Abstract
Menthol mint (Mentha arvensis L.) cultivation is significantly affected by the heavy metals like cadmium (Cd) which also imposes severe health hazards. Two menthol mint cultivars namely Kosi and Kushal were evaluated under Cd stress conditions. Impact of plant growth regulators (PGRs) like salicylic acid (SA), gibberellic acid (GA3) and triacontanol (Tria) on Cd stress tolerance was assessed. Reduced growth, photosynthetic parameters, mineral nutrient concentration, and increased oxidative stress biomarkers like electrolyte leakage, malondialdehyde, and hydrogen peroxide contents were observed under Cd stress. Differential upregulation of proline content and antioxidant activities under Cd stress was observed in both the cultivars. Interestingly, low electrolyte leakage, lipid peroxidation, hydrogen peroxide and Cd concentration in leaves were observed in Kushal compared to Kosi. Among all the PGRs tested, SA proved to be the best in improving Cd-stress tolerance in both the cultivars but Kushal responded better than Kosi.
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Heavy metal (HM) contamination of agricultural lands is becoming a significant threat to the sustainability of agro-ecosystems (Ashraf et al. 2017; Wang et al. 2017; Wani et al. 2018; Ali et al. 2018; Vardhan et al. 2019; Zaid et al. 2019b). Cadmium (Cd), one of the HMs, is a non-essential element, very toxic to plants (Wang et al. 2018; Nouairi et al. 2019; Rizwan et al. 2019; Zaid et al. 2019b). Nearly 20 million hectares of cultivable land worldwide are known to be contaminated by Cd (Liu et al. 2015; Dong et al. 2017). Once taken up by the plants, Cd retards growth, photosynthetic capacity and induces oxidative stress unexpectedly even at low doses (Lux et al. 2010; Qayyum et al. 2017). Presence of Cd in the plants greatly inhibits the photosynthetic capacity by impairing chlorophyll biosynthesis and thereby inhibiting the efficiency of proteins associated with pigment system II (PSII) and activity of carbon dioxide trapping enzyme ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase (Rubisco) (Li et al. 2015; Silva et al. 2017). Cadmium also decreases the concentration of essential mineral nutrients by decreasing their uptake and transport rate, in contrast to promoting the accumulation of osmolytes, oxidation of proteins, lipids, and macromolecules (Ali et al. 2015; Akhtar et al. 2017; Santos et al. 2017). During adaptation, plants have evolved complex strategies to cope with the adverse effects of elevated reactive oxygen species (ROS) generated due to Cd exposure in order to maintain internal redox homeostasis. The plant response to Cd stress is mainly mediated through immobilization of Cd through the cell wall and synthesis of chelators such as phytochelatins, metallothioneins and organic acids (Hasan et al. 2015). Cadmium detoxification also involves vacuolar compartmentalization and synthesis of heat shock proteins (HSPs) (Hall 2002). The adaptive strategies in the plants consist of the induction of enzymatic and non-enzymatic antioxidants (Ahmad et al. 2015) and enhanced accumulation of osmolytes (Khan et al. 2015). In plants’ abiotic stress tolerance mechanisms, several plant growth regulators (PGRs) play a critical role in enhancing tolerance against various stresses and also in phytoremediation of contaminated habitats (Wani et al. 2016; Sharma et al. 2019; Neill et al. 2019; Rostami and Azhdarpoor 2019). however, very few efforts have been made to understand the hormone crosstalk involved in the plant response to Cd stress in menthol mint plants. Exogenous applications of PGRs like salicylic acid (SA) (Liu et al. 2011; Li et al. 2019; Faraz et al. 2019), gibberellic acid (GA3) (Masood et al. 2016), and triacontanol (Tria) (Maresca et al. 2017) have been found to modulate plants’ defense responses to Cd stress in various plant species. Salicylic acid has been reported to ameliorate Ni toxicity in periwinkle (Idrees et al. 2013), mustard (Zaid et al. 2019a), Pb stress in wheat (Alamri et al. 2018), mustard (Hasanuzzaman et al. 2019), As toxicity in rice (Singh et al. 2015), Cd in wheat (Shakirova et al. 2016; Kovács et al. 2014), maize (Gondor et al. 2016), radish (Raza and Shafiq 2013), potato (Li et al. 2019) and mustard (Ahmad et al. 2011; Faraz et al. 2019). Similarly, GA3 has been reported for mitigating the adverse effects of Cd stress in mustard, Pb stress in English ryegrass (Masood and Khan 2013; He et al. 2015; Masood et al. 2016). Triacontanol is a potent primary alcoholic PGR known to promote growth, photosynthetic activity, mineral nutrient contents (Li et al. 2016) and also acts as an antioxidative agent by inhibiting enzymatic and non-enzymatic mediated peroxidative damage of cellular proteins and lipids (Asadi Karam et al. 2017).
Menthol mint (Mentha arvensis L.) an important industrial, medicinal and aromatic plant, have numerous applications in the flavorings, food, cosmetic and pharmaceutical industries (Lal 2013). Menthol, as principal secondary metabolite is extracted commercially from this plant (Rao et al. 2000; Naeem et al. 2014). However, a little is known about the differential phytoremediation capacity of cultivars of menthol mint in relation to Cd stress. Among the numerous strategies used for reducing the concentration of Cd from HM challenged soils, phytoremediation is regarded as an efficient, eco-friendly, cost-effective, economical, and aesthetically acceptable remediation strategy to reduce/minimize the danger of contamination of soil by HMs (Bauddh and Singh 2012; Guo et al. 2016). The phytoremediation potential of different plant species has been extensively studied. Manikandan and Venkatachalam (2011) worked out the tolerance capacity of menthol mint in relation to Hg stress. However, the phytoremediation capacity of menthol mint cultivars in relation to Cd stress has not been studied in detail. Moreover, the effect of Cd stress on growth, photosynthetic, mineral nutrient, antioxidants and stress responses of menthol mint is largely unknown. Therefore, the present study was planned to study the effect of Cd in two different cultivars, the applicability of PGRs to improve tolerance and differential phytoremediation capability of menthol mint cultivars.
Materials and methods
Experimental setup and plant growth regulators preparation
Menthol mint plants were grown in the earthen pots in the naturally illuminated environmental conditions of the net house at the Department of Botany, Aligarh Muslim University, Aligarh, India (27°52′N, 78°51′E, and 187.45 m altitude, average night/day temperatures, 15 ± 2 °C, 25 ± 3 respectively; relative humidity, 60 ± 5%; photosynthetically active radiation (PAR), 755 ± 20 μmol m−2 s−1; critical photoperiod, 10–12 h). Suckers of Mentha arvensis Linn. cv. Kosi and Kushal were procured from the Central Institute of Medicinal and Aromatic Plants, Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh (India). Prior to transplanting, suckers were surface sterilized with 0.01% of the HgCl2 solution and then washed vigorously with double distilled water (DDW) followed by thorough washing with deionized water. Each earthen pot used for the experiment contained 5 kg mixture of upper soil layer (0–30 cm) which was collected from an uncontaminated paddy field from nearby areas and mixed with farmyard manure (4:1). Physicochemical characteristics of the soil were: sandy loam in texture, pH (1:2) 8.0, EC (1:2) 0.59 mmhos cm−1, and 93.1, 9.4, and 155.5 mg available critical mineral nutrients namely N, P, and, K per kg of soil, respectively. A uniform dose of N, P, and K (each 25) mg/kg soil was applied. Half of the N and full of P and K were applied at the time of transplanting and the remaining N was top-dressed in two splits, the first at 35 days after transplantation (DAT) and the second at 70 DAT. Urea, single superphosphate, and muriate of potash were used as the source of N, P and K, respectively. After a fortnight of transplantation, manual thinning was carried out and 3 healthy plants per pot of uniform size were maintained. At 30 DAT, 50 µM Cd was given in the form of dilute aqueous solution of cadmium chloride (CdCl2) through roots. Three growth regulators namely SA, GA3, and Tria were sprayed at 60 DAT thrice at an interval of 15 days by using Tween–20 as a surfactant. The concentration of each growth regulator was based on earlier findings of Khan et al. (2010) and Khanam and Mohammad (2018). Stock solutions of each plant growth regulator were prepared by dissolving them in DDW and ethanol. From the stock solution, the desired quantity of each plant growth regulator (10−6 M) was made by using DDW. Each plant was sprayed with of 3 mL of PGR solution by a sprayer. In one sprinkle, the nozzle of the sprayer was adjusted in such a manner that it ejected 1 mL (approx.) of the required solution and each plant was sprinkled thrice. Each experimental pot was irrigated on alternate days with 100–150 mL of DDW. The experimental pots were arranged in complete randomized block design and were conducted in five replications. The pattern of treatments was as follows: (T1: control; T2: 10−6 M GA3; T3: 10−6 M Tria; T4: 10−6 M SA; T5: 50 µM CdCl2; T6: 50 µM CdCl2 + 10−6 M GA3; T7: 50 µM CdCl2 + 10−6 M Tria; T8: 50 µM CdCl2 + 10−6 M SA).
The plants were sampled at 100 DAT to assess various physio-biochemical attributes.
Measurement of growth and photosynthetic parameters
Growth characteristics in terms of fresh and dry mass of shoot and leaf area were measured. Plants were uprooted from pots, washed thoroughly and dried by using blotting paper and their fresh masses were noted. After recording fresh mass, plant samples were kept at 72 °C in a hot air oven until completely dried and then weighed to obtain DM. The leaf area was measured by using a leaf area meter (ADC Bioscientific, UK). The SPAD values of Chl in the leaves were estimated under natural environmental conditions by using the SPAD Chl meter (SPAD–502; Konica, Minolta Sensing, Inc., Japan). Gas exchange traits [net photosynthesis (PN), stomatal conductance (gS) and intercellular CO2 concentration (Ci)] were measured in uppermost fully expanded leaves of all plants using infrared gas analyzer (LI–COR 6400 portable photosynthesis system (LI–COR, Lincoln, NE, USA). The measurements were done on a cloudless sunny day at ambient air temperature 25 °C, light saturating intensity; PAR 760 μmol m−2 s−1, relative humidity 85% and atmospheric CO2 concentrations 370 ± 5 μmol mol−1. The activity of Rubisco (EC 4.1.1.39) was determined by the standard method of Usuda (1985) and expressed as [µ mol (CO2) m−2 s−1] Yusuf et al. (2017).
Determination of tolerance index (TI)
Tolerance index was calculated as the ratio of the mean value of treated plant dry mass to mean dry mass of control plants and expressed in percentage points.
Analysis of leaf primary mineral nutrient concentrations
Quantification of N, P and, K concentrations
Fresh leaf samples were oven dried at 72 °C for a period of 48 h. The dried material was made into fine powder and passed through a sieve of 0.42 mm in size. Samples (100 mg) were digested in H2SO4 at 110 °C for 2 h in temperature controlled Kjeldahl assembly. The contents were cooled at room temperature for 20 min and a few drops of 30% H2O2 were added. Heating and cooling were again repeated. Acid-peroxide digested leaf material (10 mL) was used for determining leaf N, P and K concentrations.
The method of Lindner (1944) was employed for N determination. The procedure of Fiske and Subbarow (1925) was adopted for P determination. The intensity of color was read at 620 nm.
The acid-peroxide digested aliquot was taken and the concentrations of K were determined by using flame photometer (Model, ELICO, CL22D, India). A blank sample was also run along and all the concentration of K was expressed in mg g−1 (DM).
Determination of oxidative stress biomarkers
Thiobarbituric acid reactive substances were determined by measuring the malondialdehyde equivalents according to the protocol of Hodges et al. (1999). The absorbance of the samples was read at 440, 532 and 600 nm and the values were expressed in (nmol TBARS g−1 (FM)).
Sullivan and Ross (1979) method was used for calculating the electrolyte leakage (EL). The electrolyte leakage was calculated by using the given formula:
The method of Jana and Choudhari (1981) was used for the quantification of H2O2. The absorbance of the reaction mixture was read at 410 nm, on a spectrophotometer (ELICO SL 171 MINI SPEC, India).
Assay of antioxidants and proline
Preparation of enzyme extract
The leaf tissue was homogenized in 50 mM phosphate buffer (pH 7.0) containing 1% polyvinylpyrrolidone. The homogenate was centrifuged at 27,600×g for 10 min at 4 °C and the supernatant obtained was used as an extract for superoxide dismutase, catalase and, peroxidase.
Determination of superoxide dismutase (SOD, EC 1.15.1.1) activity
The SOD activity was determined by monitoring the inhibition of photochemical reduction of nitroblue tetrazolium (NBT) according to the method of Giannopolitis and Ries (1977). The absorbance was read at 650 nm and one unit of SOD activity was defined as the amount of enzyme causing a 50% decrease of NBT.
Estimation of activities of catalase (CAT, EC 1.11.1.6), peroxidase (POX, EC 1.11.1.7) and glutathione reductase (GR, EC 1.6.4.2.)
The activity of CAT was measured by following the procedures of Chance and Maehly (1956). For CAT estimation, 3 mL of 0.1 M phosphate buffer (pH 6.8), 1 mL of H2O2 (0.1 M), 10–20 µL of enzyme extract and 1% of guaiacol were mixed. The reaction mixture was left undisturbed for one min at room temperature. The mixture was then titrated against 0.1 N potassium permanganate to find residual H2O2 until a joint purple color appeared for at least 15 min. Similarly, a control set was also maintained in which enzyme activity was stopped by adding H2SO4 to enzyme extract before its addition to the test tube.
Peroxidase activity was calculated according to the method described by Chance and Maehly (1956). Units of CAT and POX were expressed as [mM (H2O2) decomposed mg−1 (FM) and enzyme units (EU) g−1 (FM)], respectively.
Glutathione reductase activity was estimated by the method of Smith et al. (1988).
Determination of carotenoids
The contents of carotenoids were estimated by using the standard method of Maclachlan and Zalik (1963). The contents were calculated using the formula:
where OD = optical density of the extract at the given wavelengths (480 and 510 nm), V = final volume of extract in 80% acetone, W = fresh mass of leaf tissue (g), and d = length of the light path (1 cm).
Estimation of proline content
The method described by Bates et al. (1973) was used for the determination of proline content.
Atomic absorption spectrophotometer (AAS) analysis of root and leaf Cd
The concentrations of Cd in the root and leaf were then determined by atomic absorption spectrophotometer (GBC, 932 plus; GBC Scientific Instruments, Braeside, Australia) according to the method of Zaid and Mohammad (2018).
Determination of nitrate reductase (NR) and carbonic anhydrase (CA) activity
The activity of the NR enzyme was determined by the method of Jaworski (1971). The method of Dwivedi and Randhawa (1974) was used for measuring the activity of CA. The absorption of the reaction mixtures was read at 540 nm by spectrophotometer (ELICO SL 171 MINI SPEC, India).
Statistical analysis
The statistical analysis was performed by using by SPSS 17.0 software tool for windows 10. The percentage data and the significant differences between the means of two cultivars were determined by Duncan’s Multiple Range Test (DMRT) at P ≤ 0.05 and presented as mean ± standard error (n = 5). Each value of mean and standard error in the table and figures respectively represent five replicates.
Results
Growth characteristics
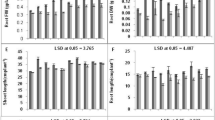
Growth traits such as the fresh and dry mass of plants and leaf area were decreased by Cd stress in both cultivars. The fresh and dry mass of shoot also followed a similar trend (Figs. 1A–D, 2B). The Cd stress decreased FM of plants by 15.34% in Kosi and 18.89% in Kushal with respect to control. The plant DM decreased by 14.30% in Kosi and 6.69% in Kushal respectively, with respect to control. The FM of the shoot in Kosi was decreased by 15.07%, and 14.49% in Kushal. Cadmium also decreased DM of shoot by 41.76% in Kosi whereas, in Kushal, a 34.27% decrease was noted. Leaf area in Kosi cultivar decreased by 8.02% and 7.79% in Kushal by Cd stress as compared to respective controls. Treatment of plants with PGRs improved all the growth traits in unstressed plants. Moreover, the follow-up treatments after Cd stress with SA, GA3, and Tria successfully countered the damage caused by Cd stress. The response of the plants treated with SA in Kushal was more effective than Kosi. Of the two cultivars, Kushal was found more responsive to SA under Cd stress as it possessed higher plant FM, DM as well as high shoot FM, DM and leaf area than Kosi cultivar.
Effect of plant growth regulators (PGRs); gibberellic acid (GA3), triacontanol (Tria) or salicylic acid (SA) grown with or without cadmium (Cd) on (A) fresh mass of plant, (B) dry mass of plant, (C) shoot fresh mass and, (D) shoot dry mass in two different cultivars of menthol mint. Data are presented as treatments mean ± SE (n = 5). The bar shows standard error and different capital and small letters represent significant differences in Kushal and Kosi cultivars among various treatments by DMRT test at P ≤ 0.05
Effect of plant growth regulators (PGRs); gibberellic acid (GA3), triacontanol (Tria) or salicylic acid (SA) grown with or without cadmium (Cd) on (A) SPAD value and, (B) leaf area of two different menthol mint cultivars. Data are presented as treatments mean ± SE (n = 5). The bar shows standard error and different capital and small letters represent significant differences in Kushal and Kosi cultivars among various treatments by DMRT test at P ≤ 0.05
Tolerance index
The cultivar Kushal showed a greater tolerance index than cultivar Kosi (Fig. 6C).
Chlorophyll content and leaf gas exchange parameters
SPAD value, Rubisco activity and all photosynthetic attributes—PN, gs, Ci decreased in the plants by the Cd stress, as compared to respective control plants (Figs. 2A, 3A–D). The Chl content diminished significantly (P ≤ 0.05) by 23.36% in Kosi and 23.31% in Kushal, compared to control plants (Fig. 2A). Cadmium treatment triggered a significant decrease in PN by 50.66% in Kosi and 26.38% in Kushal, respectively, compared to control plants (Fig. 3A). SA, GA3 and Tria application to non-stressed plants increased the SPAD value, Rubisco activity, and photosynthetic attributes. All plant growth regulators improved the photosynthetic attributes in Cd-stressed plants and recovered the damage but SA was very effective in improving Chl, Rubisco activity, gs and Ci in stressed plants. Kushal performed better than Kosi cultivar under Cd stress.
Effect of plant growth regulators (PGRs); gibberellic acid (GA3), triacontanol (Tria) or salicylic acid (SA) on two different cultivars of menthol mint grown with or without cadmium (Cd) on (A) net photosynthetic rate (PN), (B) stomatal conductance (gs), (C) internal carbon dioxide concentration (Ci) and, (D) Rubisco activity. Data are presented as treatments mean ± SE (n = 5). The bar shows standard error and different capital and small letters represent significant differences in Kushal and Kosi cultivars among various treatments by DMRT test at P ≤ 0.05
Leaf mineral nutrient contents
All the three principal mineral nutrients N, P and, K in the leaves were decreased by Cd treatments in comparison to control plants in both the cultivars (Fig. 4A–C). Nitrogen concentrations decreased by 50% in Kosi and 57.57% in Kushal, P by 39.53% in Kosi and 14.58% in Kushal and K by 49.76% and 44.97% in Kosi and Kushal, respectively as compared to the respective control plants. GA3, Tria, and SA increased all the mineral nutrient concentrations in unstressed plants. However, of all the PGRs, GA3 triggered the maximum increase in leaf N in both cultivars but Kushal was more responsive as it retained more N, P, and K concentrations under Cd persistence.
Effect of plant growth regulators (PGRs); gibberellic acid (GA3), triacontanol (Tria) or salicylic acid (SA) on two different cultivars of menthol mint grown with or without cadmium (Cd) on (A) Nitrogen (N), (B) Phosphorous (P), (C) Potassium (K), (D) thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARS) content, (E) electrolyte leakage and, (F) hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) content. The bar shows standard error and different capital and small letters represent significant differences in Kushal and Kosi cultivars among various treatments by DMRT test at P ≤ 0.05
Thiobarbituric acid reactive substances, EL, and H2O2 content
Thiobarbituric acid reactive substances, EL, and H2O2 content increased significantly under Cd treatments in both the cultivars in comparison to control plants. Cadmium increased TBARS content by 50.81% and 48.76%, H2O2 content by 53.45% and 69.83% and EL by 68.38% and 73.72% in Kosi and Kushal, respectively, over the respective control plants (Fig. 4D–F). Moreover, PGRs treatment decreased the aforesaid parameters in Cd-stressed plants and in addition to this, SA proved very effective and lowered down the values of TBARS, EL and H2O2 in Cd-stressed plants when applied as follow-up treatment. Kosi was more sensitive to Cd stress than Kushal cultivar.
Impact on the activities of antioxidant enzymes and proline content
Cadmium stress increased the activities of all antioxidant enzymes studied in both the cultivars, as compared to control plants (Fig. 5A–D). Superoxide dismutase activity increased by 50.04% in Kosi and 51.28% in Kushal, CAT by 11.46% in Kosi and 11.19% in Kushal, POX by 58.31% in Kosi and 59.82% in Kushal and GR activity significantly by 70.13% and 65.57%, respectively, in Kosi and Kushal, over the respective control plants. Treatment of PGRs to Cd stressed plants further increased the activities of SOD, CAT, POX, and GR in both the cultivars. Maximum activities of these enzymes were noted in the Cd stressed plants which received SA treatment, such that SOD values increased by 52.77% in Kosi and 54.42% in Kushal. Catalase values increased by 15.64% in Kosi and 15.68% in Kushal. Salicylic acid treatment to Cd stressed plants increased POX values by 72.18% in Kosi and 71.89% in Kushal. At the same treatments, GR values in Kosi and Kushal were increased by 75.76% and 72.39% respectively over the respective control plants. Carotenoid content increased significantly by Cd stress in both cultivars. In Kushal, Cd stress increased the Car content by 76.92% and 77.47% in Kosi with respect to unstressed plants (Fig. 6A). Moreover, PGRs treatment to Cd stressed plants increased the Car contents in both the cultivars, but out of three PGRs, SA triggered a maximum increase of 91.83% in Kosi and 91.45% in Kushal, over control plants.
Effect of plant growth regulators (PGRs); gibberellic acid (GA3), triacontanol (Tria) or salicylic acid (SA) on two different cultivars of menthol mint grown with or without cadmium (Cd) on activities of (A) superoxide dismutase (SOD), (B) catalase (CAT), (C) peroxidase (POX) and, (D) glutathione reductase (GR). Data are presented as treatments mean ± SE (n =5). The bar shows standard error and different capital and small letters represent significant differences in Kushal and Kosi cultivars among various treatments by DMRT test at P ≤ 0.05
Effect of plant growth regulators (PGRs); gibberellic acid (GA3), triacontanol (Tria) or salicylic acid (SA) on two different cultivars of menthol mint grown with or without cadmium (Cd) on (A) carotenoids content, (B) proline content and, (C) tolerance index (TI). Data are presented as treatments mean ± SE (n = 5). The bar shows standard error and different capital and small letters represent significant differences in Kushal and Kosi cultivars among various treatments by DMRT test at P ≤ 0.05
Proline content in Cd-stressed plants in both the cultivars increased significantly by 38.63% in Kosi and 42.60% in Kushal, over the respective control plants (Fig. 6B). Salicylic acid, GA3, and Tria had an additive effect on proline accumulation in both the cultivars, GA3 increased the proline content by 6.19% in Kosi, whereas, Tria increased the proline content by 3.53% with respect to Cd-treated plants. In Kushal, GA3 increased the proline content by 1.60%, and 5.83% by Tria application with respect to Cd stressed plants. However, the SA application increased the proline content maximally in both unstressed and stressed plants. In unstressed plants, SA increased proline content by 27.87% in Kosi and 37.50% in Kushal over the control pants. Nevertheless, SA in Cd-stressed plants increased proline content by 65.61% in Kosi and 61.45% in Kushal cultivars, over the control plants. Kushal accumulated high concentrations of proline in control as well in all treatments than the Kosi.
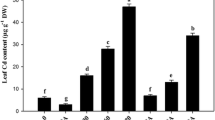
Heavy metal concentrations in root and leaf
Accumulation of Cd significantly increased in root and leaf of the Cd-treated plants in both cultivars, as compared to unstressed control (Table 1). The root Cd increased by 31.21 fold in Kosi with respect to control plants. All PGRs decreased the Cd concentrations in the root of both the cultivars, but SA decreased the Cd concentrations by 67.73% in Kosi and 58.63% in Kushal with respect to Cd stressed plants. In contrast, Cd concentrations in leaves of the Cd stressed plants increased by 20.71 fold in Kosi and 17.33 fold in Kushal with respect to non-stressed control plants (Table 1). Among the three PGR tested, SA decreased Cd concentrations in the leaves significantly by 72.41% in Kosi and 71.63% in Kushal as compared to Cd stressed plants. Kushal accumulated more Cd in roots but less in leaves and was found more responsive to SA treatment.
Activities of nitrate reductase and carbonic anhydrase
Cadmium stressed plants had decreased activities of NR and CA in the leaves, as compared to control plants. Cadmium stress diminished NR activity by 38.46% in Kosi and 26.66% in Kushal respectively with respect to control plants (Table 2). Cadmium stress also decreased CA activity by 10.68% in Kosi and 12.34% in Kushal, compared to control plants. Treatment of plants with SA, GA3, and Tria improved the activities of NR and CA in unstressed and stressed plants with respect to control plants. However, SA treatment completely recovered the damage caused by Cd stress and increased the activities of NR by 44.44% in Kushal and 35% in Kosi and CA by 26.91% in Kosi and 24.19% in Kushal respectively, over control plants (Table 2). Kushal cultivar under Cd stress was more responsive to SA treatment than Kosi.
Discussion
The present study was conducted to elucidate the responses in menthol mint cultivars that differ in Cd tolerance and to test the efficacy of PGRs in modulating Cd-induced changes. In the present study, Cd significantly reduced (P ≤ 0.05) all the plant growth attributes in both cultivars of menthol mint. The suppression of growth in both cultivars under Cd toxicity could be due to restricted uptake of water and essential mineral nutrients by roots (Dinakar et al. 2009), altered rate of cell division, cell growth and cellular structures (Ashraf et al. 2017), denaturation of protein by disruption of H–S (hydrogen-sulfur) bond. It has been revealed that Cd stress cause altered growth and development of plants (Akhtar et al. 2017), inhibition of photosynthesis (Masood et al. 2012), changes in components of the cell wall and in the metabolism of carbohydrates (Abdel Latef 2013). The cumulative ill effect of Cd stress on overall metabolism decreased growth traits in both the cultivars but the maximum reduction was noted in Kosi. The Kushal cultivar had more leaf area than Kosi which could have helped to efficiently utilize solar radiation, resulting in higher photosynthetic rate and other plant growth related attributes. The inhibitory effects of Cd stress on growth might be due to the interference of vital physio-biochemical processes including photosynthesis and translocation of mineral nutrient elements inside plant tissues (Hou et al. 2007). Cadmium-induced growth reduction in the present study was further corroborated by studies in Indian mustard (Gill et al. 2011), maize (Akhtar et al. 2017), Miscanthus spp. (Guo et al. 2016), spinach (Younis et al. 2016), chickpea (Ahmad et al. 2016). Similar Cd-induced decrease in growth traits has been reported in peppermint plants by Ahmad et al. (2018) and in menthol mint plants (Zaid and Mohammad 2018). In the present report, the decrease in plant DM in both cultivars was due to the decrease in the rate of PN, which exerted an important role in the accumulation of biomass in menthol mint plant during Cd toxicity. Reduction in the rate of photosynthesis under Cd stress is also attributed to the low biosynthesis of Chl and decreased the scavenging activity of Rubisco protein (Khan et al. 2016). However, SA improved growth traits and leaf gas exchange parameters in both cultivars (Figs. 1, 2, 3). Salicylic acid-mediated increase in the rate of photosynthesis in presence of Cd stress could have improved due to increase in Rubisco activity, which is also in accordance with the finding of Krantev et al. (2008) in maize plants under Cd stress. The salicylic acid application also modulated Cd-induced changes in both cultivars of menthol mint and these results are in line with the findings of Choudhury and Panda (2004) in rice plants. A similar increase in leaf gas exchange traits and Rubisco activity by exogenous SA application in response to Cd stress has been reported in Mentha piperita (Ahmad et al. 2018).
Findings of the present work indicated that Cd stress decreased the uptake of the mineral nutrient elements in both the cultivars (Fig. 4A–C). Nutrient imbalance by Cd stress generated negative impacts on diverse physio-biochemical processes in plants. The pronounced inhibitory effects of Cd on the essential mineral concentrations of the leaf was due to their reduced uptake and translocation which corroborates with the earlier results obtained by Gill et al. (2012); Zouari et al. (2016); Ahmad et al. (2015, 2016). The high mineral nutrient concentrations in Kushal suggest that mineral metabolism of nutrients played a vital role in the capacity of plants to maximally tolerate Cd-induced oxidative changes. However, Cd-mediated variation in mineral nutrient concentration in both cultivars could be due to prevailing genetic variation (Anjum et al. 2008). Salicylic acid application optimized the nutrient status and increased mineral nutrient concentrations in both the cultivars under Cd stress (Fig. 4A–C). A similar increase in mineral nutrient concentrations by SA in barley plants under Cd stress has been reported by Metwally et al. (2003).
The menthol mint cultivars exhibited a sharp decline in the activities of NR and CA in response to Cd stress (Table 2). This might be due to the inhibition or dysfunction of the enzyme protein by metal stress (Orcutt and Nilsen 2000). In addition to this, Cd stress also disturbed the activity of plasma membrane-localized proton pumps (Obata et al. 1996), thus restricting the uptake of nitrate which is the substrate of NR activity (Campbell 1999). Increased NR activity and N content mediated by SA under Cd stress could be due to the optimized allocation of available N under Cd stress in both cultivars which improved growth and photosynthetic traits (Figs. 1, 2, 3). A similar increase in the activity of NR due to SA treatment under Cd stress has been reported in chickpea plants by Hayat et al. (2014), tomato plants by Koc et al. (2013), peppermint plants (Ahmad et al. 2018), which are in agreement with our present results. The enzyme CA is the second most abundant zinc metalloprotein in C3 plants (Okabe et al. 1984), which catalyzes the reversible interconversion of HCO3− and CO2 in higher plants for maintaining a constant supply for Rubisco (Fariduddin et al. 2003). Cadmium stress decreased the activities of CA and Rubisco in the present study in both the cultivars. In fact, decreased Rubisco activity by Cd stress has been attributed due to the low activity of CA or Cd-Mg replacement in active centers in Cd-stressed plants (Siedlecka et al. 1998). Similar SA mediated increase in CA activity under Cd stress was reported by Alyemini et al. (2014) and Ahmad et al. (2018).
Plants have well developed antioxidant defense systems which comprise enzymatic and non-enzymatic antioxidants to fight against the ill effects of HMs’ stress (Jalmi and Sinha 2015; Rizwan et al. 2017). Exposure to Cd stress triggered the excessive production of ROS in plants which is manifested in the form of increased oxidative stress. Increased TBARS, EL and H2O2 content were observed in both cultivars under Cd stress. These parameters were lower in Kushal reflecting their higher tolerance capacity against Cd-induced oxidative stress as compared to Kosi (Figs. 4D–F). In the present study, Cd stress increased the antioxidant activities in Kushal except for SOD which showed higher in Kosi. A similar increase in the activity of SOD has earlier been reported by Syeed et al. (2011) in cultivars of mustard. Higher activities of antioxidant enzymes in Kushal under Cd stress or PGRs treatment reflects efficient detoxification of Cd as reflected in low leaf Cd concentrations and less EL, H2O2 production and TBARS content. Enhanced activities of antioxidants maintained redox pool in both cultivars and more prominently in Kushal which ultimately led to the protection of cells against Cd-induced oxidative stress that was in turn reflected in the form of low values of leakage of ions. These results are in conformity with the results of Zhang et al. (2015) in Cucumis melo, Ahmad et al. (2016) in Cicer arietinum, Han et al. (2015) in Iris hexagona. Carotenoids are lipophilic antioxidant agents in plants which have the ability to scavenge excess ROS and show a promotive effect on growth and development of plants exposed to biotic and abiotic environmental pressures (Mourato et al. 2012; El-Beltagi and Mohamed 2013). In addition, they play a principal role in regulating the photoprotection of the photosynthetic reaction center against auto-oxidation (Ashraf and Harris 2013; Gururani et al. 2015). Cadmium triggered an enhanced biosynthesis of carotenoid contents and the results are in harmony with the results of El-Beltagi and Mohamed (2013) in pea plants. The high carotenoid contents during PRGs treatment in general and during SA application in particular in Cd-stressed plants of menthol mint would be ascribed to its antioxidative and oxidative stress role. Enhanced carotenoid biosynthesis with PGRs supplementation might have reduced the oxidative stress caused by Cd toxicity in the present study. In line with our results, studies suggest that SA is known to increase carotenoid content in Nigella sativa (Kabiri et al. 2014), and in Glycine max plants (Razmi et al. 2017). Exogenous PGR treatments are known to promote the expression of genes associated with carotenoid biosynthesis pathway in plants (Cruz et al. 2018). In a more recent experiment, Zaid and Mohammad (2018) also found an enhanced carotenoid biosynthesis under Cd stress in M. arvensis plants supplied with exogenous phytohormone and mineral.
Cytosolic accumulation of compatible osmolytes is not only involved in the cell acclimation but also for sustaining the regulation of redox homeostasis potential under various environmental stresses including HMs (Ruszkowski et al. 2015; Anjum et al. 2017). Proline is one of the compatible solutes which help plants in the adjustment of the wide range of environmental extremes and serves as an adaptive means to stabilize cellular structures and functions, scavenges excess ROS, regulates redox environment (Ashraf and Foolad 2007; Bhaskara et al. 2015; Per et al. 2017). The present work revealed a differential accumulation of proline concentration in both cultivars under Cd stress. Cadmium-mediated increase in proline could be due to the increased activity of proline biosynthetic enzymes (Khan et al. 2015). Moreover, SA in the present study maintained the highest concentration of proline under stress conditions due to overexpression of genes related to proline biosyntheses such as pyrroline-5-carboxylate reductase and γ-glutamyl kinase (He et al. 2002; Maghsoudi et al. 2018; Lee et al. 2019). Kushal had always a high concentration of proline than Kosi in control as well as in all treatments and was found more tolerant to Cd stress.
It has been reported that Cd accumulates differently among different plant species and cultivars and is absorbed by either apoplastic or symplastic pathways (Kushwaha et al. 2015; Dong et al. 2017). In the present study, it was noted that roots accumulated more Cd as compared to leaves in both cultivars. This might be due to the poor root-shoot Cd translocation rate. Nonetheless, the high root and low leaf accumulation in Kushal contributed greater tolerance and well as high phytoremediation potential towards Cd stress than Kosi. This could be also one of the prime reasons that high leaf Cd concentration in Kosi generated negative effects on growth, mineral nutrients, and photosynthetic responses and increased oxidative stress. Similar tolerance to Cd stress has also been reported in bluegrass (Dong et al. 2017), miscanthus species (Guo et al. 2016) and in rice plants under Pb stress by Ashraf et al. (2017).
Conclusions
Cadmium toxicity differently hampered the growth, photosynthetic, mineral nutrient uptake in menthol mint cultivars. Out of the three PGR tested to ameliorate the Cd-induced changes, SA treatment found more promising. Enhanced osmolyte accumulation, optimum mineral metabolism, reduced oxidative stress and induced anti-oxidative defense systems were more prominent in Kushal cultivar as compared to Kosi. The effect of SA application in modulating Cd-induced changes was more conspicuous in Kushal cultivar than Kosi. Furthermore, uptaken Cd accumulated more in roots than translocated to leaves. The results showed that the menthol mint cultivars responded differentially to Cd stress tolerance. The findings presented could be helpful in evolving strategies to phytoremediate Cd from challenged habitats by selecting specific cultivar of menthol mint as well as for the development of tolerant menthol mint cultivars.
References
Abdel Latef AA (2013) Growth and some physiological activities of pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) in response to cadmium stress and mycorrhizal symbiosis. J Agric Sci Technol 15:1437–1448
Ahmad P, Nabi G, Ashraf M (2011) Cadmium-induced oxidative damage in mustard [Brassica juncea (L.) Czern. & Coss.] plants can be alleviated by salicylic acid. S Afr J Bot 77:36–44
Ahmad P, Sarwat M, Bhat NA, Wani MR, Kazi AG, Tran LSP (2015) Alleviation of cadmium toxicity in Brassica juncea L. (Czern. & Coss.) by calcium application involves various physiological and biochemical strategies. PLoS ONE 10:e0114571
Ahmad P, Abdel Latef AA, Abd_Allah EF, Hashem A, Sarwat M, Anjum NA, Gucel S (2016) Calcium and potassium supplementation enhanced growth, osmolyte secondary metabolite production, and enzymatic antioxidant machinery in cadmium-exposed chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.). Front Plant Sci 7:513
Ahmad B, Jaleel H, Sadiq Y, Khan MMA, Shabbir A (2018) Response of exogenous salicylic acid on cadmium induced photosynthetic damage, antioxidant metabolism and essential oil production in peppermint. Plant Growth Regul 86:273–286
Akhtar T, Zia-ur-Rehman M, Naeem A, Nawaz R, Ali S, Murtaza G, Rizwan M (2017) Photosynthesis and growth response of maize (Zea mays L.) hybrids exposed to cadmium stress. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:5521–5529
Alamri SAD, Siddiqui MH, Al-Khaishany MY, Ali HM, Al-Amri A, AlRabiah HK (2018) Exogenous application of salicylic acid improves tolerance of wheat plants to lead stress. Adv Agric Sci 6:25–35
Ali B, Gill RA, Yang S, Gill MB, Farooq MA, Liu D, Zhou W (2015) Regulation of cadmium-induced proteomic and metabolic changes by 5-aminolevulinic acid in leaves of Brassica napus L. PLoS ONE 10:e0123328
Ali S, Rizwan M, Zaid A, Arif MS, Yasmeen T, Hussain A, Abbasi GH (2018) 5-Aminolevulinic acid-induced heavy metal stress tolerance and underlying mechanisms in plants. J Plant Growth Regul 37:1423–1436
Alyemini MN, Hayat Q, Wijaya L, Hayat S (2014) Effect of salicylic acid on the growth, photosynthetic efficiency and enzyme activities of leguminous plant under cadmium stress. Not Bot Hort Agro Cluj Nap 42:440–445
Anjum NA, Umar S, Ahmad A, Iqbal M, Khan NA (2008) Ontogenic variation in response of Brassica campestris L. to cadmium toxicity. J Plant Interact 3:189–198
Anjum SA, Ashraf U, Tanveer M, Khan I, Hussain S, Shahzad B, Wang LC (2017) Drought induced changes in growth, osmolyte accumulation and antioxidant metabolism of three maize hybrids. Front Plant Sci 8:69
Asadi Karam E, Keramat B, Asrar Z, Mozafari H (2017) Study of interaction effect between triacontanol and nitric oxide on alleviating of oxidative stress arsenic toxicity in coriander seedlings. J Plant Interact 12:14–20
Ashraf M, Foolad MR (2007) Roles of glycinebetaine and proline in improving plant abiotic stress tolerance. Environ Exp Bot 59:206–216
Ashraf MHPJC, Harris PJC (2013) Photosynthesis under stressful environments: an overview. Photosynthetica 51:163–190
Ashraf U, Hussain S, Anjum SA, Abbas F, Tanveer M, Noor MA, Tang X (2017) Alterations in growth, oxidative damage, and metal uptake of five aromatic rice cultivars under lead toxicity. Plant Physiol Biochem 115:461–471
Bates L, Waldron R, Teare I (1973) Rapid determination of free proline for water stress studies. Plant Soil 39:205–207
Bauddh K, Singh RP (2012) Cadmium tolerance and its phytoremediation by two oil yielding plants Ricinus communis (L.) and Brassica juncea (L.) from the contaminated soil. Int J Phytoremediat 14:772–785
Bhaskara GB, Yang TH, Verslues PE (2015) Dynamic proline metabolism: importance and regulation in water limited environments. Front Plant Sci 6:484
Campbell HW (1999) Nitrate reductase structure, function and regulation: bridging the gap between biochemistry and physiology. Annu Rev Plant Biol 50:277–303
Chance B, Maehly AC (1956) Assay of catalase and peroxidases. Methods Enzymol 2:764–775
Choudhury S, Panda SK (2004) Role of salicylic acid in regulating cadmium induced oxidative stress in Oryza sativa L. roots. Bull J Plant Physiol 30:95–110
Cruz AB, Bianchetti RE, Alves FRR, Purgatto E, Peres LEP, Rossi M, Freschi L (2018) Light, ethylene and auxin signaling interaction regulates carotenoid biosynthesis during tomato fruit ripening. Front Plant Sci 9:1370
Dinakar N, Nagajyothi PC, Suresh S, Damodharam T, Suresh C (2009) Cadmium induced changes on proline, antioxidant enzymes, nitrate and nitrite reductases in Arachis hypogaea L. J Environ Biol 30:289–294
Dong Q, Xu PX, Wang ZL (2017) Differential cadmium distribution and translocation in roots and shoots related to hyper-tolerance between tall fescue and Kentucky Bluegrass. Front Plant Sci 8:113
Dwivedi R, Randhawa NS (1974) Evolution of a rapid test for the hidden hunger of zinc in plants. Plant Soil 40:445–451
El-Beltagi HS, Mohamed HI (2013) Alleviation of cadmium toxicity in Pisum sativum L. seedlings by calcium chloride. Not Bot Horti Agrobot 41:157–168
Faraz A, Faizan M, Sami F, Siddiqui H, Hayat S (2019) Supplementation of salicylic acid and citric acid for alleviation of cadmium toxicity to Brassica juncea. J Plant Growth Regul. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-019-10007-0
Fariduddin Q, Hayat S, Ahmad A (2003) Salicylic acid influences net photosynthetic rate, carboxylation efficiency, nitrate reductase activity, and seed yield in Brassica juncea. Photosynthetica 41:281–284
Fiske CH, Subbarow Y (1925) The colorimetric determination of phosphorus. J Biol Chem 66:375–400
Giannopolitis CN, Ries SK (1977) Superoxide dismutases II. Purification and quantitative relationship with water-soluble protein in seedlings. Plant Physiol 59:315–318
Gill SS, Khan NA, Tuteja N (2011) Differential cadmium stress tolerance in five Indian mustard (Brassica juncea L.) cultivars: an evaluation of the role of antioxidant machinery. Plant Sig Behav 6:293–300
Gill SS, Khan NA, Tuteja N (2012) Cadmium at high dose perturbs growth, photosynthesis and nitrogen metabolism while at low dose it up regulates sulfur assimilation and antioxidant machinery in garden cress (Lepidium sativum L.). Plant Sci 182:112–120
Gondor OK, Pál M, Darkó É, Janda T, Szalai G (2016) Salicylic acid and sodium salicylate alleviate cadmium toxicity to different extents in maize (Zea mays L.). PLoS ONE 11:e0160157
Guo H, Hong C, Chen X, Xu Y, Liu Y, Jiang D, Zheng B (2016) Different growth and physiological responses to cadmium of the three Miscanthus species. PLoS ONE 11:e0153475
Gururani MA, Venkatesh J, Tran LSP (2015) Regulation of photosynthesis during abiotic stress-induced photoinhibition. Mol Plant 8:1304–1320
Hall JL (2002) Cellular mechanisms for heavy metal detoxification and tolerance. J Exp Bot 53:1–11
Han Y, Chen G, Chen Y, Shen Z (2015) Cadmium toxicity and alleviating effects of exogenous salicylic acid in Iris hexagona. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 95:796–802
Hasan M, Ahammed GJ, Yin L, Shi K, Xia X, Zhou Y, Zhou J (2015) Melatonin mitigates cadmium phytotoxicity through modulation of phytochelatins biosynthesis, vacuolar sequestration, and antioxidant potential in Solanum lycopersicum L. Front Plant Sci 6:601
Hasanuzzaman M, Matin MA, Fardus J, Hasanuzzaman M, Hossain MS, Parvin K (2019) Foliar application of salicylic acid improves growth and yield attributes by upregulating the antioxidant defense system in Brassica campestris plants grown in lead-amended soils. Acta Agrobot 72:1765. https://doi.org/10.5586/aa.1765
Hayat S, Hayat Q, Alyemeni MN, Ahmad A (2014) Salicylic acid enhances the efficiency of nitrogen fixation and assimilation in Cicer arietinum plants grown under cadmium stress. J Plant Interact 9:35–42
He CY, Zhang JS, Chen SY (2002) A soybean gene encoding a proline-rich protein is regulated by salicylic acid, an endogenous circadian rhythm and by various stresses. Theor Appl Genet 104:1125–1131
He S, He Z, Wu Q, Wang L, Zhang X (2015) Effects of GA3 on plant physiological properties, extraction, subcellular distribution and chemical forms of Pb in Lolium perenne. Int J Phytoremediat 17:1153–1159
Hodges DM, DeLong JM, Forney CF, Prange RK (1999) Improving the thiobarbituric acid-reactive- substances assay for estimating lipid peroxidation in plant tissues containing anthocyanin and other interfering compounds. Planta 207:604–611
Hou W, Chen X, Song G, Wang Q, Chang CC (2007) Effects of copper and cadmium on heavy metal polluted water body restoration by duckweed (Lemna minor). Plant Physiol Biochem 45:62–69
Idrees M, Naeem M, Aftab T, Khan MMA (2013) Salicylic acid restrains nickel toxicity, improves antioxidant defence system and enhances the production of anticancer alkaloids in Catharanthus roseus (L.). J Hazard Mat 252:367–374
Jalmi SK, Sinha AK (2015) ROS mediated MAPK signaling in abiotic and biotic stress-striking similarities and differences. Front Plant Sci 6:769
Jana S, Choudhari MA (1981) Glycolate metabolism of three submerged aquatic angiosperms during ageing. Aquat Bot 12:345–354
Jaworski EG (1971) Nitrate reductase assay in intact plant tissues. Biochem Biophy Res Commun 43:1274–1279
Kabiri R, Nasibi F, Farahbakhsh H (2014) Effect of exogenous salicylic acid on some physiological parameters and alleviation of drought stress in Nigella sativa plant under hydroponic culture. Plant Prot Sci 50:1
Khan MN, Siddiqui MH, Mohammad F, Naeem M, Khan MMA (2010) Calcium chloride and gibberellic acid protect linseed (Linum usitatissimum L.) from NaCl stress by inducing antioxidative defence system and osmoprotectant accumulation. Acta Physiol Plant 32:121
Khan MIR, Nazir F, Asgher M, Per TS, Khan NA (2015) Selenium and sulfur influence ethylene formation and alleviate cadmium-induced oxidative stress by improving proline and glutathione production in wheat. J Plant Physiol 173:9–18
Khan NA, Asgher M, Per TS, Masood A, Fatma M, Khan MIR (2016) Ethylene potentiates sulfur-mediated reversal of cadmium inhibited photosynthetic responses in mustard. Front Plant Sci 7:1628
Khanam D, Mohammad F (2018) Plant growth regulators ameliorate the ill effect of salt stress through improved growth, photosynthesis, antioxidant system, yield and quality attributes in Mentha piperita L. Acta Physiol Plant 40:188
Koc E, Üstun AS, Celik N (2013) Effect of exogenously applied salicylic acid on cadmium chloride-induced oxidative stress and nitrogen metabolism in tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum L.). Turk J Biol 37:361–369
Kovács V, Gondor OK, Szalai G, Darkó É, Majláth I, Janda T, Pál M (2014) Synthesis and role of salicylic acid in wheat varieties with different levels of cadmium tolerance. J Hazard Mater 280:12–19
Krantev A, Yordanova R, Janda T, Szalai G, Popova L (2008) Treatment with salicylic acid decreases the effect of cadmium on photosynthesis in maize plants. J Plant Physiol 165:920–931
Kushwaha A, Rani R, Kumar S, Gautam A (2015) Heavy metal detoxification and tolerance mechanisms in plants: implications for phytoremediation. Environ Rev 24:39–51
Lal RK (2013) Adaptability patterns and stable cultivar selection in menthol mint (Mentha arvensis L.). Indus Crops Prod 50:176–181
Lee BR, Zhang Q, Park SH, Islam MT, Kim TH (2019) Salicylic acid improves drought-stress tolerance by regulating the redox status and proline metabolism in Brassica rapa. Hort Environ Biotechnol 60:31–40
Li S, Yang W, Yang T, Chen Y, Ni W (2015) Effects of cadmium stress on leaf chlorophyll fluorescence and photosynthesis of Elsholtzia argyi—a cadmium accumulating plant. Int J Phytoremediat 17:85–92
Li X, Zhong Q, Li Y, Li G, Ding Y, Wang S, Chen L (2016) Triacontanol reduces transplanting shock in machine-transplanted rice by improving the growth and antioxidant systems. Front Plant Sci 7:872
Li Q, Wang G, Wang Y, Yang D, Guan C, Ji J (2019) Foliar application of salicylic acid alleviate the cadmium toxicity by modulation the reactive oxygen species in potato. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 172:317–325
Lindner RC (1944) Rapid analytical methods for some of the more common inorganic constituents of plant tissues. Plant Physiol 19:76–89
Liu C, Guo J, Cui Y, Lü T, Zhang X, Shi G (2011) Effects of cadmium and salicylic acid on growth, spectral reflectance and photosynthesis of castor bean seedlings. Plant Soil 344:131–141
Liu Y, Xiao T, Baveye PC, Zhu J, Ning Z, Li H (2015) Potential health risk in areas with high naturally-occurring cadmium background in southwestern China. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 112:122–131
Lux A, Martinka M, Vaculík M, White PJ (2010) Root responses to cadmium in the rhizosphere: a review. J Exp Bot 62:21–37
Maclachlan S, Zalik S (1963) Plastic structure, chlorophyll concentration, free amino acid composition of chlorophyll mutant of barley. Can J Bot 41:1053–1062
Maghsoudi K, Emam Y, Niazi A, Pessarakli M, Arvin MJ (2018) P5CS expression level and proline accumulation in the sensitive and tolerant wheat cultivars under control and drought stress conditions in the presence/absence of silicon and salicylic acid. J Plant Interact 13:461–471
Manikandan R, Venkatachalam P (2011) Risk assessment of mercury ion heavy metal exposure on physiological and biochemical changes and DNA damage using RAPD analysis in Mentha arvensis seedlings. Plant Cell Biotechnol Mol Biol 12:41–50
Maresca V, Sorbo S, Keramat B, Basile A (2017) Effects of triacontanol on ascorbate-glutathione cycle in Brassica napus L. exposed to cadmium-induced oxidative stress. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 144:268–274
Masood A, Khan NA (2013) Ethylene and gibberellic acid interplay in regulation of photosynthetic capacity inhibition by cadmium. J Plant Biochem Physiol 1:111
Masood A, Iqbal N, Khan NA (2012) Role of ethylene in alleviation of cadmium-induced photosynthetic capacity inhibition by sulphur in mustard. Plant Cell Environ 35:524–533
Masood A, Khan MIR, Fatma M, Asgher M, Per TS, Khan NA (2016) Involvement of ethylene in gibberellic acid-induced sulfur assimilation, photosynthetic responses, and alleviation of cadmium stress in mustard. Plant Physiol Biochem 104:1–10
Metwally A, Finkemeier I, Georgi M, Dietz KJ (2003) Salicylic acid alleviates the cadmium toxicity in barley seedlings. Plant Physiol 132:272–281
Mourato M, Reis R, Martins LL (2012) Characterization of plant antioxidative system in response to abiotic stresses. In: Montanaro G (ed) A focus on heavy metal toxicity, advances in selected plant physiology aspects. InTech, Rijeka, pp 23–44
Naeem M, Idrees M, Aftab T, Alam MM, Khan MMA, Uddin M, Varshney L (2014) Employing depolymerised sodium alginate, triacontanol and 28-homobrassinolide in enhancing physiological activities, production of essential oil and active components in Mentha arvensis L. Ind Crops Prod 55:272–279
Neill EM, Byrd MC, Billman T, Brandizzi F, Stapleton AE (2019) Plant growth regulators interact with elevated temperature to alter heat stress signaling via the unfolded protein response. Sci Rep BioRxiv. https://doi.org/10.1101/532796
Nouairi I, Jalali K, Essid S, Zribi K, Mhadhbi H (2019) Alleviation of cadmium-induced genotoxicity and cytotoxicity by calcium chloride in faba bean (Vicia faba L. var. minor) roots. Physiol Mol Biol Plants. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-019-00681-5
Obata H, Inoue N, Umebayashi M (1996) Effect of Cd on plasma membrane ATPase from plant roots differing in tolerance to Cd. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 42:361–366
Okabe K, Yang SY, Tsuzuki M, Miyachi S (1984) Carbonic anhydrase: its content in spinach leaves and its taxonomic diversity studied with anti-spinach leaf carbonic anhydrase antibody. Plant Sci Lett 33:145–153
Orcutt DM, Nilsen ET (2000) The physiology of plants under stress, volume 2: soil and biotic factors. Wiley, Hoboken
Per TS, Khan NA, Reddy PS, Masood A, Hasanuzzaman M, Khan MIR, Anjum NA (2017) Approaches in modulating proline metabolism in plants for salt and drought stress tolerance: phytohormones, mineral nutrients and transgenics. Plant Physiol Biochem 115:126–140
Qayyum MF, ur Rehman MZ, Ali S, Rizwan M, Naeem A, Maqsood MA, Ok YS (2017) Residual effects of monoammonium phosphate, gypsum and elemental sulfur on cadmium phytoavailability and translocation from soil to wheat in an effluent irrigated field. Chemosphere 174:515–523
Rao BR, Kaul PN, Mallavarapu GR, Srinivasaiyer R (2000) Comparative composition of whole herb, flowers, leaves and stem oils of cornmint (Mentha arvensis Lf piperascens Malinvaud ex Holmes). J Essen Oil Res 12:357–359
Raza SH, Shafiq F (2013) Exploring the role of salicylic acid to attenuate cadmium accumulation in radish (Raphanus sativus). Int J Agric Biol 15:547–552
Razmi N, Ebadi A, Daneshian J, Jahanbakhsh S (2017) Salicylic acid induced changes on antioxidant capacity, pigments and grain yield of soybean genotypes in water deficit condition. J Plant Interact 12:457–464
Rizwan M, Ali S, Qayyum MF, Ok YS, Zia-ur-Rehman M, Abbas Z, Hannan F (2017) Use of maize (Zea mays L.) for phytomanagement of Cd-contaminated soils: a critical review. Environ Geochem Health 39:259–277
Rizwan M, Ali S, ur Rehman MZ, Adrees M, Arshad M, Qayyum MF, Imran M (2019) Alleviation of cadmium accumulation in maize (Zea mays L.) by foliar spray of zinc oxide nanoparticles and biochar to contaminated soil. Environ Pollut 248:358–367
Rostami S, Azhdarpoor A (2019) The application of plant growth regulators to improve phytoremediation of contaminated soils: a review. Chemosphere 220:818–827
Ruszkowski M, Nocek B, Forlani G, Dauter Z (2015) The structure of Medicago truncatula δ1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate reductase provides new insights into regulation of proline biosynthesis in plants. Front Plant Sci 6:869
Santos LR, Batista BL, Lobato AKS (2018) Brassinosteroids mitigate cadmium toxicity in cowpea plants. Photosynthetica 56(2):591–605
Shakirova FM, Allagulova CR, Maslennikova DR, Klyuchnikova EO, Avalbaev AM, Bezrukova MV (2016) Salicylic acid-induced protection against cadmium toxicity in wheat plants. Environ Exp Bot 122:19–28
Sharma L, Priya M, Kaushal N, Bhandhari K, Chaudhary S, Dhankher PO, Vara Prasad PV, Siddique HMK, Nayyar H (2019) Plant growth regulating molecules as thermoprotectants: functional relevance and prospects for improving heat tolerance in food crops. J Exp Bot. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erz333
Siedlecka A, Samuelsson G, Gardeström P, Kleczkowslci LA, Krupa Z (1998) The “activatory model” of plant response to moderate cadmium stress - relationship between carbonic anhydrase and rubisco. In: Garab G (ed) Photosynthesis: mechanisms and effects. Springer, Dordrecht
Silva AJ, Nascimento CWA, Gouveia-Neto AS (2017) Assessment of cadmium phytotoxicity alleviation by silicon using chlorophyll a fluorescence. Photosynthetica 55:648–654
Singh AP, Dixit G, Mishra S, Dwivedi S, Tiwar M, Mallick S, Tripathi RD (2015) Salicylic acid modulates arsenic toxicity by reducing its root to shoot translocation in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Front Plant Sci 6:340
Smith LK, Vierheller TL, Thorne CA (1988) Assay of glutathione reductase in crude tissue homogenates using 5,5-thiobis (2-nitrobenzoic acid). Anal Biochem 175:408–413
Sullivan CY, Ross WM (1979) Selecting the drought and heat resistance in grain sorghum. In: Mussel H, Staples RC (eds) Physiology in crop plants. Wiley, New York, pp 263–328
Syeed S, Anjum NA, Nazar R, Iqbal N, Masood A, Khan NA (2011) Salicylic acid-mediated changes in photosynthesis, nutrients content and antioxidant metabolism in two mustard (Brassica juncea L.) cultivars differing in salt tolerance. Acta Physiol Plant 33:877–886
Usuda H (1985) The activation state of ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase in maize leaves in dark and light. Plant Cell Physiol 26:1455–1463
Vardhan KH, Kumar PS, Panda RC (2019) A review on heavy metal pollution, toxicity and remedial measures: current trends and future perspectives. J Mol Liq. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2019.111197
Wang X, Zhang C, Qiu B, Ashraf U, Azad R, Wu J, Ali S (2017) Biotransfer of Cd along a soil-plant-mealybug-ladybird food chain: a comparison with host plants. Chemosphere 168:699–706
Wang J, Fang Y, Tian B, Zhang X, Zeng D, Guo L, Xue D (2018) New QTLs identified for leaf correlative traits in rice seedlings under cadmium stress. Plant Growth Regul 85:329–335
Wani SH, Kumar V, Shriram V (2016) Phytohormones and their metabolic engineering for abiotic stress tolerance in crop plants. Crop J 4:162–176
Wani W, Masoodi KZ, Zaid A, Wani SH, Shah F, Meena VS, Mosa KA (2018) Engineering plants for heavy metal stress tolerance. Rend Lin Sci Fis e Nat 29:709–723
Younis U, Malik SA, Rizwan M, Qayyum MF, Ok YS, Shah MHR, Ahmad N (2016) Biochar enhances the cadmium tolerance in spinach (Spinacia oleracea) through modification of Cd uptake and physiological and biochemical attributes. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:21385–21394
Yusuf M, Fariduddin Q, Khan TA, Hayat S (2017) Epibrassinolide reverses the stress generated by combination of excess aluminum and salt in two wheat cultivars through altered proline metabolism and antioxidants. S Afr J Bot 112:391–398
Zaid A, Mohammad F (2018) Methyl jasmonate and nitrogen interact to alleviate cadmium stress in Mentha arvensis by regulating physio-biochemical damages and ROS detoxification. J Plant Growth Regul 37:1331–1348
Zaid A, Mohammad F, Wani SH, Siddique KM (2019a) Salicylic acid enhances nickel stress tolerance by up- regulating antioxidant defense and glyoxalase systems in mustard plants. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 180:575–587
Zaid A, Bhat JA, Wani SH, Masoodi KZ (2019b) Role of nitrogen and sulfur in mitigating cadmium induced metabolism alterations in plants. J Plant Sci Res 35:121–141
Zhang Y, Xu S, Yang S, Chen Y (2015) Salicylic acid alleviates cadmium-induced inhibition of growth and photosynthesis through upregulating antioxidant defense system in two melon cultivars (Cucumis melo L.). Protoplasma 252:911–924
Zouari M, Ahmed CB, Elloumi N, Bellassoued K, Delmail D, Labrousse P, Rouina BB (2016) Impact of proline application on cadmium accumulation, mineral nutrition and enzymatic antioxidant defense system of Olea europaea L. cv Chemlali exposed to cadmium stress. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 128:195–205
Acknowledgements
Abbu Zaid is thankful to Aligarh Muslim University, Aligarh, and UGC-New Delhi India for financial assistance in the form of research fellowship No. BTM-2015-04-GH-7403. We acknowledge Professor Govindjee Govindjee (Professor Emeritus of Biophysics and Plant Biology in the Departments of Plant Biology, Biochemistry and the Center of Biophysics & Computational Biology, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Urbana, USA) for editing our MS and for making suggestions to improve our paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zaid, A., Mohammad, F. & Fariduddin, Q. Plant growth regulators improve growth, photosynthesis, mineral nutrient and antioxidant system under cadmium stress in menthol mint (Mentha arvensis L.). Physiol Mol Biol Plants 26, 25–39 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-019-00715-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-019-00715-y