Abstract
Bacillus species, generally regarded as soil microorganisms, are present in human gastrointestinal tract (GIT) in quantities, which cannot be explained by their entrance with food only. They are capable of growing in GIT and interacting with intestinal microbiota and host organism by excretion of enzymes and low-molecular weight compounds, which exert digestion-facilitating, antagonistic, immunomodulating, antiviral, anticancer properties or mediate cell communication. For better understanding of its probiotic potential, we have sequenced genome of Bacillus altitudinis B-388 using mate-pair technology. It allowed us to improve quality of the genome sequence. The number of contigs decreased from 59 to 8. N50 contig length increased by four times. The number of identified genes raised from 3730 to 3774 (3645 proteins and 73 RNAs) with the reduction of frameshifted genes. The calculated size of B. altitudinis B-388 genome is 3,743,699 bp, with a G + C content of 41.17 mol%. Additional incomplete prophage sequence in genome of B. altitudinis B-388 was revealed. It was found that cryptic plasmid encodes SoxR, an oxidative stress response regulator. To date, the reported sequence is the most thorough presentation of B. altitudinis genome among four whole-genome sequences of this species deposited in GenBank.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
1 Introduction
Representatives of the genus Bacillus are widespread in the environment and traditional fermented meals. Therefore, they easily get to human intestine with food and drinks. Now, species of the genus Bacillus are regarded as resident rather than transient microorganisms in human GIT [1]. By secretion of enzymes, production of antibiotics and other small compounds, Bacillus species influence on intestinal microbiota as well as on human GIT. Bacillus altitudinis was described as a new species in 2006 during analysis of air samples collected at 41 km in atmosphere [2]. Later, it was found to be abundant in marine and soil environments. Additionally to high UV resistance, B. altitudinis possesses antagonistic traits in respect to fungi [3] and produces extracellular glucanase, xylanase, protease which can contribute to meal digestion [4–6] as well as autoinducer-2, a quorum sensing molecule which mediates interspecies signalling and affects bacterial behaviour [7]. Ribonuclease secreted by B. altitudinis is a homologue of B. pumilus binase showing antiviral and antitumour activities [8–10]. Decoding of B. altitudinis genome will generate an accurate reference for understanding its probiotic potential. Here, mate-pair next-generation sequencing was used to improve whole genome contigs obtained for B. altitudinis B-388 earlier [11].
2 Material and Methods
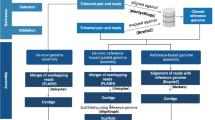
For genomic DNA extraction, B. altitudinis B-388 was grown on LB medium for 16–18 h. DNA isolation was performed using PureLink Genomic DNA Kit (Invitrogen, USA). Genomic DNA was sheared acoustically with a HydroShear DNA Shearing Device (Gene Machines, USA). Fragments with sizes of 2–3 and 5–6 kb were selected on an agarose gel. Two mate-pair libraries with an insert size of 2 and 5 kb were generated using SOLiD Mate-Paired Library Kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA). Ligation with adaptors and circularization were performed with the help of Ion Xpress Barcode Adapters 1–16 Kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA). Sequencing and initial sequencing data analysis were perform on the platform of Ion Personal Genome Machine System (Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA) and Torrent Suite Software (Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA), respectively. GS De Novo Assembler (Newbler software suite), v3.0 was used for genome assembly. The genome was annotated using the NCBI Prokaryotic Genome Annotation Pipeline version 3.1. Identification of prophage sequences within bacterial genome was performed using PHAST web server [12].
3 Results and Discussion
Genome of B. altitudinis B-388 was sequenced using whole-genome shotgun sequencing approach in 2014 [11]. By that time, it was a second B. altitudinis sequencing project (GenBank Acc. No JOVS00000000.1) after its type strain 41KF2b which was released early in 2014 under GenBank acc. No ASJC00000000.1. The sequencing with 20-fold overall B. altitudinis B-388 genome coverage resulted in obtaining of 59 contigs with an N50 size of 127,734 bp [11]. Contig 45 was assumed to represent a plasmid of 4,528 bp. The size of the genome was estimated to be 3,706,590 bp.
Accurate microbial genome sequence information is important for discovering genetic changes upon comparative analysis of microbial strains, understanding of genes regulation and prognostics of functional activities of the strains. Mate-pair sequencing allows decreasing gap regions and number of contigs with extending scaffold lengths compared to initial de novo whole genome sequencing. In this work mate-pair sequencing of B. altitudinis B-388 was performed with 262× overall genome coverage. For 2 kb and 5 kb insert libraries 72,295 and 75,268 reads were obtained, correspondingly. 19 contigs with an N50 size of 466,626 bp forming eight scaffolds with an N50 size of 865,860 bp were generated. The genome size was calculated as 3,743,699 bp. Gapped regions represent 0.08 % of total genome length. During annotation, 3645 protein coding sequences and 73 RNAs were detected. The number of frameshifted genes decreased twice compared to the results of de novo sequencing (Table 1). It was found that the scaffold 8 represents a cryptic plasmid of 4,529 bp encoding two hypothetical proteins, Rep protein and DNA-binding protein SoxR, involved in oxidative stress response. In addition to two prophages found in genome of B. altitudinis B-388 upon initial annotation, another incomplete phage sequence was revealed after mate-pairing (Table 1). Comparative analysis of B. altitudinis genome characteristics obtained after application of different sequencing techniques to four different strains demonstrated their high similarity with variation in prophage number and plasmid content (Table 1).
4 Conclusions
Thus, by implication of mate-pair sequencing approach, we have improved the quality of B. altitudinis genome sequence, which will be used for comparative and functional studies involving this species. To date, the reported sequence is the most thorough presentation of B. altitudinis genomes deposited in GenBank.
References
Fakhry, S., Sorrentini, I., Ricca, E., De Felice, M., Baccigalupi, L. (2008). Characterisation of spore forming Bacilli isolated from the human gastrointestinal tract. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 105, 2178–2186.
Shivaji, S., Chaturvedi, P., Suresh, K., Reddy, G. S., Dutt, C. B., Wainwright, M., et al. (2006). Bacillus aerius sp. nov., Bacillus aerophilus sp. nov., Bacillus stratosphericus sp. nov. and Bacillus altitudinis sp. nov., isolated from cryogenic tubes used for collecting air samples from high altitudes. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 56, 1465–1473.
Sunar, K., Dey, P., Chakraborty, U., Chakraborty, B. (2015). Biocontrol efficacy and plant growth promoting activity of Bacillus altitudinis isolated from Darjeeling hills, India. Journal of Basic Microbiology, 55, 91–104.
Madhuri, A., Nagaraju, B., Harikrishna, N., Reddy, G. (2012). Production of alkaline protease by Bacillus altitudinis GVC11 using castor husk in solid-state fermentation. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 167, 1199–1207.
Mao, S., Lu, Z., Zhang, C., Lu, F., Bie, X. (2013). Purification, characterization, and heterologous expression of a thermostable β-1,3-1,4-glucanase from Bacillus altitudinis YC-9. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 169, 960–975.
Thite, V. S., & Nerurkar, A. S. (2015). Xylanases of Bacillus spp. isolated from ruminant dung as potential accessory enzymes for agro-waste saccharification. Letters in Applied Microbiology, 60, 456–466.
Qian, Y., Kando, C. K., Thorsen, L., Larsen, N., Jespersen, L. (2015). Production of autoinducer-2 by aerobic endospore-forming bacteria isolated from the West African fermented foods. FEMS Microbiology Letters. doi:10.1093/femsle/fnv186.
Dudkina, E., Ulyanova, V., Shah Mahmud, R., Khodzhaeva, V., Dao, L., Vershinina, V., et al. (2016). Three-step procedure for preparation of pure Bacillus altitudinis ribonuclease. FEBS Open Bio, 6, 24–32.
Shah Mahmud, R., & Ilinskaya, O. N. (2013). Antiviral activity of binase against the pandemic Influenza A (H1N1) virus. Acta Naturae, 5, 44–51.
Mitkevich, V. A., Kretova, O. V., Petrushanko, I. Y., Burnysheva, K. M., Sosin, D. V., Simonenko, O. V., et al. (2013). Ribonuclease binase apoptotic signature in leukemic Kasumi-1 cells. Biochimie, 95, 1344–1349.
Shah Mahmud, R., Ulyanova, V., Malanin, S., Dudkina, E., Vershinina, V., et al. (2015). Draft whole-genome sequence of Bacillus altitudinis strain B-388, a producer of extracellular RNase. Genome Announcements. doi:10.1128/genomeA.01502-14.
Zhou, Y., Liang, Y., Lynch, K., Dennis, J. J., Wishart, D. S. (2011). PHAST: a fast phage search tool. Nucleic Acids Research. doi:10.1093/nar/gkr485.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the program of competitive growth of the Kazan Federal University and Russian Foundation for Basic Research no. 16-34-00448. The research was performed using the equipment of the Interdisciplinary Center for Collective Use of KFU (ID RFMEFI59414X0003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Vera Ulyanova and Raihan Shah Mahmud contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ulyanova, V., Shah Mahmud, R., Malanin, S. et al. Improving Bacillus Altitudinis B-388 Genome Scaffolding Using Mate-Pair Next-Generation Sequencing. BioNanoSci. 7, 85–87 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12668-016-0304-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12668-016-0304-z