Abstract
Background
Gender differences in orthostatic tolerance in the elderly are poorly studied and understood.
Methods
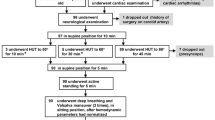
48 healthy elderly over 65 years (24 women), free from medication and without chronic diseases, were subjected to head-up tilt (HUT) tests: 30° for 10 min and 70° for 40 min. Blood pressures, stroke volume, total peripheral resistance, blood pressure variability, heart rate variability and baroreceptor sensitivity were measured and test terminations due to vasovagal syncope or unbearable presyncopal symptoms were registered.
Results
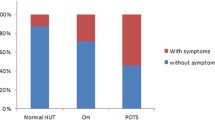
Mean age was 72; women and men differed in body mass index; 22.2 versus 24.8, respectively (p < 0.01). Mean blood pressures were lower among women, with 88 and 98 mmHg, respectively (p < 0.01) (rest) and 86 and 96 mmHg (p < 0.01) (tilt 30°). Mean total peripheral resistance index was significantly higher among women during 70° tilt, 13.5 versus 10.8 (p < 0.01); no gender differences in heart rate were seen. Women had lower LF/HF ratio (an index of sympathovagal balance) at rest and during 30° tilt (both p < 0.05); other heart rate variability measures and baroreceptor sensitivity did not differ. Two women, 9 %, and 8 men, 33 %, terminated head-up tilt test due to vasovagal syncope or presyncopal symptoms. Gender difference was marginally significant (p = 0.05, log-rank test). Higher heart rate at rest (p < 0.01) was the only variable significantly associated with the risk of syncope.
Conclusions
Our results indicate that elderly men have poorer orthostatic tolerance during protracted postural stress than women of the same age. The underlying reason might be differences in vascular rather than cardiac autonomic control.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ferrer A, Formiga F, Plana-Ripoll O, Tobella MA, Gil A, Pujol R (2012) Risk of falls in 85-year-olds is associated with functional and cognitive status: the Octabaix Study. Arch Gerontol Geriatr 54:352–356
Lehtola S, Koistinen P, Luukinen H (2006) Falls and injurious falls late in home-dwelling life. Arch Gerontol Geriatr 42:217–224
Wofford JL, Heuser MD, Moran WP, Schwartz E, Mittelmark MB (1994) Community surveillance of falls among the elderly using computerized EMS transport data. Am J Emerg Med 12:433–437
Lofthus CM, Osnes EK, Falch JA, Kaastad TS, Kristiansen IS, Nordsletten L, Stensvold I, Meyer HE (2001) Epidemiology of hip fractures in Oslo, Norway. Bone 29:413–418
Tinetti ME, Speechley M, Ginter SF (1988) Risk factors for falls among elderly persons living in the community. N Engl J Med 319:1701–1707
Moya A, Sutton R, Ammirati F, Blanc JJ, Brignole M, Dahm JB, Deharo JC, Gajek J, Gjesdal K, Krahn A, Massin M, Pepi M, Pezawas T, Ruiz GR, Sarasin F, Ungar A, van Dijk JG, Walma EP, Wieling W (2009) Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of syncope (version 2009). Eur Heart J 30:2631–2671
Brignole M (2006) Distinguishing syncopal from non-syncopal causes of fall in older people. Age Ageing 35(Suppl 2):ii46–ii50
Ungar A, Mussi C, Del RA, Noro G, Abete P, Ghirelli L, Cellai T, Landi A, Salvioli G, Rengo F, Marchionni N, Masotti G (2006) Diagnosis and characteristics of syncope in older patients referred to geriatric departments. J Am Geriatr Soc 54:1531–1536
Jonsson PV, Lipsitz LA, Kelley M, Koestner J (1990) Hypotensive responses to common daily activities in institutionalized elderly. A potential risk for recurrent falls. Arch Intern Med 150:1518–1524
Shaw FE, Kenny RA (1997) The overlap between syncope and falls in the elderly. Postgrad Med J 73:635–639
Grenon SM, Xiao X, Hurwitz S, Sheynberg N, Kim C, Seely EW, Cohen RJ, Williams GH (2006) Why is orthostatic tolerance lower in women than in men? Renal and cardiovascular responses to simulated microgravity and the role of midodrine. J Investig Med 54:180–190
Convertino VA (1998) Gender differences in autonomic functions associated with blood pressure regulation. Am J Physiol 275:R1909–R1920
Franke WD, Johnson CP, Steinkamp JA, Wang R, Halliwill JR (2003) Cardiovascular and autonomic responses to lower body negative pressure: do not explain gender differences in orthostatic tolerance. Clin Auton Res 13:36–44
Laitinen T, Niskanen L, Geelen G, Lansimies E, Hartikainen J (2004) Age dependency of cardiovascular autonomic responses to head-up tilt in healthy subjects. J Appl Physiol 96:2333–2340
Barnett SR, Morin RJ, Kiely DK, Gagnon M, Azhar G, Knight EL, Nelson JC, Lipsitz LA (1999) Effects of age and gender on autonomic control of blood pressure dynamics. Hypertension 33:1195–1200
Romero-Ortuno R, Cogan L, Foran T, Fan CW, Kenny RA (2010) Using the Finometer to examine sex differences in hemodynamic responses to orthostasis in older people. Blood Press Monit. 15:8–17
Barantke M, Krauss T, Ortak J, Lieb W, Reppel M, Burgdorf C, Pramstaller PP, Schunkert H, Bonnemeier H (2008) Effects of gender and aging on differential autonomic responses to orthostatic maneuvers. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 19:1296–1303
Fortin J, Habenbacher W, Heller A, Hacker A, Grullenberger R, Innerhofer J, Passath H, Wagner C, Haitchi G, Flotzinger D, Pacher R, Wach P (2006) Non-invasive beat-to-beat cardiac output monitoring by an improved method of transthoracic bioimpedance measurement. Comput Biol Med 36:1185–1203
Imholz BP, Wieling W, van Montfrans GA, Wesseling KH (1998) Fifteen years experience with finger arterial pressure monitoring: assessment of the technology. Cardiovasc Res 38:605–616
Malik et al (1996) Heart rate variability: standards of measurement, physiological interpretation and clinical use. Task Force of the European Society of Cardiology and the North American Society of Pacing and Electrophysiology. Circulation 93:1043–1065
Bertinieri G, di Rienzo M, Cavallazzi A, Ferrari AU, Pedotti A, Mancia G (1985) A new approach to analysis of the arterial baroreflex. J Hypertens 3(Suppl 3):S79–S81
Parry SW, Reeve P, Lawson J, Shaw FE, Davison J, Norton M, Frearson R, Kerr S, Newton JL (2009) The Newcastle protocols 2008: an update on head-up tilt table testing and the management of vasovagal syncope and related disorders. Heart 95:416–420
Galizia G, Abete P, Mussi C, Noro G, Morrione A, Langellotto A, Landi A, Cacciatore F, Masotti G, Rengo F, Marchionni N, Ungar A (2008) Role of early symptoms in assessment of syncope in elderly people: results from the Italian Group for the Study of Syncope in the Elderly. J Am Geriatr Soc 57:18–23
Brignole M, Menozzi C, Del RA, Costa S, Gaggioli G, Bottoni N, Bartoli P, Sutton R (2000) New classification of haemodynamics of vasovagal syncope: beyond the VASIS classification. Analysis of the pre-syncopal phase of the tilt test without and with nitroglycerin challenge. Vasovagal Syncope International Study. Europace. 2:66–76
Levy MN, Pappano AJ (2007) Cardiovascular physiology, 9th edn. Mosby Elsevier, Amsterdam
Parry SW, Norton M, Pairman J, Baptist M, Wilton K, Reeve P, Sutcliffe K, Newton JL (2009) Impedance cardiography: a role in vasovagal syncope diagnosis? Age Ageing 38:718–723
Monahan KD, Ray CA (2004) Gender affects calf venous compliance at rest and during baroreceptor unloading in humans. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 286:H895–H901
Lindenberger M, Lanne T (2007) Decreased capillary filtration but maintained venous compliance in the lower limb of aging women. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 293:H3568–H3574
Tomiyama H, Yamashina A, Arai T, Hirose K, Koji Y, Chikamori T, Hori S, Yamamoto Y, Doba N, Hinohara S (2003) Influences of age and gender on results of noninvasive brachial-ankle pulse wave velocity measurement–a survey of 12517 subjects. Atherosclerosis 166:303–309
Smith JJ, Porth CJ (1991) Posture and the circulation: the age effect. Exp Gerontol 26:141–162
Ludwig DA, Vernikos J, Wade CE, Convertino VA (2001) Blood pressure changes during orthostatic stress: evidence of gender differences in neuroeffector distribution. Aviat Space Environ Med 72:892–898
Groothuis JT, Thijssen DH, Kooijman M, Paulus R, Hopman MT (2008) Attenuated peripheral vasoconstriction during an orthostatic challenge in older men. Age Ageing 37:680–684
Gelman S (2008) Venous function and central venous pressure: a physiologic story. Anesthesiology 108:735–748
Shibao C, Grijalva CG, Raj SR, Biaggioni I, Griffin MR (2007) Orthostatic hypotension-related hospitalizations in the United States. Am J Med 120:975–980
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Oslo University Hospital
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mellingsæter, M.R., Wyller, V.B., Wyller, T.B. et al. Gender differences in orthostatic tolerance in the elderly. Aging Clin Exp Res 25, 659–665 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40520-013-0092-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40520-013-0092-z