Abstract
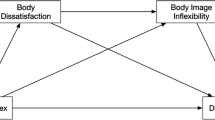
The present study explored the links between cognitive restraint and body image in obese adolescents when compared with normal-weight adolescents according to sex. Body image was measured on the Body Esteem Scale and cognitive restraint by means of the Three-Factor Eating Questionnaire Revised 18-item version (TFEQ-R18). Although the results did not reveal any significant correlation between overall scores on these two measures, subscale scores showed that the obese adolescents used cognitive restraint more than the normal-weight adolescents did as a strategy for regulating their diet and were less satisfied with their body image. The normal-weight adolescents’ use of cognitive restraint was correlated with body-weight dissatisfaction. Despite these differences, the two populations shared several characteristics. All the adolescents were dissatisfied with the way they thought that others saw them. The loss of control was one of their major concerns, although in the obese adolescents, it went hand in hand with major emotional investment. The results suggest that these are the variables responsible for adolescents’ eating habits, regardless of their weight. The most discriminating variable when crossed with weight was sex, with girls being less satisfied with their body image, especially when they were obese.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schachter S, Rodin J (1974) Obese humans and rats. Erlbaum Halstead, Washington, DC
Rodin J (1981) Current status of the internal-external hypothesis for obesity: what went wrong? Am Psychol 36:361–372
Herman CP, Mack D (1975) Restrained and unrestrained eating. J Personal 43:647–660
Herman CP, Polivy J (1984) A boundary model for the regulation of eating. In: Stunkard AJ, Stellar E (eds) Eating and its disorders. Raven, New York, pp 141–156
Williamson DA, Lawson OJ, Brooks ER et al (1995) Association of body mass with dietary restraint and disinhibition. Appetite 25:31–41
Cash T, Pruzinski T (2002) Body image: a handbook of theory, research, and clinical practice. Guilford Press, New York
Rosen JC (1996) Body image assessment and treatment in controlled studies of eating disorders. Int J Eat Disord 20:331–343
Striegel-Moore RH, Franko DL (2002) Body image issues among girls and women. In: Cash TF, Pruzinsky T (eds) Body image: a handbook of theory, research and clinical practice. Guilford Press, London, pp 183–191
Wallon H (1959) Kinesthésie et image visuelle du corps propre chez l’enfant. Enfance 12:252–263
Videon TM, Manning CK (2003) Influences on adolescent eating patterns: the importance of family meals. J Adolesc Health 32:365–373
Tiggemann M (2004) Body image across the life span: stability and change. Body Image 1:29–41
Littleton H, Ollendick T (2003) Negative body image and disordered eating behaviour in children and adolescents: what places youth at risk and how can these problems be prevented? Clin Child Fam Psychol Rev 6:51–66
Abric JC (1994) Pratiques Sociales et Représentations. PUF, Paris
Grilo CM, Wilfley DE, Brownell KD, Rodin J (1994) Teasing, body image and self-esteem in a clinical sample of obese women. Addict Behav 19:443–450
Hoffmann-Müller B, Amstad H (1994) Body image, weight and eating behavior in adolescents. Praxis 83:1336–1342
Adami GF, Marinari GM, Bressani A, Testa S, Scopinaro N (1998) Body image in binge eating disorder. Obes Surg 8:517–519
Schwartz MB, Brownell KD (2004) Obesity and body image. Body Image 1:43–56
Feingold A, Mazzella R (1998) Gender differences in body image are increasing. Psychol Sci 9:190–195
Finemore J, Holt KE, McCabe MP, Ricciardelli LA (2003) A biopsychosocial model for understanding body image and body change strategies among children. Appl Dev Psychol 24:475–495
Cash TF, Roy RE (1999) Pounds of flesh: weight, gender, and body images. In: Sobal J, Maurer D (eds) Interpreting weight: the social management of fatness and thinness. Hawthorne, Aldine de Gruyter, pp 209–228
Levine MP, Smolak L (2002) Body image development in adolescence. In: Cash TF, Pruzinsky T (eds) Body image: a handbook of theory, research and clinical practice. Guilford Press, London, pp 74–82
Spear BA (2006) Does dieting increase the risk for obesity and eating disorders? J Am Diet Assoc 106:523–525
Caflish M, Paris V (2000) L’adolescent obèse: Un casse-tête ou un défi? Médecine et Hygiène 58:2566–2568
Raich RM, Torras-Clarasó J, Mora M (1997) Analisis estructural de variables influyentes en la aparicion de alteraciones de la conducta alimentaria. Psicologia Conductual 1:55–70
Gualldi-Russo E, Albertini A, Argnani L, Celenza F, Nicolucci M, Toselli S (2008) Weight status and body image perception in Italian children. J Hum Nutr Diet 21:39–45
Stunkard AJ, Wadden TA (1992) Psychological aspects of severe obesity. Am J Clin Nutr 55:5245–5325
Foster GD, Wadden TA, Vogt RA (1997) Body image in obese women before, during, and after weight loss treatment. Health Psychol 16:226–229
Valtolina GG (1998) Body-size estimation by obese subjects. Percept Mot Skills 86:1363–1374
Gallant AR, Tremblay A, Pérusse L et al (2010) The Three-Factor Eating Questionnaire and Body Mass Index in Adolescents: results from the Quebec Family Study. Br J Nutr 7:1–6
Rand CSW, Kuldau JM (1991) Restrained eating (weight concerns) in the general population and among students. Int J Eat Disord 10:699–708
Cole TJ, Bellizi MC, Flegal KM et al (2000) Establishing a standard definition for child overweight and obesity worldwide: international survey. BMJ 320:1240–1243
Mendelson BK, Mendelson MJ, White DR (2001) Body-esteem scale for adolescents and adults. J Personal Assess 76:90–106
de Lauzon B, Romon M, Deschamps V et al (2004) The Three-Factor Eating Questionnaire-R18 is able to distinguish among different eating patterns in a general population. Nutr Epidemiol 134:2372–2380
Karlsson J, Persson L-O, Sjöström L, Sullivan M (2000) Psychometric properties and factor structure of the Three-Factor Eating Questionnaire (TFEQ) in obese men and women. Results from the Swedish Obese Subjects (SOS) study. Int J Obes 24:1715–1725
Espnes GA, Klomsten AT, Skaalvik EM (2004) Physical self-concept and sports. Do gender differences still exist? Sex Roles 50:119–127
Harter S (1988) The self-perception profile for adolescents. University of Denver, Denver
Ricciardelli LA, Holt KE, McCabe MP, Finemore J (2003) A biopsychosocial model for understanding body image and body change strategies among children. Appl Dev Psychol 24:475–495
Harter S (1993) Causes and consequences of low self-esteem in children and adolescents. In: Baumeister RF (ed) Self-esteem: the puzzle of low self-regard. Plenum, New York, pp 87–116
Robins RW, Trzniewski KH, Tracy JL et al (2002) Global self-esteem across the lifespan. Psychol Aging 17:423–434
Bruch H (1984) Les Yeux et le Ventre. L’Obèse, l’Anorexique. Paris, Editions Payot et Rivages
Guilbaud O, Corcos M, Chambry J et al (2000) Alexithymie et dépression dans les troubles des conduites alimentaires. L’Encéphale 26:1–6
Stice E, Sysko R, Roberto C, Allison S (2010) Are dietary restraint scales valid measures of dietary restriction? Additional objective behavioral and biological data suggest not. Appetite 54:331–339
Attie I, Brooks-Gunn J (1989) Development of eating problems in adolescent girls: a longitudinal study. Dev Psychol 25:70–79
Killen JD, Taylor CB, Hayward C et al (1996) Weight concerns influence the development of eating disorders: a 4-year prospective study. J Consult Clin Psychol 64:936–940
Stice E (2002) Risk and maintenance factors for eating pathology: a meta-analytic review. Psychol Bull 128:825–848
Rierdan J, Koff E, Stubbs ML (1989) A longitudinal analysis of body image as a predictor of the onset and persistence of adolescent girls’ depression. J Early Adolesc 9:454–466
Stice E, Hayward C, Cameron R et al (2000) Body image and eating disturbances predict onset of depression in female adolescents: a longitudinal study. J Abnorm Psychol 109:438–444
Neumark-Sztainer D (2003) Obesity and eating disorder prevention: an integrated approach? Adolesc Med State Art Rev 14:159–173
Hilbert A, Tuschen-Caffier B, Vogele C (2002) Effects of prolonged and repeated body image exposure in binge eating disorder. J Psychosom Res 52:137–144
Levine MP, Piran N (2004) The rôle of body image in the prevention of eating disorders. Body Image 1:57–70
Stice E, Shaw HE (2002) Role of body dissatisfaction in the onset and maintenance of eating pathology: a synthesis of research findings. J Psychosom Res 5:985–993
Jansen A, Bollen D, Tuschen-Caffier B et al (2008) Mirror exposure reduces body dissatisfaction and anxiety in obese adolescents: a pilot study. Appetite 51:214–217
Killen JD, Taylor CB, Hayward C, Haydel KF, Wilson DM, Hammer L (1996) Weight concerns influence the development of eating disorders: a 4-year prospective study. J Consult Clin Psychol 64:936–940
Stice E, Orjada K, Tristan J (2006) Trial of psychoeducational eating disturbance intervention for college women: a replication and extension. Int J Eat Disord 39:233–239
Smolak L (2004) Body image in children and adolescents: where do we go from here? Body Image 1:15–28
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Megalakaki, O., Mouveaux, M., Hubin-Gayte, M. et al. Body image and cognitive restraint are risk factors for obesity in French adolescents. Eat Weight Disord 18, 289–295 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40519-013-0027-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40519-013-0027-x