous studies proposed a correlation between the trophic status of the environment and the burst size of bacteriophage burst size (Hwang and Cho 2002; Parada et al. 2006). However, this correlation needs further verification, as some phages isolated from eutrophic environments (such as RPP1 and RD-1410Ws-01) have small burst size. Therefore, we should consider these factors when comparing the burst size of different phages.
Genome analysis
We assembled a 21,781 bp linear dsDNA genome from Illumina high-throughput sequencing (Table 1). To verify the physical size of the Gxv1 genome, we performed a gel electrophoresis assay. The results indicated that the genome was complete (data not shown). BlastN analysis against the IMG/VR database showed that the genome of phage Gxv1 has a high homology with B. subtilis phage phi29 (19,282 bp) (Pečenková and Pačes 1999) and B. velezensis phage vB_BveP-Goe6 (19,105 bp) (Schilling et al. 2018), and the genome-wide similarity is 93.62% and 92.39%, respectively. The GC contents of phage Gxv1 (39.69%) are comparable with those of phage phi29 (39.99%) and phage vB_BveP-Goe6 (39.99%). The tRNAscan-SE program indicated that the Gxv1 genome has no tRNA sequences. A lack of tRNA was also found in phage phi29 and phage vB_BveP-Goe6. tRNA is associated with high genome length, high codon usage bias, and high virulence (Marc et al. 2007). No putative CRISPR protospacer was predicted in the Gxv1 genome by searching against the viral spacer database of IMG/VR (Paez-Espino et al. 2016).
Using GeneMarkS software, we predicted 34 genes from the Gxv1 genome. The annotation results based on the NCBI database showed that 10 of 34 genes are unknown (Fig. 3), which accounts for 29.41% of the total genes. It has been reported that a high proportion of the predicted genes of bacteriophages do not match with any other known sequences in the databases (Pedulla et al. 2003), particularly the predicted bacteriophage genes from viromes (Jin et al. 2019). Among the 34 predicted genes, 20 genes are transcribed in the left direction, and the 14 remaining genes are transcribed in the right direction (Fig. 3). Similar to other phages, the genome of phage Gxv1 is tightly arranged, given that 88.51% of the genome encodes the gene product and that the average gene density is 1.56 genes per kb.
Annotated genome map of phage Gxv1. Genes are depicted by leftward-oriented or rightward-oriented arrows according to the predicted direction of transcription. Gene annotations (DNA replication, transcriptional regulator, structure, lysis, and unknown) are colored according to the legend below the figure, and the gene number is marked above each gene
The Gxv1 genome encodes eight genes (g03 to g06, g28, g30, g31, and g34) that are related to DNA replication. DNA polymerase (g04), DNA polymerase type B (g05), and primer terminal protein (g06) were identified in the left arm of the genome. In phage phi29, DNA polymerase forms a heterodimer with the primer terminal protein, recognizes the 5′-end replication origins of the linear genome, and starts DNA replication (Alicia et al. 2012). Therefore, it is likely that the products of g04, g05, and g06 interact with one another and initiate phage DNA replication. The protein sequence similarity of DNA polymerase between Gxv1 and phi29 implies that DNA polymerase of Gxv1 may also possess strand displacement DNA synthesis activities with high processivity and fidelity (Blanco et al. 1989). However, the enzymatic characteristics and potential industrial applications of the DNA polymerase of Gxv1 should be experimentally evaluated in the future. An ssDNA-binding protein-encoding gene (g08) was identified in the Gxv1 genome. A previous study showed that phage-encoded ssDNA-binding proteins are essential proteins in the DNA replication of phi29-like viruses (Gascón et al. 2000).
Two genes encode putative transcriptional regulators that have a helix–turn–helix DNA-binding motif (g07 and g10), indicating the possible elaborate regulation of Gxv1 gene expression. For double-stranded DNA phage, the holing–endolysin system is a typical host lysis mode (Jin et al. 2013; Taehyun et al. 2007). The Gxv1 genome contains both two lytic genes, namely holing-encoding gene (g20) and endolysin-encoding gene (g21). No lysogeny-related genes were identified in the Gxv1 genome, indicating that it cannot follow a lysogeny strategy. Gxv1 harbored three genes encoding DNA packaging proteins (g22, g24, and g26), which are essential for the cleavage of multimeric phage DNA and the following translocation of phage DNA into empty capsids.
Eight structural genes (g12–g19) were identified in the Gxv1 genome. These genes include those encoding head morphogenesis protein (g12), major capsid protein (g13), capsid fiber protein (g14), distal tube protein (g15), upper collar protein (g16), lower collar protein (g17), pre-neck appendage protein (g18), and an unknown structural protein (g19). No obvious capsid fibers were observed in the TEM image of phage virions (Fig. 1) because they may be dissociated from the capsid during virion purification. Previous studies suggested that these fibers may enhance the attachment of virions onto the host cell wall (Ye and Rossmann 2011).
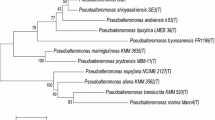
Homology with other phi29-like bacteriophages
Based on the protein sequences of the DNA polymerase g04 and the major capsid protein g13, we built neighbor-joining phylogenetic trees (Fig. 4). Consistent with the IMG/VR annotation results, the analysis of the phylogenetic trees indicated that Gxv1 is most homologous with Bacillus phage phi29 and Bacillus phage vB_BveP-Goe6. Thus, we selected these two closely related bacteriophages for further multiple genome alignment analysis with Gxv1, using Mauve software (Fig. 5). The results of the genome alignment also showed that the genome of Gxv1 shares a high level of sequence similarity and common gene order with Bacillus phage phi29. Most region of the Gxv1 genome is well conserved with phage phi29 (Fig. 5). However, some genomic regions (g22–g25 and g28–ag30) seem unique to Gxv1 and have no homologs in public viral databases. This region contains genes encoding DNA packing protein, DNA replication protein, and unknown protein, and its origin remains unclear. The relatively high genomic similarity between Gxv1 and phi29 indicates that seamount bacteriophages may not possess substantial levels of genetic endemicity as observed in seamount fauna. We speculate that the geographical isolation of seamounts may have fewer impacts on seamount microorganisms than fauna since microorganisms are more prone to migrate across geographical obstacles along with ocean currents and thus have more opportunities for genetic exchanges. However, Gxv1 is the first reported phage isolated from seamount environments; more phages from seamount should be isolated and characterized to support our hypothesis.
Neighbor-joining phylogenetic trees of phage Gxv1 based on DNA polymerase (a) and major capsid protein (b). The scale bar indicates five nucleotide substitutions per 100 nucleotides. Numbers indicating bootstrap values of 100 trials are shown. The accession numbers of DNA polymerase or major capsid protein are shown along with the species names. The DNA polymerase of Bacillus thuringiensis was used as outgroup. DNA polymerase and major capsid protein from phage Gxv1 were marked in red
Conclusion
We isolated a novel lytic bacteriophage Gxv1, which is a new member of the genus Salasvirus and the family Podovirida, from deep-sea seamount sediments. Although seamounts are considered as hotspots of biodiversity and biomass, no phages from seamounts have been reported. Our findings will help improve our understanding of viral diversity and virus–host interactions in deep-sea seamounts.
Materials and methods
Isolation and purification of phage Gxv1
Bacillus sp. WP4 strain was isolated from deep-sea seamount sediments in the western Pacific Ocean at a depth of 5786 m (17° 10′ 17.40″ N, 153° 37′ 5.52″ E). Phage plaques were observed during the culture of Bacillus sp. WP4, which was grown at 28 °C in 2216E solid medium (0.01% ferric phosphate, 0.1% yeast extract, 0.5% tryptone, 1.5% agar in seawater, pH 7.6). Gxv1 virions were purified by polyethylene glycol precipitation methods (Colombet et al. 2008). In brief, plaques were cultivated for expansion in liquid 2216 medium. The phage-containing supernatant was collected after the culture was centrifuged at 15,000g and 4 °C for 15 min. Polyethylene glycol 8000 was added at a final concentration of 10% (w/v) and incubated at 4 °C for more than 12 h. The precipitated phages were collected by centrifugation at 15,000g for 30 min at 4 °C and resuspended in SM buffer (100 mmol/L NaCl, 8 mmol/L MgSO4, 50 mmol/L Tris–HCl at pH 7.5). The resulting phage concentrate was filtered through a 0.22-μm filter and subjected to morphologic observation and DNA extraction.
Transmission electron microscopy
One drop (30 μl) of purified Gxv1 virions was adsorbed onto a 200-mesh carbon-coated copper grid. After staining with 1% phosphotungstic acid for 1 min, the samples were examined at 80 kV with JEOL JEM2100F TEM (JEOL, Tokyo, Japan).
One-step growth curve
One-step growth curve analysis was conducted to characterize the infectivity and replication ability of Gxv1. Gxv1 was mixed with exponentially growing Bacillus sp. WP4 with a multiplicity of infection (MOI) of 0.01 and incubated at 25 °C in the dark for 30 min. The cells were pelleted by centrifugation, re-suspended in 2216E medium, and diluted with fresh medium for 100 times to avoid possible secondary infection. The cells were cultured at 25 °C with continuous shaking. The samples were collected at different time points between 0 and 8 h post-infection. Viral abundance was quantified using double-agar overlay plaque assay. After the latent period, Gxv1 underwent a single-phage burst. Burst size, which indicates the average number of virions released per infected host cell, was calculated as the ratio between the number of plaque-forming units after and before the phage burst.
Phage DNA extraction
Prior to phage DNA extraction, the purified phage particles were treated with DNase I (Sangon Biotech, China) at 37 °C for 2 h to remove external-free DNA fragments. The phage particles were lysed with a combination of proteinase K (30 mg/ml, final concentration), SDS (1% w/v, final concentration), and EDTA (5 μmol/L) at 55 °C for 3 h. The lysate was then mixed with an equal volume of phenol/chloroform/isoamyl alcohol (25:24:1). The supernatant was collected by centrifugation at 15,000g for 5 min, sequentially purified by adding chloroform/isoamyl alcohol (24:1), and centrifuged at 15,000g for 10 min. The supernatant was mixed with isoamyl alcohol to precipitate the DNA. The precipitate was then washed with cold 70% ethanol twice and then air-dried. The purified DNA was resuspended in TE buffer (10 mmol/L Tris–HCl, 1 mmol/L EDTA, pH 8.0) and stored at − 20 °C until further analysis.
Genome sequencing and sequence analyses
Ultrasonic Cell Disruptor (M220, Covaris) was used to cut the DNA sample into fragments of ~ 400–500 bp. The fragments were used as template to create a library using the TruSeq DNA Sample Prep Kit (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA). The prepared library was subjected to paired-end sequencing (2 × 150 bp) on an Illumina HiSeq 4000 platform at Shanghai Majorbio Bio-pharm Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). After quality control, the read sequences were assembled using SOAP de novo v2.04. Genes were predicted using the GeneMarkS online server, and tRNA sequences were searched using the tRNAscan-SE server. Translated genes were annotated by comparing with known protein sequences in the NCBI database using the BLASTP program with a threshold of E value < 10–5 and identity > 30%. Genome maps were generated based on the gene prediction and annotation results using Java Operon. The genome sequence of Gxv1 was searched against the Viral Sequence database of Integrated Microbial Genomes/Virus (IMG/VR) database (E value < 10−5) to identify the homologs of the Gxv1 genome (Paez-Espino et al. 2016). The genome sequence of Gxv1 was searched against the Viral Spacer database of IMG/VR database (E value < 10−5) to identify any putative CRISPR protospacers within the Gxv1 genome. Phylogenetic analysis of DNA polymerase was conducted based on the neighbour joining method using MEGA version 5.1 with 100 bootstrap replicates. The collinear analysis of the Gxv1 genome with two closely related genomes was performed using Mauve genome alignment software.
Data availability
The complete genome sequence for Bacillus phage Gxv1 was deposited in GenBank database under the accession number MT459794.
References
Ackermann HW (2001) Frequency of morphological phage descriptions in the year 2000. Arch Virol 146:843–857
Alicia DP, Laurentino V, Miguel DV, Margarita S (2012) Involvement of residues of the 29 terminal protein intermediate and priming domains in the formation of a stable and functional heterodimer with the replicative DNA polymerase. Nucleic Acids Res 40:3886–3897
Ana MA, Javier A, Carlos VJ, Fernanda MM, Alicia O, Minerva E, Ana M, Stuart H (2012) Is there a seamount effect on microbial community structure and biomass? The case study of Seine and Sedlo seamounts (northeast Atlantic). PLoS ONE 7:e29526
Anderson DL, Hickman DD, Reilly BE (1966) Structure of Bacillus subtilis bacteriophage phi 29 and the length of phi 29 deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol 91:2081–2089
Blanco L, Bernad A, Lázaro JM, Martí G, Garmendia C, Salas M (1989) Highly efficient DNA synthesis by the phage phi 29 DNA polymerase. Symmetrical mode of DNA replication. J Biol Chem 264:8935–8940
Chen A, Gui GF, Zhuo Y, Chai YQ, Xiang Y, Yuan R (2015) Signal-off electrochemiluminescence biosensor based on phi29 DNA polymerase mediated strand displacement amplification for microRNA detection. Anal Chem 87:6328–6334
Chiang OE, Quiñones RA (2007) Relationship between viral and prokaryotic abundance on the Bajo O’Higgins Seamount (Humboldt Current System off Chile). Sci Mar 71:37–46
Colombet J, Robin A, Lavie L, Bettarel Y, Cauchie HM, Sime-Ngando T (2008) Virioplankton ‘pegylation’: use of PEG (polyethylene glycol) to concentrate and purify viruses in pelagic ecosystems. J Microbiol Methods 71:212–219
Forges BRD, Koslow JA, Poore GCB (2000) Diversity and endemism of the benthic seamount fauna in the southwest Pacific. Nature 405:944–947
Gascón I, Lázaro JM, Salas M (2000) Differential functional behavior of viral phi29, Nf and GA-1 SSB proteins. Nucleic Acids Res 28:2034–2042
Gollner S, Kaiser S, Menzel L, Jones DOB, Brown A, Mestre NC, van Oevelen D, Menot L, Colaço A, Canals M, Cuvelier D, Durden JM, Gebruk A, Egho GA, Haeckel M, Marcon Y, Mevenkamp L, Morato T, Pham CK, Purser A et al (2017) Resilience of benthic deep-sea fauna to mining activities. Mar Environ Res 129:76–101
Hamidi SV, Ghourchian H, Tavoosidana G (2015) Real-time detection of H5N1 influenza virus through hyperbranched rolling circle amplification. Analyst 140:1502–1509
Hillier JK, Watts AB (2007) Global distribution of seamounts from ship-track bathymetry data. Geophys Res Lett 34:173–180
Hwang CY, Cho BC (2002) Virus-infected bacteria in oligotrophic open waters of the East Sea, Korea. Aquat Microb Ecol 30:1–9
Ito J, Meinke W, Hathaway G, Spizizen J (1973) Studies on Bacillus subtilis bacteriophage φ15. Virology 56:110–122
Jin M, Ye T, Zhang X (2013) Roles of bacteriophage GVE2 endolysin in host lysis at high temperatures. Microbiol SGM 159:1597–1605
Jin M, Guo X, Zhang R, Qu W, Gao B, Zeng R (2019) Diversities and potential biogeochemical impacts of mangrove soil viruses. Microbiome 7:58
Koslow JA, Gowlettholmes K, Lowry JK (2001) Seamount benthic macrofauna off southern Tasmania: community structure and impacts of trawling. Mar Ecol Prog 4:111–125
Marc BB, Massimo V, Eduardo R (2007) Causes for the intriguing presence of tRNAs in phages. Genome Res 17:1486–1495
Meijer WJ, Horcajadas JA, Salas M (2001) φ29 family of phages. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 65:261–287
Morato T, Hoyle SD, Allain V, Nicol SJ (2010) Seamounts are hotspots of pelagic biodiversity in the open ocean. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA 107:9707–9711
Paez-Espino D, Chen IMA, Palaniappan K, Ratner A, Chu K, Szeto E, Pillay M, Huang J, Markowitz VM, Nielsen T (2016) IMG/VR: a database of cultured and uncultured DNA viruses and retroviruses. Nucleic Acids Res 45:457–465
Parada V, Herndl GJ, Weinbauer MG (2006) Viral burst size of heterotrophic prokaryotes in aquatic systems. J Mar Biol Assoc UK 86:613–621
Pečenková T, Pačes V (1999) Molecular phylogeny of φ29-like phages and their evolutionary relatedness to other protein-primed replicating phages and other phages hosted by gram-positive bacteria. J Mol Evol 48:197–208
Pedulla ML, Ford ME, Houtz JM, Karthikeyan T, Wadsworth C, Lewis JA, Jacobs-Sera D, Falbo J, Gross J, Pannunzio NR (2003) Origins of highly mosaic mycobacteriophage genomes. Cell 113:171–182
Rogers AD (2019) Threats to seamount ecosystems and their management. In: Sheppard C (ed) World seas: an environmental evaluation, 2nd edn. Academic Press, New York, pp 427–451
Rohwer F, Thurber RV (2009) Viruses manipulate the marine environment. Nature 459:207–212
Rowden AA, Dower JF, Schlacher TA, Consalvey M, Clark MR (2010) Paradigms in seamount ecology: fact, fiction and future. Mar Ecol 31:226–241
Salas M (1983) A new mechanism for the initiation of replication of Φ 29 and adenovirus DNA: priming by the terminal protein. In: Doerfler W (ed) The molecular biology of adenoviruses 1. Springer, Berlin, pp 89–106
Salas M (2007) 40 years with bacteriophage ø29. Annu Rev Microbiol 61:1–22
Schilling T, Hoppert M, Daniel R, Hertel R (2018) Complete genome sequence of vB_BveP-Goe6, a virus infecting Bacillus velezensis FZB42. Genome Announc 6:e00008–00018
Suttle CA (2005) Viruses in the sea. Nature 437:356–361
Taehyun P, Struck DK, Deaton JF, Ry Y (2007) Topological dynamics of holins in programmed bacterial lysis. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA 103:19713–19718
Wessel P, Sandwell D, Kim SS (2010) The global seamount census. Oceanography 23:24–33
Ye X, Rossmann MG (2011) Structure of bacteriophage φ29 head fibers has a supercoiled triple repeating helix-turn-helix motif. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA 108:4806–4810
Zhao Y, Zhao Y, Zheng S, Zhao L, Li X, Zhang W, Grégori G, Xiao T (2020) Virioplankton distribution in the tropical western Pacific Ocean in the vicinity of a seamount. MicrobiologyOpen 9:e1031
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by China Ocean Mineral Resources R&D Association (No. DY135-B-04), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41976084), and the Scientific Research Foundation of Third Institute of Oceanography, MNR (No. 2019013).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MJ and RZ designed the experiments. XG, TZ, and MJ performed the experiments, analyzed the data, and wrote the manuscript. All authors edited and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All the authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Animal and human rights statement
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Edited by Jiamei Li.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, X., Zhang, T., Jin, M. et al. Characterization of Bacillus phage Gxv1, a novel lytic Salasvirus phage isolated from deep-sea seamount sediments. Mar Life Sci Technol 3, 13–19 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42995-020-00074-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42995-020-00074-8