Abstract
Couples in Turkey exhibit son preference through son-biased differential stopping behavior that does not cause a sex ratio imbalance in the population. Demand for sons leads to lower ratios of boys to girls in larger families but higher ratios in smaller families. Girls are born earlier than their male siblings, and son-biased fertility behavior is persistent in response to decline in fertility over time and across households with parents from different backgrounds. Parents use contraceptive methods to halt fertility following a male birth. The sibling sex composition is associated with gender disparities in health. Among third- or later-born children, female infant mortality is 1.5 percentage points lower if the previous sibling is male. The female survival advantage, however, disappears if the previous sibling is female. Having an older female sibling shifts the gender gap in infant mortality rate by 2 percentage points in favor of males. The improvement in infant mortality is strongest in favor of males who have no older male siblings.
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
“A manly man shall have a son, a manly one.”
Turkish proverb
In human populations with no prenatal intervention, the ratio of males to females at birth tends to be constant (Hesketh and Xing 2006). Moreover, if parents have no gender preference, the sex of children within a family is expected to follow a binomial distribution. However, an extensive body of literature shows that parents with a son preference skew the sex composition of their children via gender discrimination in relative care and fertility-stopping rules.
The case of “missing women,” a phenomenon that Sen (1990) brought to the public’s attention, refers to a substantial deficit of girls in the population resulting from sex-selective abortion and excess female mortality. Every year, 2 million girls worldwide under age 5 are estimated to be missing. Of these, 70 % were never born (World Bank 2011). The implications of persistent, abnormally high sex ratios in South Asia and elsewhere have been studied extensively.Footnote 1
Differential stopping behavior (henceforth, DSB), on the other hand, implies that parents with a preference for sons would continue to bear children until they have a desired number of boys (Basu and De Jong 2010). Without prenatal manipulation, DSB alone does not alter the population sex ratio or the sex ratio across birth parities at the aggregate level. However, assuming that parents can have a finite number of children, then as a result of DSB, females have a greater number of siblings and are born relatively earlier than their male siblings (Basu and De Jong 2010; Clark 2000; Yamaguchi 1989).
In this article, I focus on family composition in Turkey, a patriarchal society with strong son preference and Muslim identity but without any history of surplus males in the population. I provide strong evidence of DSB in the absence of prenatal sex selection. By using population data and birth statistics, I show that (1) the long-term trend of sex ratio at birth hovers around the natural level in Turkey, and (2) as in most parts of the world, under-5 mortality is slightly higher for males than for females. Family-level data show that the sex ratios are also balanced across birth parities. As predicted by the DSB model, however, the sex ratio at last birth is highly skewed in favor of males, and males are more likely to grow up in smaller families.
Next, I exploit the first child’s sex outcome—a purely random process in the absence of prenatal sex selection—to identify the causal effects of son preference on fertility behaviors. Parents have fewer children if the first child is male than if the first child is female. The number of children in families with firstborn daughters is, on average, 6.7 % larger than families with firstborn sons. I show that contraceptive use is the only mechanism through which couples halt fertility after a male birth. Quantile regression results indicate that despite the lower fertility predicted by more schooling, higher age at first birth, and urbanization along with other characteristics, the strong response to the absence of sons is persistent.
Sibling sex composition is associated with significant health disparities between boys and girls. I argue that parents are more likely to proceed to the next parity after a female birth and favor sons in health investment if the older sibling is female. Among third- or later-born children, although the overall infant mortalityFootnote 2 rate is higher for males than females, the female survival advantage disappears if the previous sibling is female. Girls with an older male sibling are 1.5 percentage points more likely to survive to age 1, whereas the gender difference in mortality completely vanishes among those with an older female sibling. I provide additional evidence that the improvement in infant mortality is strongest in favor of males who have no older male siblings.
The results of this study suggest that DSB causes important early-life disparities through allocative preference in favor of sons among families who are seeking a boy. Importantly, DSB is common in countries that are geographically close and culturally similar to Turkey, notably in Central Asia and North Africa (Basu and De Jong 2010; Filmer et al. 2009; Yount et al. 2000). Thus, the results documented here have the potential to inform health policy not just in Turkey but in other countries as well.
A Simple Model
Consider a simple illustration of DSB with a three-period model in which there are N couples, each of which has a target of one son, and the maximum number of children per couple is three. Assuming that sex distribution at birth is binomial with equal probabilities, N / 2 couples will have a boy as their first child, and the other N / 2 will have a girl. Those who bear a firstborn son would discontinue childbearing because their target has been met. As a result, N / 2 families will have a family composition of a single boy (B). The remaining N / 2 couples will have a second child, of which N / 4 will have a firstborn girl and a second-born boy (GB). At this point, these families will also stop childbearing because they have reached their target. The remaining N / 4 families will have a third child, of which N / 8 will have a firstborn girl, a second-born girl, and a third-born boy (GGB), while N / 8 will have a firstborn girl, a second-born girl, and a third-born girl (GGG). In this hypothetical society, the family composition will be as follows: N / 2 families will have B; N / 4, GB; N / 8, GGB; and another N / 8, GGG.
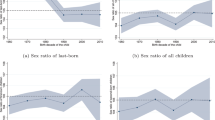
The theoretical implications of such a stopping rule on family composition is shown in Table 1. First and foremost, the population sex ratio is balanced. There are equal numbers of males and females born in the population, 7N / 8 children of each sex. The sex ratio is also perfectly balanced within parities. There are N / 2 males and females born as the first child, N / 4 as the second, and N / 8 as the third. DSB, however, changes the sex composition within families. For example, as shown in Table 1, single-child families are exclusively male. The number of males and females are equal in families with two children, and the sex ratio is 0.20 in families with three children. Accordingly, the sex ratio at last birth (henceforth, SRLB) is highly male-skewed. In families with one or two children, the last birth is always male. The SRLB is balanced only among families with three children, which is a mechanical result of the three-children maximum.
Basu and De Jong (2010) provided the simulated effects of DSB on family composition with different combinations of maximum and desired numbers of boys, showing similar results. Seidl (1995) and Jensen (2003) each used slightly different models, but their implications were also similar: the desire for boys leads to lower (higher) ratios of boys to girls in larger (smaller) families, the SRLB is male-skewed, and girls are born earlier than their male siblings.
Relevant Literature on Stopping Rules
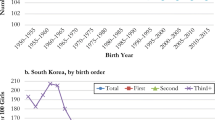
A rich empirical literature documents the effects of DSB in countries where son preference has historically been strong. Among others, Park (1983) and Park and Cho (1995) showed that the sex ratio of siblings in small families in Korea is skewed in favor of boys and that sex ratio at the last birth is also highly male-skewed. In India, where smaller families have higher proportion of boys, son targeting is especially pronounced in rural areas and exhibits substantial regional variation (Basu and De Jong 2010; Clark 2000). The same patterns have been observed in Vietnam (Pham et al. 2012). In these countries, DSB interacts with the common practice of sex-selective abortion. In China and India, Ebenstein (2007) demonstrated that women continue conceiving until they bear sons, but an excess number of girls conceived in-between are missing. Hesketh and Xing (2006) showed that in 1992 in South Korea, at the peak of the gender discrimination at birth, the sex ratios were 1.13, 1.96, and 2.29 for the second, third, and fourth birth parity, respectively.
Fertility-stopping rules are also prevalent in countries with balanced sex ratios. Filmer et al. (2009) found strong DSB patterns in Central Asia. In rural Menoufia, Egypt, Yount et al. (2000) found that son-biased family planning translates into fewer births among families with living sons. Basu and De Jong (2010) confirmed this finding at the country level in Egypt. In a more striking study, Dahl and Moretti (2008) showed that U.S. parents are significantly more likely to have an additional child when the previous children are all girls.
Data and Descriptive Analysis
Data
The aggregate data come from several different sources. Population sex ratios are calculated from the Population Censuses and Address Based Population Registration System (henceforth, ABPRS), a register-based census that collects demographic data based on the place of usual residence. Both sources of data are provided by the Turkish Statistical Institute (henceforth, TurkStat) and include the entire population. Population estimates by sex and five-year age groups are available in the 1985, 1990, and 2000 Population Censuses, while ABPRS provides population estimates for the period from 2008 to 2013 on an annual basis. In addition, TurkStat provides yearly birth statistics collected by the Central Population Administrative System (MERNIS) from 2001 to 2013. The data include all births in Turkey that were registered with each district population office.
Household-level analysis is based on the 1993, 1998, 2003, and 2008 waves of the Turkish Demographic and Health Survey (TDHS). In this nationally representative survey, the pooled data contain 28,151 married or previously married women aged 15 to 49, including their complete fertility histories, family planning prevalence, and demographic characteristics. The analysis sample includes 25,600 women, all of whom have given birth at least once.
Population Sex Ratios
To document the sex ratio trends at birth and among children under age 5, I calculate the number of boys per girl for each year that the data are available. Figure 1 shows the estimated sex ratios from 1985 to 2013, with the y-axis scaled to the commonly accepted natural sex ratio range at birth (1.02–1.08 boys per girl). The population sex ratios are strikingly balanced over the last 28 years in Turkey. The sex ratio for children under 5 years old varies between 1.05 and 1.065. Correspondingly, birth statistics follow a similar trend. From 2001 to 2013, 1.055 to 1.057 males were born for every female born. In comparison, from 1962 to 1980 in 24 European countries, the aggregate ratio of male to female births was between 1.05 and 1.07 (Coale 1991).
Sex ratio trends. The figure shows the estimated sex ratios at birth and under age 5 from different data sources. Census estimates show the sex ratio under age 5 and are gathered from Population Censuses (1985, 1990, and 2000) and Address Based Population Registration System (ABPRS; 2008–2013). Vital statistics show the sex ratio at birth and are gathered from Central Population Administrative System (2001–2013). Turkish Demographic and Health Survey (TDHS) estimates are from author’s calculations, with the y axis scaled to the commonly accepted natural sex ratio range at birth (1.02–1.08 boys per girl), and x axis labels are shown only for the years that the data were available
Figure 1 includes the sex ratios at birth from each survey year in TDHS as well. To investigate the differential gender mortality, I also calculate the sex ratios for those who survived to age 5. Overall, TDHS does a good job of replicating the sex ratios calculated from the censuses. The point estimates are not statistically different from the population sex ratios. The consistency of reported sex ratios in TDHS relative to the population data speaks to the accuracy of reporting in the survey. Importantly, the under-5 sex ratio is less than the sex ratio at birth for each survey year, indicating a lower male-female ratio for the survivors. Like in most countries, this is a natural result of higher under-5 mortality for boys compared with girls.Footnote 3 In the pooled TDHS data, approximately 92 of every 1,000 females die before age 5, compared with 100 for males, thus indicating a significant difference in under-5 mortality rates.
Altogether, the aggregate data show no evidence of sex-selective abortion or excess female infant mortality for the study period during which abortion was legal for up to 10 weeks of gestation.Footnote 4
Family Sex Ratios
To explore the role of DSB in sibling sex composition, I use family-level data from the TDHS and start by disaggregating the sex ratio analysis by sibship size. Sibship size refers to the number of children who are alive,Footnote 5 and sex ratio is the average number of boys per girl within a family. In the presence of a son-biased stopping rule, parents tend to halt fertility after a male birth. Therefore, sex ratios should be biased in favor of boys in small families and gradually decrease with the number of siblings.
The TDHS spans a period in which Turkey witnessed both a leap in economic development and a dramatic decline in fertility.Footnote 6 The decline in fertility coupled with rapid economic development might have changed both the gender preference and the ability to satisfy such preference. In the interest of capturing the time trend in fertility choices, the results are reported separately for each survey year.
Table 2 shows the sex ratios by total number of living children for each survey year. As predicted by the DSB hypothesis, males are more likely to be in single-child or two-child families. Despite the consistent decrease in average family size from 1993 to 2008, the sex ratio imbalance conditional on number of children remains persistent. For example, the pooled estimates show that on average, there are 1.2 boys per girl in families with fewer than three children (column 5, panel A). The sex ratio is 1.11 in three-child families and still in favor of boys, although to a lesser extent. On the other hand, girls predominate in families with more than three children: the ratio of boys to girls plunges to 0.92 in families with five or more children. The female surplus in large families lowers the sex ratio to 1.04 at the aggregate level. The overall sex ratio is balanced for each survey year as well. Strikingly, skewed sex ratios, conditional on sibship size, are similar in different survey years, showing a consistency in male-biased reproductive behavior between 1993 and 2008 (columns 1–4, panel A).
In panel B of Table 2, the sample is restricted to women aged 35 to 49 in order to observe the sex ratios among the couples who have most likely finished childbearing. The sex ratio imbalance is even greater in nearly completed families. In small families (number of children ≤3), the average sex ratio is 1.21, falling to 0.94 among those with more than three children.
The SRLB is another measure to test the presence of son-targeting fertility behavior. If parents are more likely to cease childbearing after a male birth, the SRLB should be male-skewed. Table 3 shows the average sex ratios by total number of births and birth order, with the SRLB depicted in bold. The panel A contains calculations for the full sample, and panel B is restricted to women aged 35 to 49. In both panels, independent of the mother’s birth history, the last birth is consistently male-skewed: families seek boys at all birth parities. In panel A, the number of males per female is slightly above 1.20 at last birth, even among very large families. For example, the SRLB among couples with six births is 1.23, while the same families’ earlier parities are highly female-skewed. This may imply an unusually strong persistence in seeking a boy. Alternatively, this finding may indicate the “gambler’s fallacy” in son targeting: if parents believe that the sex of the next child is contingent on the existing sibling sex composition, they are less likely to stop childbearing after having a girl than couples who are aware of the fact that each child’s sex is an independent event.
Panel B of Table 3 shows that son preference is revealed more strongly among nearly completed families. Families with three or fewer children exhibit abnormal sex ratios in favor of boys at all parities (columns 1–3, panel B); for those with more than three children, only the SRLB is male-skewed. Earlier birth parities in large families are highly female-skewed because couples continue childbearing after a female birth. For example, in families with four births, the sex ratio ranges between 0.90 and 0.94 for the first three births, while the SRLB is 1.31, which is a clear indicator of families stopping once they reach a son (row 4, panel B).
As a robustness check for the prenatal sex selection at higher birth parities, I conducted several tests. The sex ratio for second-born children conditional on a firstborn daughter is 1.04 and not skewed. The sex ratio for third-born children after two females is 1.02. Last, without conditioning on the sex composition of previous births, the sex ratios for the second, third, and fourth births are 1.05, 1.02, and 1.05, respectively. In countries with prenatal sex selection, the likelihood of sex-selective abortion is substantially higher if the previous births are all females, and the sex ratios become more imbalanced at higher birth parities. This is not the case in Turkey, where parents apply male-biased stopping rules but do not practice sex-selective abortion.
To summarize, DSB is the only mechanism by which couples in Turkey pursue son preference, and prenatal sex selection is not a common practice. As documented in the existing literature, the skewed sex ratio distribution conditional on family size is persistent despite the economic development and fertility decline. The next section offers an empirical strategy to identify the changes in fertility behavior that have led to the patterns shown earlier.
Empirical Analysis
Identification Strategy
Without prenatal manipulation, the sex of the firstborn child is a random draw. Parents with a son preference, however, respond differently to this exogenous shock, thus making it possible to exploit the first child’s sex as a source of an exogenous variation in order to identify the causal effects of son preference on several fertility decisions. The reduced-form equation in this context is as follows:
where y irt is the fertility outcome (number of pregnancies, number of children born, number of children alive, and indicators for current contraceptive use and having any pregnancy termination in the past)Footnote 7 for mother i, who is living in region r, and was interviewed in survey year t. Z is an indicator of a firstborn female, and X is a vector of family background covariates (mother’s age; age at first birth; years of education; ethnicity; husband’s age and years of education; rural residence; coresidence of husband’s parents; and dummy variables for whether the marriage was arranged, and husband’s family or husband paid bride price). θ r and δ t control for survey-year and region fixed effects, and ω rt captures the region-specific year fixed effects. Importantly, adjusting for these control variables in Eq. (1) does not affect the estimated parameter τ given that Z is random. It does, however, improve precision.Footnote 8
The parameter τ reflects the effect of a firstborn daughter compared with a firstborn son on couple’s fertility decisions. As mentioned earlier, male infant mortality is higher purely for biological reasons; therefore, Z might affect y through both differential mortality rate for males and son targeting. For example, a woman might be more likely to have another pregnancy if the first child dies and the mortality risk is higher among male children. To isolate the effect of son preference from the male differential mortality, Eq. (1) controls for the survival status of the first child. The regression sample is restricted to the women with a singleton first birth, who represent 99.1 % of the total sample. Although these adjustments make no statistical difference in the estimation results, they avoid a potential confusion in the interpretation of τ.
For causal inference, the error term in Eq. (1) should be uncorrelated with Z. This threat to identification is a major concern in countries with abnormal sex ratios at birth because the child’s sex is a prenatal choice in light of the common practice of sex-selective abortion. In such cases, children’s sex is likely to be correlated with unobserved family characteristics. There is no fully robust test to validate the exogeneity assumption, but comparing the families with firstborn sons and firstborn daughters is helpful. Observed family characteristics can altogether explain more than 50 % of the variation in sibship size. Thus, despite not being perfect, the comparison is highly informative regarding the validity of the random assignment assumption. As a further examination, I estimate the following regression:
using a logit model and report the joint χ2-test result for the null hypothesis that all the estimated coefficients in the right side of Eq. (2) are jointly equal to 0.
When estimating Eq. (1), I use ordinary least squares (OLS) as well as the Poisson likelihood function when the response variable is a count: that is, number of pregnancies, number of children born, and number of children alive. There are two reasons to go beyond the standard linear model. First, the functional form in the Poisson model ensures a positive predicted value for each family. Second, Poisson estimates show the percentage change in sibship size induced by a female birth, which is an alternative indicator that shows the change in fertility level with respect to the baseline fertility preference. The effect of a firstborn female on family size depends on couples’ competency at fertility control; hence, the deviation from the baseline fertility level might be a better indicator when comparing families with different backgrounds because it takes into account the overall family planning behavior.
Estimation Results on Fertility
I present the family background characteristics by first child’s sex in Table 4. There are no statistically significant differences between families with firstborn sons and those with firstborn daughters with regard to any of the sample characteristics. The p value for the overall χ2 statistic from the regression in Eq. (2) is .53, with an extremely low pseudo-R 2. Strictly speaking, the coefficient vectors Φ, δ t , and θ r in Eq. (2) are jointly equal to 0.Footnote 9 Given the large sample size, the data strongly support the assumption that the sex outcome of the first child is not manipulated. Additionally, the overall sex ratio is balanced among higher parities independent of the first child’s sex. The sex ratio of subsequent siblings is 1.04, both in families with firstborn sons and in those with firstborn daughters.
DSB sharply affects the average number of siblings. In Table 5, the pooled sample OLS estimates show that women with firstborn daughters have about 0.20 more pregnancies, 0.19 more births, and 0.18 more living children than women with firstborn sons (columns 1–3, panel A). The maximum likelihood estimate from the Poisson model reveals that this corresponds to a 6.7 % increase in number of living children (column 3, panel A).
Results in panels (B) through (D) of Table 5 are based on separate regressions for each age group. The estimated DSB effects on family size are small for the youngest cohort and are similarly large for the older age categories. The increase in sibship size induced by a firstborn female for the youngest mother cohort aged 15 to 29 is 0.06 children, or 3.4 % (column 3, panel B). The estimated family size effects are much higher for the older cohorts. If the first child is female, women aged 30 to 39 have approximately 0.25 more children, corresponding to an 8.3 % increase in number of living children (column 3, panel C). The results are quantitatively similar for the oldest cohort (column 3, panel D). The discrepancy of the estimates between young and old cohorts is due to the fact that some of the young women have not had, and are still pursuing, a son. The change in contraceptive use behavior among young couples confirms this argument. Women aged 15 to 29 with firstborn daughters are 2.6 percentage points less likely to use either a traditional or modern contraceptive method than those with firstborn sons (column 4, panel A).Footnote 10 The difference is weaker in older cohorts (column 4, panels C and D).
Irrespective of age category, the probability of pregnancy termination is unrelated to the first child’s sex, suggesting that families do not use abortion for reaching the desired sex composition (column 5, panels A–D). Nevertheless, the results must be interpreted with caution because pregnancy termination is self-reported, and the survey question does not allow the researcher to identify whether the termination was a health-related procedure.Footnote 11 Underreporting of abortion cases would bias the estimated coefficient toward 0.
The change in fertility behaviors induced by the first child’s sex reveals two important findings. First, son preference has a sizable impact on family size through DSB. Second, women are more likely to use contraceptive methods when the firstborn child is male. In other words, contraceptives are used as a tool for stopping fertility after a son.
Heterogeneous Effects on Fertility
Pooled-sample estimates might mask heterogeneous effects on families with different backgrounds. A common way to reveal treatment heterogeneity is to interact the treatment indicator—in this case, the firstborn female indicator—with family characteristics. The results from the interaction effects are included in Online Resource 1, Tables S3–S6. Overall, the effect of a firstborn female on number of living children is similar across survey years, suggesting that son targeting endures despite the decline in fertility over time. A firstborn female significantly increases the sibship size for all the subgroups, categorized by parents’ education level, type of marriage, or residential status. With the exception of educated women, the percentage changes in number of children are statistically indistinguishable. The relative family size effect among women with secondary or higher education is significantly smaller.
A recent alternative to interaction effects is to use a set of covariates to predict outcomes among the untreated group. The regression coefficients from the sample of untreated group are then used to predict outcomes for the full sample. Separate treatment effects can be estimated for each group after stratifying the predicted values into quantiles. This procedure thus creates an index of predicted outcomes by using all the relevant covariates instead of interacting each one with the treatment dummy variable. Abadie et al. (2013), however, showed that the OLS estimator is severely biased in finite samples as a result of overfitting, and recommended using either leave-one-out (LOO) or repeated split sample (RSS) estimators. The LOO estimator avoids overfitting simply by excluding each observation when estimating the coefficients used to calculate its own predicted value. Alternatively, the RSS estimator randomly divides prediction sample into two groups and uses only one of them for prediction. When this is repeated many times and averaged over the number of repetitions, the small sample bias vanishes.Footnote 12
I use the families with firstborn sons as the “control” group and use endogenous determinants of fertility level (mother’s age at first birth, father’s and mother’s years of education, region, and rural residency) to predict number of siblings. Duflo (2012) noted that decrease in fertility and increase in age at first birth are highly correlated with higher income and education. Urbanization and migration from agricultural to industrial regions are also associated with economic growth and prosperity. Note that this prediction step involves simply dividing the sample into quantiles and is not concerned with causality. The key assumption for the causal identification is that within each predicted fertility quantile, the sex of the first child is random.
Table 6 reports both adjusted and unadjusted differences for each fertility quintile using LOO and RSS algorithms.Footnote 13 Unadjusted differences are simple differences in the average number of children among families with firstborn females and firstborn males for the corresponding quintile (columns 1 and 3). As before, adjusted differences control for the full set of covariates (columns 2 and 4). The similarity of the unadjusted and adjusted results speaks to the exogeneity of Z i , and the type of estimator used does not make a statistical difference in the estimated quantile treatment effects.
Stratification reveals high variation in number of children across fertility quintiles. At the lowest predicted fertility quintile, families with firstborn sons bear on average 1.69 children compared with 4.41 children for the highest quintile (column 5, \( {\widehat{\uptau}}_1 \) and \( {\widehat{\uptau}}_5 \)). The number of additional children induced by a female first birth also declines in response to lower fertility, but the relative change is strongest at the median level (column 6, \( {\widehat{\uptau}}_3 \)). If the first child is female, number of children increases by 0.077 children (4.6 %) among women in the lowest predicted fertility quintile (columns 4 and 6, \( {\widehat{\uptau}}_1 \)). The change in number of siblings is 0.23 children (9.4 %) at the middle quintile and 0.27 children (6 %) for the highest quintile. Considering the significant family size differences between predicted fertility quintiles, DSB shows a relatively flat response to decline in fertility. Son preference is significantly prevalent at each fertility level, even among families with 1.69 children, and causes similar relative changes in the number of siblings. In other words, the lower fertility predicted by better education, more income, and urbanization neither eliminate nor drastically change the son-biased fertility preference.
Health Effects on Children
In addition to changing fertility behavior and causing differences in sibling sex composition, DSB might also give rise to health disparities between boys and girls. Rosenblum (2013) developed an economic model in which sibling sex composition leads to a differential allocation of family resources among boys and girls. In this framework, sons provide a future economic gain to parents, but daughters come with a future economic burden. The economic gain from an extra son is larger if the existing proportion of sons is relatively small in the family; therefore, the smaller the proportion of boys, the greater the incentive for households to favor boys in health investment (Rosenblum 2013).
I use a difference-in-differences approach similar to Rosenblum’s (2013) to test the sibling sex composition hypothesis. In the absence of prenatal sex selection, the sex of the child is random at any birth parity. If the older sibling is a girl, however, families have an incentive to invest more in boys at the next parity. Therefore, in the case of male-biased allocative preference, the gender difference in health investments should lead to a relative male advantage in health if the previous sibling is female.
Table 7 compares the observable characteristics of parents by each child’s sex for each of the first four birth parities. Family backgrounds of first-, second-, and third-born boys are identical to first-, second-, and third-born girls, respectively. Mother’s age and age at first birth, which are expected to be correlated, are somewhat statistically higher for mothers who have a fourth-born boy than mothers who have a fourth-born girl, but the differences are very small. Like earlier, I use a logit model to test whether all the differences in the means reported in the table are jointly equal to 0. The p values for the joint χ2 tests are indicated under the observable characteristics for each birth order. None of the p values indicate a significant difference between families of boys and girls.
The exogenous variation in children’s sex, however, causes significant changes in the sibling sex composition and family size. Families who had a female child are more likely to have a subsequent birth, and on average have higher fertility. For example, mothers who have a second-born female have 0.16 more births and are 4.8 percentage points more likely to have additional children: a clear indication of stopping after a male birth (panel B, heading 2). Consistent with the previous findings, the differential stopping behavior is clear across all birth parities.
To investigate the change in gender health gap induced by the previous sibling’s sex, I use several different versions of the following difference-in-differences estimator:
where y i is the early-life health outcome (infant mortality and nutrition), Z i1 is a female indicator for child i, and Z i2 is a dummy variable equal to 1 if the older sibling is female. For example, when the sample is restricted to second-born children and the outcome is the infant mortality, μ1 shows the girl-boy difference in infant mortality if the first child is male, whereas μ1 + μ3 shows the same difference if the first child is female. Thus μ3 is the difference-in-differences estimator and is expected to be positive if a previous female sibling causes boys to be more valuable and to shift the infant mortality gender gap in favor of males. The expected differences would also be positive for the probability of stunting and being underweight given that they both indicate poor nutrition.
I begin with presenting the regression results for the second-born children. This provides the most generalizable estimates because (1) the sex of the firstborn child is random, and (2) most families in Turkey have at least two children. Although the sex of children is random at any parity, parents who proceed to the next birth parity after a female birth might be different from parents who proceed to the next birth parity after a male birth. Therefore, restricting the sample to second-born children attempts to address the self-selection of families into higher birth orders because families typically have at least two children. In other words, Z i1 and Z i2 in Eq. (3) are both plausibly exogenous.
The difference-in-differences estimator, nevertheless, is still informative in regard to resource allocation by gender, even for higher birth orders. For example, assume that parents who have a second-born girl are identical to parents who have a second-born boy but that those who have a third child after a second-born girl are wealthier than those who have a third child after a second-born boy. In this case, independent of their gender, children who have an older male sibling would have poorer health than children who have an older female sibling because of wealth differences between parents. In other words, Z i1 in Eq. (3) is still purely exogenous, while Z i2 is not. However, in this example, μ2 captures the wealth differences triggered by the previous sibling’s sex, whereas the interaction term μ3 shows the gender differential effect of having an older female sibling. If only boys are better off by having an older female sibling, which is an evidence of a treatment heterogeneity, this might be an indicator of a male-biased allocative preference. It is important to note that the results for children in higher birth orders are less generalizable because the sample is restricted to households with relatively high fertility. However, they reflect potentially important behavioral responses to the gender composition within a family.
In TDHS, the retrospective birth history includes mortality information covering all births by the same mother. For the infant mortality estimations, I restrict the sample to children who were born at least one year before the date of interview. The nutrition outcomes are available only for children under age 5. Anthropometric measurements are constructed by taking the height and weight of children, and a child’s immunization is self-reported if an official immunization record is missing. Following the definitions of the World Health Organization (WHO), I create two dichotomous outcome variables that reflect the child’s nutritional status: (1) stunting, which refers to being less than 2 standard deviations below the age- and gender-normalized median height for the reference population; and (2) being underweight, which refers to being less than 2 standard deviations below the age- and gender-normalized median weight for the reference population.
Table 8 presents the regression results for the second-born children. Columns under the heading (1) show the infant mortality rates for the second-born children by the firstborn and the second-born siblings’ sex compositions. Independent of the first child’s sex, second-born girls have a lower mortality rate than second-born boys, although the estimated difference is insignificant in all cases. Overall, there is no indication of improvement in male mortality compared with female mortality preceded by a female birth. These findings hold for the nutrition outcomes as well. Although the estimated probabilities of stunting and being underweight are slightly higher for girls with an older female sibling, the difference-in-differences estimators are not statistically significant.
Gender disparities in health, however, emerge among third- or later-born children. Columns under the heading (1) in Table 9 show the mean infant mortality rates for third- or later-born boys and girls. Female infant mortality is significantly lower than the male infant mortality by 1.5 percentage points if the previous sibling is male. The biological female advantage, however, disappears if the previous sibling is female. The difference-in-differences estimate shows a statistically significant shift, by 2 percentage points, in female-male mortality gap induced by having an older female sibling. The point estimates are identical after controlling for birth order fixed effects and other covariates. Results are, moreover, similar when the outcome is defined as under-5 mortality.Footnote 14 The nutrition estimates suggest a similar pattern, but the statistical inference is weaker because of the small sample sizes. In all the regressions, standard errors are clustered by mother in order to capture any correlations in the health outcomes of siblings.
Importantly, Table 9 shows that the difference-in-differences estimator is mostly driven by the improvement in male mortality. Female infant mortality rates are similar independent of the older sibling’s gender. Male infant mortality rate is, however, 1.4 percentage points lower for males who have an older female sibling than for males who have an older male sibling. The difference is highly significant in both adjusted and unadjusted regressions.
If families are more likely to value sons who are preceded by daughters, then one would expect the male improvement in infant mortality to be the strongest among males who do not have an older male sibling. Table S7 in Online Resource 1 provides supportive evidence of such a pattern by comparing the girl-boy mortality differences between third-born children with the following older sibling sex compositions: two males, one male and one female, and two females. Again, female infant mortality rates are similar independent of the sex composition of the previous siblings. Male infant mortality, however, gradually improves with the number of older female siblings. The gender difference in infant mortality is 2.4 percentage points in favor of males among children with two older female siblings compared with those with two older male siblings. (See Online Resource 1, panel 3 of Table S7.)
I further investigate the gender differences in immunization outcomes for BCG (Bacillus Calmette-Guérin), DPT (diphtheria, pertussis, tetanus), polio, and MMR (measles, mumps, rubella) vaccinations. Overall, independent of the previous sibling’s sex, the differences in vaccination rates between males and females are small and not statistically significant.Footnote 15 This result is not surprising given that immunization rates are high in Turkey: child vaccination is free and part of routine procedure in public hospitals.
Discussion
In Turkey, the trend in the sex ratio at birth fluctuates around the commonly accepted natural sex ratio, with no evidence or documented history of sex-selective abortion. On the other hand, couples exhibit strong son preference through family planning and are more likely to halt fertility after a male birth. My analysis reveals that contraceptive use after a male birth is a contributing factor to an abnormal sex ratio distribution conditional on sibship size. I provide additional evidence that abortion is not a common practice for reaching the desired sex composition.
Still, the demand for sons is persistent in response to decline in fertility over time and across households with parents from different backgrounds. These findings are consistent with Yount et al. (2000), who showed that the dramatic increase in modern contraceptive use in Egypt from the 1980s to the early 1990s resulted in a decline in fertility but had no impact on son preference. My findings further suggest that families that increase their fertility as a result of a previous female birth favor males in health investment. Similar to Rosenblum’s (2013) findings for India, boys are better off if they have older female siblings. In other words, the empirical evidence suggests that families who are seeking a boy show allocative preference in favor of sons once they are born.
The significant changes in family structures and health discrepancies reported here raise the question of what would happen if parents did not persistently seek sons. One prediction is that girls and boys would have a similar number of siblings, which would improve equality in intrahousehold resource allocation (Becker and Lewis 1974). Lee (2007) provided empirical evidence on quantity-quality trade-off in Korea, showing that the exogenous increase in family size caused by a firstborn female decreases the investment in education for each sibling. Another prediction is that boys would be less likely to be born in the last parity. Black et al. (2005) showed that the negative impact of the higher birth order is largest for last-born children. One possibility therefore, is that the absence of son-biased fertility behavior could further improve gender equality at birth, although by favoring males. More importantly, females who grow up in households with a high proportion of females would be better off because the gender discrimination in health investment emerges predominantly in these large households.
Notes
Death of a child younger than 1 year.
Females are less likely to die from infections and respiratory ailments because of their stronger immune system (Drevenstedt et al. 2008).
The abortion law was passed in 1983 and remains with slight modifications up to the present time.
Because 77.2 % of deaths in the sample occurred within the first year after birth, sex ratios for children who are alive seem to be accurate approximations of the actual sibling sex composition.
The annual average GDP per capita growth was around 2.71 % between 1993 and 2008, which corresponds with an increase in real GDP per capita from 5,435 to 7,730 in constant 2005 U.S. dollars. The World Bank estimated that the total fertility rate declined from 2.8 births per woman in 1993, to 2.1 in 2008, corresponding to a 25 % decline in the total fertility rate (http://data.worldbank.org).
In the survey, pregnancy termination is defined as having a miscarriage, an abortion, or stillbirth.
Table S1 in Online Resource 1 documents the results from the OLS regressions with and without adjustment for covariates.
See Table S2 in Online Resource 1 for the full set of individual coefficients.
Traditional methods include coitus interruptus, periodic abstinence, and vaginal douche. Modern methods include oral contraceptives, the Pill, injections, female or male condom, intrauterine device, and sterilization.
Specifically, the survey question asked the following: “Has the respondent had ever had a pregnancy that was terminated by a miscarriage, abortion, or stillbirth, i.e., did not result in a live birth?”
See Abadie et al. (2013) for the detailed description of the methodology.
Jeremy Ferwerda provides a Stata routine, available online (https://ideas.repec.org/c/boc/bocode/s457801.html).
Coefficients for death of a child under age 5 are not reported but are available upon request from the author.
See Online Resource 1, Table S8, for the results.
References
Abadie, A., Chingos, M. M., & West, M. R. (2013). Endogenous stratification in randomized experiments (NBER Working Paper No. 19742). Cambridge, MA: National Bureau of Economic Research.
Basu, D., & De Jong, R. (2010). Son targeting fertility behavior: Some consequences and determinants. Demography, 47, 521–536.
Becker, G. S., & Lewis, H. G. (1974). Interaction between quantity and quality of children. In T. W. Schultz (Ed.), Economics of the family: Marriage, children, and human capital (pp. 81–90). Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press.
Black, S. E., Devereux, P. J., & Salvanes, K. G. (2005). The more the merrier? The effect of family size and birth order on children’s education. Quarterly Journal of Economics, 120, 669–700.
Chung, W., & Gupta, M. D. (2007). The decline of son preference in South Korea: The roles of development and public policy. Population and Development Review, 33, 757–783.
Clark, S. (2000). Son preference and sex composition of children: Evidence from India. Demography, 37, 95–108.
Coale, A. J. (1991). Excess female mortality and the balance of the sexes in the population: An estimate of the number of “missing females.” Population and Development Review, 17, 517–523.
Dahl, G. B., & Moretti, E. (2008). The demand for sons. Review of Economic Studies, 75, 1085–1120.
Drevenstedt, G. L., Crimmins, E. M., Vasunilashorn, S., & Finch, C. E. (2008). The rise and fall of excess male infant mortality. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 105, 5016–5021.
Duflo, E. (2012). Women empowerment and economic development. Journal of Economic Literature, 50, 1051–1079.
Ebenstein, A. (2007). Fertility choices and sex selection in Asia: Analysis and policy (SSRN Working Paper No. 965551). doi:10.2139/ssrn.965551
Edlund, L., & Lee, C. (2013). Son preference, sex selection and economic development: The case of South Korea (NBER Working Paper No. 18679). Cambridge, MA: National Bureau of Economic Research.
Filmer, D., Friedman, J., & Schady, N. (2009). Development, modernization, and child-bearing: The role of family sex composition. World Bank Economic Review, 23, 371–398.
Guilmoto, C. Z., & Duthé, G. (2013). Masculinization of birth in Eastern Europe. Population and Societies, 506, 1–4.
Hesketh, T., & Xing, Z. W. (2006). Abnormal sex ratios in human populations: Causes and consequences. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 103, 13271–13275.
Jayachandran, S. (2014). Fertility decline and missing women (NBER Working Paper No. 20272). Cambridge, MA: National Bureau of Economic Research.
Jensen, R. T. (2003). Equal treatment, unequal outcomes? Generating sex inequality through fertility behavior (Working paper). Cambridge, MA: School of Government, Harvard University.
Lee, J. (2007). Sibling size and investment in children’s education: An Asian instrument. Journal of Population Economics, 21, 855–875.
Park, C. B. (1983). Preference for sons, family size, and sex ratio: An empirical study in Korea. Demography, 20, 333–352.
Park, C. B., & Cho, N.-H. (1995). Consequences of son preference in a low-fertility society: Imbalance of the sex ratio at birth in Korea. Population and Development Review, 21, 59–84.
Pham, B. N., Adair, T., Hill, P. S., & Rao, C. (2012). The impact of the stopping rule on sex ratio of last births in Vietnam. Journal of Biosocial Science, 44, 181–196.
Qian, N. (2008). Missing women and the price of tea in China: The effect of sex-specific earnings on sex imbalance. Quarterly Journal of Economics, 123, 1251–1285.
Rosenblum, D. (2013). The effect of fertility decisions on excess female mortality in India. Journal of Population Economics, 26, 147–180.
Seidl, C. (1995). The desire for a son is the father of many daughters. Journal of Population Economics, 8, 185–203.
Sen, A. (1990). More than 100 million women are missing. New York Review of Books. Retrieved from http://www.nybooks.com/articles/1990/12/20/more-than-100-million-women-are-missing/
World Bank. (2011). World development report 2012: Gender equality and development. Washington, DC: World Bank.
Yamaguchi, K. (1989). A formal theory for male-preferring stopping rules of childbearing: Sex differences in birth order and in the number of siblings. Demography, 26, 451–465.
Yount, K. M., Langsten, R., & Hill, K. (2000). The effect of gender preference on contraceptive use and fertility in rural Egypt. Studies in Family Planning, 31, 290–300.
Acknowledgments
I thank three anonymous referees who provided insightful comments on earlier versions of the manuscript. I received valuable input from Ted Joyce, Wim Vijverberg, Stephen O’Connell, Mike Grossman, David Jaeger, and Alper Dinçer. Seminar participants at CUNY Institute for Demographic Research, The Graduate Center, Bahçeşehir University, Hunter College, and Koç University provided extensive and helpful comments. Special thanks go to the Schindler sisters for their editorial feedback.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Online resource 1
(PDF 370 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Altindag, O. Son Preference, Fertility Decline, and the Nonmissing Girls of Turkey. Demography 53, 541–566 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13524-016-0455-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13524-016-0455-0