Abstract
Ankle impingement is a common condition occurring secondary to sprain or repeated microtrauma. Clinical symptoms are chronic pain located in the affected region and limited range of ankle motion. There are three types of ankle impingement syndrome: anterior impingement, which can be subdivided into anterolateral, anteromedial and purely anterior impingement; posterior impingement, which can be subdivided into posterior and posteromedial impingement; and calcaneal peroneal impingement which is secondary to planovalgus foot deformity. This paper evaluates physiological and clinical elements of these three types of ankle impingement syndrome as well as the role of ultrasound (US) imaging and US-guided treatment.
Riassunto
I conflitti di caviglia sono comuni, a seguito di distorsioni o di microtraumi ripetitivi, i sintomi clinici associati sono dolore cronico dalla topografia variabile e limitazione, più o meno dolorosa, dei movimenti. Complessivamente esistono tre tipi di conflitti: anteriori che possono essere suddivisi in antero-laterali, antero-mediali e anteriori puri, posteriori che possono essere divisi in posteriori e postero-mediali e calcaneo-peroneale, secondario al piede piatto valgo. Dei vari tipi di conflitto vengono valutati la fisiologia, la clinica, l’imaging ed il ruolo dell’ecografia. Viene infine considerata la possibilità di trattamenti terapeutici eco-guidati.
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Ankle impingement is a common condition occurring secondary to sprain or repeated microtrauma. Clinical symptoms include chronic pain located in the affected region and limited range of ankle motion. These clinical abnormalities are related to interposition of more or less calcified synovial tissue in the joint space. They are often associated with bone and soft tissue abnormalities in varying proportions. For example, bone abnormalities are predominant in posterior impingement but secondary to soft tissue lesions in anterolateral impingement. Most cases of impingement are preceded by episodes of acute or chronic instability [1].
There are three types of ankle impingement:
-
anterior impingement, which can be subdivided into anterolateral, anteromedial and purely anterior impingement;
-
posterior impingement, which can be subdivided into posterior and posteromedial impingement; and
-
calcaneal peroneal impingement which is secondary to planovalgus foot deformity.
Posterior impingement
Physiological and clinical features
Posterior impingement is the result of repeated microtrauma (in ballet dancers or soccer players) or injury placing the ankle in forced plantar flexed position, generally in a neutral position. It is caused by a “pincer” effect on the structures located between the calcaneus and the posterior lip of the tibia bone. This effect is linked to the morphology of the posterolateral process of the talus:
-
If it is long or if there is an os trigonum (which is commonly the case), bone abnormalities are predominant. Instability of the syndesmosis or synchondrosis of the os trigonum and injuries (microtrauma) to the prominent posterolateral process will be encountered whereas soft tissue abnormalities will be limited.
-
If it is short, soft tissue abnormalities will be evident at the posterior talofibular ligament, the posterior intermalleolar ligament, the posterior tibioperoneal ligament, the capsule and the flexor hallucis longus tendon. The disorder is not always caused by an acute trauma, and the onset of symptoms is usually gradual and progressive over weeks [2].
Imaging
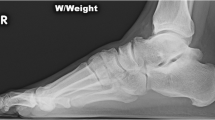
Imaging is an essential tool in the diagnosis of posterior impingement (Fig. 1) and for a differential diagnosis (Fig. 2) involving tendinopathy of the Achilles tendon and Haglund’s syndrome. In the acute phase, X-ray examination in the lateral view is the most informative for the detection of posterior malleolus fractures of the tibia and abnormalities of the posterolateral process of the talus. It is, therefore, necessary to establish if the process is long and if there are signs of fracture or instability of the syndesmosis or synchondrosis of the os trigonum. In the chronic phase, X-rays are the basic starting point for the diagnosis of ankle impingement (Fig. 1b). Even though they are non-specific, it is necessary to look for morphological abnormalities, such as posterior joint space narrowing linked to the onset of arthropathy. Computed tomography (CT) can depict the morphology of the posterolateral process of the talus, specify the appearance of the gap and provide signs of instability of the os trigonum.
Posterior ankle impingement. a Longitudinal scan showing the posterolateral process of the talus (star) with no sign of synovitis. b CT arthrography with reconstruction in the sagittal plane showing rupture due to pseudoarthrosis (white arrow) in the posterolateral process (star), not identified on US image. 1 Achilles tendon; 2 calcaneus; 3 tibia
Differential diagnosis: posterior impingement or secondary osteochondromatosis. US imaging, longitudinal view (a) and axial view (b), shows the presence of calcific density (white arrows) of the posterior cavity of the ankle. X-ray (c) shows the presence of osteochondromatosis of the posterior process (white arrows) and anterior recess (arrowheads) associated with joint space narrowing (black arrow)
CT arthrography allows assessment of bones and ligaments and provides information about possible chondropathy affecting the posterior aspect of the joint. It also permits a correct morphological analysis of the posterior cavity of the talus and reveals the presence of synovial hypertrophy and foreign bodies. The presence of contrast agent in the cavity will suggest instability of the os trigonum or pseudoarthrosis. Magnetic resonance (MR) imaging is the method of choice as it provides a study of bones and soft tissues. T1-weighted sequences are used for identifying the bones and for an accurate morphological analysis of the posterolateral process of the talus. Bone marrow edema within the talus is a common finding, particularly if the examination is carried out shortly after the injury or after excessive plantar flexion [3, 4]. In our experience, signal abnormalities are most often observed in case of hypertrophy of the posterolateral tubercle, followed by disorders involving the posterior lip of the talus and the upper aspect of the calcaneus.
MR imaging is particularly useful as it provides evaluation of the soft tissues including the posterior capsule, posterior intermalleolar ligament and the flexor hallucis longus tendon. Intravenous injection of contrast agent is not always required but may be useful for detecting small synovial disorders [1]. Finally, it is possible to perform selective injection of local anesthetic using lidocaine or corticosteroids under US guidance in an attempt to relieve pain [5].
US imaging
US imaging is performed using a high-frequency linear probe (Figs. 1, 2). Sagittal views are useful for identifying the location of the recess; however, sometimes a lower frequency probe (10–12 MHz) may be more adequate for evaluating the deep structures adjacent to the anterior aspect of Kager’s triangle. First step is to locate a possible fluid collection in the posterior recess, even though this finding is non-specific. Also axial views are important for possibly identifying tenosynovitis of the flexor hallucis longus tendon and communication between the tendon and the medial recess. US imaging performed as the first examination in the work up of these patients furthermore provides a differential diagnosis (Fig. 2) including enthesitis, tendinopathy and impingement between the Achilles tendon and the calcaneus in connection with Haglund’s syndrome.
Posteromedial impingement
Physiological and clinical features
Posterior impingement occurs due to inversion injury with damage to the anterior and lateral capsular ligaments (usually the anterior talofibular ligament) and kickback injury with damage to the deep tibiotalar component of the medial collateral ligament trapped between the medial malleolus and the medial portion of the talus [6]. Posterior symptoms gradually appear, while clinical signs disappear from the anterolateral aspect of the ankle.
According to Koulouris et al. [7], the most commonly involved structure in posteromedial impingement is the posterior tibiotalar ligament which presents with hypertrophic scarring and fibrous tissue. The lesion rarely affects the posteromedial capsule only, as it is generally associated with lesions of the posterior tibial and flexor hallucis longus tendons [8].
Imaging
MR imaging (Fig. 3) is the imaging examination of choice as it permits identification of coexisting anterolateral and posteromedial capsule ligament lesions and particularly associated osteochondral lesions [8].
According to Koulouris et al. [7], MR imaging always reveals the loss of striped appearance and disappearance of the underlying fat of the posterior tibiotalar bundle of the medial collateral ligament. This injury extends to the capsule in the deep layers, and in the superficial layers to the flexor tendons, particularly the posterior tibial tendon.
Messiou et al. [9] reported that synovial lesions were constant in a series of nine patients, whereas tibiotalar ligament lesions were less frequent (4 out of 9 patients). Gadolinium is useful for detecting synovial lesions which are sometimes difficult to detect using T1- or T2-weighted sequences.
US imaging
In US imaging, there is a loss of striped appearance of the posterior portion of the medial collateral ligament. The excellent spatial resolution of US imaging allows depiction of avulsion injuries and small calcifications such as calcified metaplasia of the ligaments which may be missed at MR imaging. On the other hand, it may be difficult to distinguish capsular lesions from deep ligament lesions. Color Doppler US often shows areas of hyperemia in areas of architectural disorganization. Tendon abnormalities occur particularly in tenosynovitis. Structural abnormalities of the tendon are rare in the initial phase.
Anterolateral impingement
Physiological and clinical features
Anterolateral impingement occurs secondary to inversion injury and it generally causes anterolateral pain which is aggravated by dorsiflexion, eversion and flexion in single leg stance. There may be soft tissue swelling. Usually this disorder is not associated with laxity. However, given the type of initial trauma, anterior talofibular ligament injuries are common. Obliteration of the anterolateral recess is the result of synovial hyperplasia secondary to post-traumatic hemorrhage and/or abnormal scarring of the anterior talofibular ligament [10].
The presence of an additional hypertrophic bundle of the anterior and distal tibiofibular ligament has also been reported as a cause of anterolateral impingement [11] but in our experience this phenomenon is uncommon.
Imaging (Figs. 4, 5) is useful for a positive diagnosis of impingement and the differential diagnosis including other disorders, such as delayed healing of the ligament, articular cartilage lesions, the presence of intra-articular foreign bodies or peroneal tendon disorders [12]. According to a recent study, chondral or osteochondral lesions may be associated with abnormal growth of scar tissue and synovial abnormalities, but their presence or absence does not seem to affect the long-term prognosis after arthroscopic synovectomy [13].
Imaging
X-rays are essential for the detection of foreign bodies in the anterolateral recess as well as abnormalities of the talar dome caused by degenerative ankle disorder. Dynamic X-ray examinations should always be performed when there is clinical suspicion of laxity.
MR imaging can show synovial hypertrophy in the anterolateral recess and possible chronic damage to the anterior talofibular ligament which may appear thinned, torn or thickened. Diagnostic ability of MR imaging depends on the degree of joint distension which may be limited by the presence or absence of joint effusion or contrast agent. Sensitivity and specificity vary greatly in the literature [14].
MR arthrography or CT arthrography may increase the diagnostic accuracy. According to a study by Robinson et al. [15], MR arthrography is the gold standard in the study of anterolateral impingement; diagnostic, accuracy is 97 %, sensitivity 96 %, specificity 97 %, negative predictive value (NPV) 89 % and positive predictive value (PPV) 100 %. However, it is important to keep in mind that radiological abnormalities of the anterolateral recess are common also in asymptomatic patients (almost 60 % of a control group studied by Robinson). This means that a correct diagnosis requires an accurate comparison between clinical and radiological findings.
CT arthrography is a useful examination in the diagnosis of anterolateral impingement, because it can provide a positive diagnosis of impingement and visualization of articular cartilage injuries, which are frequently associated. Diagnosis is based on the presence of a distinctly irregular appearance of the anterolateral recess and/or the presence of a fluid-filled nodular formation [16]. Sensitivity and specificity of CT arthrography are 97 and 71 %, respectively, when compared with arthroscopy considered as the gold standard [12].
US imaging
The main point of reference in US evaluation of the anterolateral portion is the anterior talofibular ligament. Axial scans are performed with inversion and internal rotation of the ankle, as this position permits assessment of the continuity of the ligament fibers. Sagittal scans are performed with the probe positioned perpendicular to the anterior talofibular ligament to analyze the relationship between the inferior aspect of the ligaments and the chondral plane of the lateral portion of the talus. The examination is facilitated by the presence of joint effusion which provides a natural contrast between the bone structure and the soft tissue lesions.
Using a small probe, it is possible to induce pain when the probe exerts pressure on the synovial mass, which in turn exerts pressure on the lateral portion of the cartilage of the talus. In this maneuver, described by McCarthy to increase sensitivity of the examination, the fibula exerts pressure on the tibia to evidence the synovial mass. The mere presence of a mass with variable echogenicity deep in the anterior talofibular ligament cannot in itself justify a diagnosis of impingement. The size of the mass is an important criterion, but controversial: more than 7 mm according to Cochet and more than 10 mm according to McCarthy. Also the echogenicity of the mass is subject to debate: the mass is usually heterogeneous, but the presence of a homogeneous hyperechoic mass is more frequent in asymptomatic patients [17]. However, hyperemia revealed by color or power Doppler US is a finding which indicates the pathological character of a mass located in the anterolateral recess [12]. A biconvex appearance and thickening of the ligament is, in our experience, a further sign of impingement.
Diagnostic performance of US imaging is lower than that of other methods which use contrast-induced opacification. According to a study published by Cochet et al. [12], the diagnostic performance of US imaging versus arthroscopy before and after intra-articular injection of contrast agent (CT arthroscopy), sensitivity and specificity were 77 and 55 %, respectively, before opacification and 85 and 71 %, respectively, after opacification. However, US is inexpensive, widely available and of high diagnostic value, and it is furthermore very useful in the treatment of patients, particularly US guidance of targeted injections.
Anteromedial impingement
Physiological and clinical features
Anteromedial impingement occurs mainly secondary to microtrauma in supination (inversion) or in case of chronic ankle instability [1] which eventually leads to chronic synovitis (Figs. 6, 7) and the formation of osteophytes which are responsible for fluid collections in the anteromedial cavity, between the anterior side of the tibia and the medial side of the talar neck [18]. Anteromedial impingement may be associated with anterior and/or anterolateral impingement as well as chondral lesions and is suspected in the presence of anteromedial elective pain increased by dorsal flexion. However, also plantar flexion and inversion can trigger the pain.
Dorsiflexion reduces the volume of the articular joint space at the anteromedial aspect thereby compressing the hypertrophic synovial tissue which is painful [19].
The widely used term “osteophytes” may lead to confusion because there is no real osteoarthritis [20], and the term “bone spurs” should therefore be preferred. They are located in an area of no loading on the anterior aspect of the tibia and medial malleolus and/or on the medial side of the neck of the talus. The presence of bone spurs is not sufficient for the diagnosis. In fact, according to two radiographic studies [21, 22], similar formations were found in 50 % of cases in a series of asymptomatic athletes.
Synovial hypertrophy is located anteromedially to the deep tibiotalar fascia of the deltoid ligament (a fascia which is difficult to detect both at dissection and at arthroscopy) [23, 24].
A study of 11 surgical patients revealed synovial hypertrophy and thickening of the anterior fascia of the tibiotalar ligament in 8 patients with bone proliferation of the talar neck; in 3 patients associated with chondropathy of the talus and in 6 patients associated with anterolateral impingement [23].
Imaging
Standard X-ray examination (in orthogonal anteroposterior and lateral views) is insufficient for the diagnosis, because the anteromedial aspect of the tibiotalar joint is concealed by the projection of the lateral aspect of the tibia which is larger.
In order to overcome this problem, a specific angle of incidence has been described in the literature [20], i.e., the anteromedial impingement (AMI) view. It is a lateral view with double obliquity (craniocaudal inclination of 45° with the foot in plantar flexion and external rotation of 30°), which provides a correct visualization of the anteromedial aspect of the joint evidencing possible bone proliferations.
It has been shown that sensitivity in the detection of tibial and talar bone spurs (also referred to as osteophytes) is 40 and 32 %, respectively, if only standard examination is carried out, but it increases to 85 and 73 %, respectively, if AMI view is performed [25]. Dynamic imaging is essential if acquired or genetic ligamentous laxity is suspected.
MR imaging, especially after intravenous injection of contrast medium, permits detection of synovial lesions (Fig. 7b) and abnormalities of the anterior and deep medial collateral ligament. MR imaging is performed also to detect or rule out other causes of chronic pain, particularly pain affecting the talar dome [1].
Intra-articular injection of contrast medium (CT arthrography or MR arthrography) seems to be the most appropriate technique for a correct diagnosis of anteromedial impingement [26].
US imaging
B-mode US can detect synovial lesions in the medial premalleolar region, and Color Doppler US is useful for detecting hyperemia, which may be inconstant, but painful. US imaging also permits visualization of osteophytes, which may be missed at X-ray examination if they are small and if the AMI view is not performed. US is also useful for evidencing or excluding injury to the spring ligament, posterior tibial tendinopathy or injury to the flexor retinaculum. It is a widely used imaging technique, but the outcome is reliable mainly when it is positive. However, US imaging limits the use of examinations requiring intra-articular contrast opacification.
Anterior impingement
Physiological and clinical features
Anterior impingement is rarely isolated, and it is frequently associated with anterolateral and/or anteromedial impingement. The first cases described in the literature occurred in football players and ballet dancers, and it was manifested by anterior pain, which was aggravated by dorsiflexion. This condition is frequently related to direct microtrauma (football).
Imaging
X-ray examination in lateral projection is the most useful method for detecting and describing bone spurs (Fig. 8a). Oblique AMI views should be performed systematically to identify possible medial osteophytes. On the MR imaging scan, the bones adjacent to the areas of impact (front lip of the tibia, talar neck) may show abnormal signal intensity, synovial thickening and effusion [27]. In advanced stages, there will be a more or less marked fluid collection, geodic cavities and bone marrow edema. Injection of gadolinium does not seem to increase the performance of MR imaging in the diagnosis of anterior impingement [28].
US imaging
Also in this case, sagittal views are the most informative showing synovial thickening of the anterior ankle joint recess (Fig. 8). This thickening is often associated with the presence of small foreign bodies. Hyperemia is of inconstant degree, but always correlated with clinical symptoms.
The role of US in the treatment of ankle impingement
In our institute, treatment of ankle impingement includes injection of anesthetics (Figs. 9, 10), and it is always carried out when diagnostic imaging has detected synovial involvement whether or not associated with a bone component. US guidance improves accuracy and reduces pain and complications. The use of small US probes, generally referred to as “golf clubs”, facilitates perimalleolar injection. Aseptic precautions must be rigorous and include thorough skin disinfection and sterile US probe cover. Contraindications may be local (skin infection) or systemic (coagulation disorders, sepsis, uncontrolled diabetes), but they are rare [29].
Anterolateral ankle impingement, injection of anesthetics. a Axial T2-weighted MR scan with fat saturation shows synovitis of the posterior recess of the ankle (star) and fluid collection in the sheath of the flexor hallucis longus tendon (arrowhead). US imaging: probe position (white line), needle path under US guidance and axial scans to monitor the needle at the flexor hallucis longus tendon (b) and the posterolateral process of the talus (c)
Selective injection of lidocaine 1 % permits a test, and prognosis is favorable, when the test is positive [5]. Relative rest is desirable on the day following the injection; a second injection can be administered if only partial resolution of symptoms is obtained after the first injection [30].
The aim of anesthetic injection is to reduce clinical symptoms and the need for surgery thereby ensuring an earlier return to normal activities. In a study reporting on anesthetic injection in athletes with posterior impingement, Robinson [2] observed no recurrence in the treated patients, with the exception of those who had an os trigonum.
Another study reported the benefit of anesthetic injection (one or two injections) in patients with unstable synchondrosis affecting the posterolateral process of the talus [9].
In our institution, US guidance is preferred to radiological guidance, as US does not expose the patient and the operators to ionizing radiation and because no contrast agent is required. If the lesion is large, US easily permits injection in more than one area (fibrous scar, joint recess, tendon sheath, syndesmosis) in the same session. If necessary, US furthermore permits dry needling of a fibrous nodule before injection of steroids, a procedure which cannot be carried out under fluoroscopic control.
US imaging can also detect neurovascular pedicles; this is particularly useful in the management of posterior and posteromedial impingement of the posterior tibial neurovascular bundle.
References
Robinson P, White LM (2002) Soft-tissue and osseous impingement syndromes of the ankle: role of Imaging in diagnosis and management. Radiographics 22:1457–1471
Robinson P, Bollen SR (2006) Professional ankle impingement in professional soccer players: effectiveness of sonographically guided therapy. AJR Am J Roentgenol 187:53–58
Karasick D, Schweitzer ME (1996) The os trigonum syndrome: imaging features. AJR Am J Roentgenol 166:125–129
Bureau NJ, Cardinal E, Hobden R, Aubin B (2000) Posterior ankle impingement syndrome: MR imaging findings in seven patients. Radiology 215:497–503
Mitchell MJ, Bielecki D, Bergman AG, Kursunoglu-Brahme S, Sartoris DJ, Resnick D (1995) Localization of specific joint causing hindfoot pain: value of injecting local anesthesia into individual joints during arthrography. AJR Am J Roentgenol 164:1473–1476
Paterson RS, Brown JN (2001) The posteromedial impingement lesion of the ankle: a series of six cases. Am J Sports Med 29:550–557
Koulouris G, Connell D, Schneider T, Edwards W (2003) Posterior tibiotalar ligament injury resulting in posteromedial impingement. Foot Ankle Int 24:575–583
Lee JC, Calder JD, Healy JC (2008) Posterior impingement syndromes of the ankle. Semin Musculoskelet Radiol 12(2):154–169
Messiou C, Robinson P, O’Connor PJ, Grainger A (2006) Subacute posteromedial impingement of the ankle in athletes: MR imaging evaluation and ultrasound guided therapy. Skeletal Radiol 35:88–94
Liu SH, Raskin A, Osti L, Baker C, Jacobson K, Finerman G et al (1994) Arthroscopic treatment of anterolateral ankle impingement. Arthroscopy 10:215–218
Bassett FH, Gates HS, Billys JB, Morris HB, Nikolaou PK (1990) Talar impingement by the anteroinferior tibiofibular ligament. J Bone Joint Surg Am 72-A:55–59
Cochet H, Pelé E, Amoretti N, Brunot S, Lafenêtre O, Hauger O (2010) Anterolateral ankle impingement: diagnostic performance of MDCT arthrography and sonography. AJR Am J Roentgenol 194(6):1575–1580
Mardani-Kivi M, Mirbolook A, Khajeh-Jahromi S, Hassanzadeh R, Hashemi-Motlagh K, Saheb-Ekhtiari K (2013) Arthroscopic treatment of patients with anterolateral impingement of the ankle with and without chondral lesions. J Foot Ankle Surg 52(2):188–191
Jordan LK 3rd, Helms CA, Cooperman AE, Speer KP (2000) Magnetic resonance imaging findings in anterolateral impingement of the ankle. Skeletal Radiol 29(1):34–39
Robinson P, White LM, Salonen DC, Daniels TR, Ogilvie-Harris D (2001) Anterolateral impingement of the ankle: MR arthrographic assessment of the anterolateral recess. Radiology 221:186–190
Hauger O, Moinard M, Lasalarie JC, Chauveaux D, Diard F (1999) Anterolateral compartment of the ankle in the lateral impingement syndrome: appearance on CT arthrography. AJR Am J Roentgenol 173:685–690
Mc Carthy CL, Wilson DJ, Coltman TP (2008) Anterolateral ankle impingement: findings and diagnostic accuracy with ultrasound imaging. Skeletal Radiol 37(3):209–216
Egol KA, Parisien JS (1997) Impingement syndrome of the ankle caused by a medial meniscoid lesion. Arthroscopy 13:522–525
Ray RG, Gusman DN, Christensen JC (1994) Anatomical variation of the tibial plafond: the anteromedial tibial notch. J Foot Ankle Surg 33:419–426
van Dijk CN, Wessel RN, Tol JL, Maas M (2002) Oblique radiograph for the detection of bone spurs in anterior ankle impingement. Skeletal Radiol 31:314–321
Stoller SM, Hekmat F, Kleiger B (1984) A comparative study of the frequency of anterior impingement exostosis of the ankle in dancer and non-dancer. Foot Ankle 4:201–202
Massada JL (1991) Ankle overuse injuries in soccer players: morphological adaptation of the talus in the anterior impingement. J Sports Med Phys Fitness 31:447–451
Mosier-La Clair SM, Monroe MT, Manoli A (2000) Medial impingement syndrome of the anterior tibiotalar fascicle of the deltoid ligament of the talus. Foot Ankle Int 21:385–391
Golano P, Vega J, de Leeuw PA, Malagelada F, Manzanares MC, Götzens V et al (2010) Anatomy of the ankle ligaments: a pictorial essay. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 18(5):557–569
Tol JL, Verhagen RA, Krips R, Maas M, Wessel R, Dijkgraaf MG et al (2004) The anterior ankle impingement syndrome: diagnostic value of oblique radiographs. Foot Ankle Int 25(2):63–68
Robinson P, White LM, Salonen D, Ogilvie-Harris D (2002) Anteromedial impingement of the ankle: using MR arthrography to assess the anteromedial recess. AJR Am J Roentgenol 178(3):601–604
Robinson P (2007) Impingement syndromes of the ankle. Eur Radiol 17(12):3056–3065
Haller J, Bernt R, Seeger T, Weissenback A, Tuchler H, Resnick D (2006) MR-imaging of anterior tibiotalar impingement syndrome: agreement, sensitivity and specificity of MR-imaging and indirect MR-arthrography. Eur J Radiol 58:450–460
Yablon CM (2013) Ultrasound-guided interventions of the foot and ankle. Semin Musculoskelet Radiol 17:60–68
Chow S, Brandser E (1998) Diagnostic and therapeutic foot and ankle injections. Semin Musculoskelet Radiol 2:421–432
Conflict of interest
Lionel Pesquer, Stephane Guillo, Philippe Meyer, Olivier Hauger declare that they have no conflict of interest related to this study.
Informed consent
No patient information is included in this study.
Human & animal studies
This article does not contain any studies involving human or animal subjects performed by the any of the authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pesquer, L., Guillo, S., Meyer, P. et al. US in ankle impingement syndrome. J Ultrasound 17, 89–97 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40477-013-0054-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40477-013-0054-5