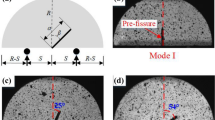
Abstract
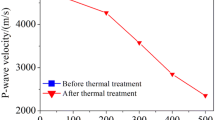
It’s necessary to understand mechanical and thermal fracture characteristics of hot dry rock under cyclic thermal loading to exploit geothermal resources. In this paper, the P-wave velocity test, saturated water absorption test and tensile test were carried out for hollow cylindrical granite samples after cyclic thermal shock. The influences of granite type, heating temperature (100–650 °C) and the number of thermal shock cycles were analyzed in the experimental study. In order to deeply study granite’s fracture and degradation mechanism during cyclic thermal shock, a grain-breakable numerical model which could catch the initiation and propagation of both inter- and intra-granular fractures was established by using the Discrete Element Method. The experimental results demonstrated that granite showed a significant reduction in P-wave velocity and tensile strength, and increase in porosity after cyclic thermal shock, more evident at higher heating temperature. These variations mainly occurred in the first 5 cycles, particularly in the first cycle, at all test temperatures. Cyclic thermal shock treatments introduced both grain-boundary and intra-granular fractures in rock samples, which was the key reason for the varying values of granite’s physical and mechanical characteristics. Thermal fractures increased remarkably after one cycle of heating–cooling treatments. With the increase of thermal loading cycles, the fractures showed a noticeable increasing trend in the first 5 cycles, then changed slightly in the following cycles, which agreed well with the experimental data. Thermal fractures propagated and expanded, accompanied by the closure of a few fractures as the thermal shock cycle increased. Inter- and intra-granular fracture behaviors were determined by test temperature and thermal shock cycles.
Article highlights
-
The P-wave velocity and porosity of granite vary significantly after cyclic heating and liquid nitrogen cooling treatments.
-
Granite’s tensile mechanical properties are determined by granite type, heating temperature, and thermal shock cycles.
-
Inter- and intra-granular fracture behaviors of granite during cyclic thermal shock are numerically obtained by using grain-breakable model.

































Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Data availability
The date and material used to support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding authors upon request.
References
Browning J, Meredith P, Gudmundsson A (2016) Cooling-dominated cracking in thermally stressed volcanic rocks. Geophys Res Lett 43:8417–8425. https://doi.org/10.1002/2016GL070532
Cai C, Li G, Huang Z et al (2014) Journal of natural gas science and engineering experimental study of the effect of liquid nitrogen cooling on rock pore structure. J Nat Gas Sci Eng 21:507–517. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jngse.2014.08.026
Cermak V, Rybach L (1982) Thermal properties: Thermal conductivity and specific heat of minerals and rocks. Landolt-Bornstein Zahlenwerte und Funktionen aus Naturwissenschaften und Tech. Neue Ser. 305–343
Côté J, Konrad J-M (2005) Thermal conductivity of base-course materials. Can Geotech J 42:61–78. https://doi.org/10.1139/t04-081
Fei Y (1995) Thermal expansion. In: Ahrens TJ (ed) Mineral physics and crystallography: a handbook of physical constants. American Geophysical Union, Washington, pp 29–44
Freire-Lista DM, Fort R, Varas-Muriel MJ (2016) Thermal stress-induced microcracking in building granite. Eng Geol 206:83–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2016.03.005
Gao F, Stead D, Elmo D (2016) Numerical simulation of microstructure of brittle rock using a grain-breakable distinct element grain-based model. Comput Geotech 78:203–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2016.05.019
Ge Z, Sun Q (2018) Acoustic emission (AE) characteristics of granite after heating and cooling cycles. Eng Fract Mech 200:418–429. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfracmech.2018.08.011
Itasca (2004) UDEC user manual. Itasca Consulting Group Inc. UDEC Version 4.0, Minneapolis
Kim K, Kemeny J, Nickerson M (2014) Effect of rapid thermal cooling on mechanical rock properties. Rock Mech Rock Eng 47:2005–2019. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-013-0523-3
Kumari WGP, Beaumont DM, Ranjith PG et al (2019) An experimental study on tensile characteristics of granite rocks exposed to different high-temperature treatments. Geomech Geophys Geo-Energy Geo-Resour 5:47–64. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40948-018-0098-2
Kumari WGP, Ranjith PG, Perera MSA et al (2018a) Hydraulic fracturing under high temperature and pressure conditions with micro CT applications: geothermal energy from hot dry rocks. Fuel 230:138–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2018.05.040
Kumari WGP, Ranjith PG, Perera MSA et al (2017) Temperature-dependent mechanical behaviour of Australian Strathbogie granite with different cooling treatments. Eng Geol 229:31–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2017.09.012
Kumari WGP, Ranjith PG, Perera MSA, Chen BK (2018b) Experimental investigation of quenching effect on mechanical, microstructural and flow characteristics of reservoir rocks: thermal stimulation method for geothermal energy extraction. J Pet Sci Eng 162:419–433. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.petrol.2017.12.033
Lan H, Martin CD, Hu B (2010) Effect of heterogeneity of brittle rock on micromechanical extensile behavior during compression loading. J Geophys Res 115:B01202. https://doi.org/10.1029/2009JB006496
Li B, Ju F (2018) Thermal stability of granite for high temperature thermal energy storage in concentrating solar power plants. Appl Therm Eng 138:409–416. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2018.04.071
Liu H, Zhang K, Shao S, Ranjith PG (2020) Numerical investigation on the cooling-related mechanical properties of heated Australian Strathbogie granite using discrete element method. Eng Geol 264:105371. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2019.105371
Liu Q, Qian Z, Wu Z (2019) Micro/macro physical and mechanical variation of red sandstone subjected to cyclic heating and cooling: an experimental study. Bull Eng Geol Environ 78:1485–1499. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-017-1196-z
Liu YD, Lin J, Feng YJ, Si LP (2018) Research on tensile strength of rock based on hydraulic fracturing method. Yantu Lixue/Rock Soil Mech 39:1781–1788. https://doi.org/10.16285/j.rsm.2016.1442
Nicksiar M, Martin CD (2014) Factors affecting crack initiation in low porosity crystalline rocks. Rock Mech Rock Eng 47:1165–1181. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-013-0451-2
Rong G, Peng J, Cai M et al (2018) Experimental investigation of thermal cycling effect on physical and mechanical properties of bedrocks in geothermal fields. Appl Therm Eng 141:174–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2018.05.126
Shao S, Wasantha PLP, Ranjith PG, Chen BK (2014) Effect of cooling rate on the mechanical behavior of heated Strathbogie granite with different grain sizes. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 70:381–387. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2014.04.003
Siratovich PA, Villeneuve MC, Cole JW et al (2015) Saturated heating and quenching of three crustal rocks and implications for thermal stimulation of permeability in geothermal reservoirs. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 80:265–280. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2015.09.023
Tan X, Konietzky H, Chen W (2016) Numerical simulation of heterogeneous rock using discrete element model based on digital image processing. Rock Mech Rock Eng 49:4957–4964. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-016-1030-0
Voake T, Nermoen A, Ravnås C et al (2019) Influence of temperature cycling and pore fluid on tensile strength of chalk. J Rock Mech Geotech Eng 11:277–288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrmge.2018.12.004
Wei W, Shao Z, Chen W et al (2021) Heating process and damage evolution of microwave absorption and transparency materials under microwave irradiation. Geomech Geophys Geo-Energy Geo-Resour 7:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40948-021-00284-z
Weng L, Wu Z, Liu Q (2020) Influence of heating/cooling cycles on the micro/macrocracking characteristics of Rucheng granite under unconfined compression. Bull Eng Geol Environ 79:1289–1309. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-019-01638-4
Yang J, Fu LY, Zhang W, Wang Z (2019) Mechanical property and thermal damage factor of limestone at high temperature. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 117:11–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2019.03.012
Yang S-Q, Ranjith PG, Jing H-W et al (2017) An experimental investigation on thermal damage and failure mechanical behavior of granite after exposure to different high temperature treatments. Geothermics 65:180–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geothermics.2016.09.008
Zhang S, Huang Z, Huang P et al (2018a) Numerical and experimental analysis of hot dry rock fracturing stimulation with high-pressure abrasive liquid nitrogen jet. J Pet Sci Eng 163:156–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.petrol.2017.12.068
Zhang S, Huang Z, Zhang H et al (2018b) Experimental study of thermal-crack characteristics on hot dry rock impacted by liquid nitrogen jet. Geothermics 76:253–260. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geothermics.2018.08.002
Zhou H, Jiang Y, Lu JJ et al (2018) Development of hollow cylinder torsional apparatus for rock. Yantu Lixue/Rock Soil Mech 39:1535–1542. https://doi.org/10.16285/j.rsm.2016.2481
Zhu WC, Tang CA (2004) Micromechanical model for simulating the fracture process of rock. Rock Mech Rock Eng 37:25–56. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-003-0014-z
Funding
This study was supported by the Future Scientists Program of China University of Mining and Technology (Grant No. 2020WLKXJ057) and the Postgraduate Research & Practice Innovation Program of Jiangsu Province (Grant No. KYCX20_1981).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, H., Zhang, K., Liu, T. et al. Experimental and numerical investigations on tensile mechanical properties and fracture mechanism of granite after cyclic thermal shock. Geomech. Geophys. Geo-energ. Geo-resour. 8, 18 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40948-021-00325-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40948-021-00325-7