Abstract
Abnormal physiological responses of plant cultures such as shoot tip necrosis, callus, and hyperhydricity are some of the most difficult challenges in shoot micropropagation, and their causes are not well understood. Five Murashige and Skoog mineral salt factors, which influence the growth of pear shoot cultures, were tested in a five-dimensional surface response experimental design. Pyrus communis ‘Old Home × Farmingdale 87,’ ‘Horner 51,’ and ‘Winter Nelis’; Pyrus dimorphophylla; and Pyrus ussuriensis ‘Hang Pa Li’ shoot cultures were grown on 43 computer-designed treatments to represent the design space of all possible treatment combinations. Analysis of shoot response to these treatments identified the factors that both contributed to physiological disorders and remedied them. Undesirable callus formation was common for pear shoots cultured on standard medium and decreased on formulations with increased NH4NO3, Fe, and mesos (CaCl2, KH2PO4, and MgSO4) for most genotypes. Shoot tip necrosis varied with the genotype, but low mesos or low nitrogen concentrations contributed to the necrosis. Hyperhydricity was more prominent with low mesos or low NH4NO3. Hooked and upwardly curled new leaves were seen in most genotypes and resulted from use of low mesos in P. communis and low nitrogen for ‘Hang Pa Li’ and P. dimorphophylla. Fasciation and hypertrophy were seen infrequently and resulted from wide imbalances in several nutrients simultaneously. In general, standard concentrations of Murashige and Skoog iron and micros combined with high mesos and moderate nitrogen compounds produced normal shoots without physiological disorders.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Physiological abnormalities are a common problem in micropropagation and are reported to result from a variety of causes. Hyperhydricity, shoot tip necrosis, callus formation, hooked and curled new leaves, fasciation, and hypertrophy are all observed during micropropagation in many types of shoot cultures. Although some physiological conditions such as hyperhydricity, shoot tip necrosis, and callus formation are common, others like hooked leaves, fasciation, and hypertrophy are rarely mentioned. A number of studies attempted to determine the causes of these disorders, but no overarching answers were forthcoming. Hazarika (2006) summarized the literature on morphophysiological disorders as they relate to transplantation and acclimatization of shoot cultures, but did not address disorders during multiplication or general micropropagation.
Shoot morphogenesis is highly dependent on cellular interactions, environmental factors, and genetics, which are probably involved in many physiological disorders (Hamant and Traas 2010). Plant growth regulators are often implicated in physiological disorders as well (Bosela and Michler 2008). Nutrient supply affects callus growth, organogenesis, and embryogenesis in callus tissues (Kintzios et al. 2001; Chauhan and Kothari 2004; Kintzios et al. 2004; Niedz and Evens 2007). In general, optimum callus formation requires more K, P, and Ca than organogenic cultures, and callus also tends to take up more nitrogen (Kintzios et al. 2004).
Shoot tip necrosis (STN) is a complex problem in woody plant cultures, caused by the interaction of a variety of factors, such as medium type, Ca, B, and the culture environment (Bairu et al. 2009). Ethylene and deficiencies in Ca and Mg induce STN in rose cultures (Podwyszynska and Goszczynska 1998). The availability of nutrients is also important in STN, and the actual nutrition of the shoot cultures may be related to uptake and not just the amount of nutrients in the medium (Bairu et al. 2009).
Of the in vitro physiological disorders, hyperhydricity is probably the most common and problematic, especially in commercial micropropagation (Ziv 1991). Hyperhydricity of shoot cultures results in shoots that appear translucent and water soaked and possess brittle leaves, short internodes, thickened stems and leaves, and a shiny, dark green, glassy appearance (Paques 1991). This abnormality affects the cuticle, stomata, chloroplast structure, vascular structure, and the size of intercellular spaces (Hazarika 2006). Hyperhydric plants do not multiply well, grow poorly, and do not acclimate well in the greenhouse (Ziv 1991; Hazarika 2006). High losses were noted in the commercial production of several horticultural crops due to hyperhydricity (Paques 1991; Yadav et al. 2003). Growth medium type, agar concentration, container, environment, mineral nutrients, cytokinins, and osmotic state can all influence hyperhydricity (Bottcher et al. 1988; Paques 1991; Debergh et al. 1992; Bosela and Michler 2008). Agar concentration is highly correlated with hyperhydricity and may affect hydraulic conductance, thereby affecting nutrient uptake. In a study of hydraulic conductivity and diffusion in plant tissue culture gelling agents, hydraulic conductivity decreased as the gel concentration increased, but diffusion of all but macromolecules was constant and similar to water (Ishida et al. 2000). Nutrients provided by the agar itself may also affect plant growth. High relative humidity and nutrient-rich media often combine to produce hyperhydricity in shoot cultures (Ziv 1991). Fasciation, a flattening and abnormal branching of the stem or meristem, is rarely mentioned in the tissue culture literature, but it is also associated with hyperhydricity (Ziv 1991; Bosela and Michler 2008). Fasciation may appear in plants due to genetic, pathological, or environmental causes. Altered phyllotaxy and stem broadening are common in this disorder as a result of the breakdown of the meristem structure (Leyser et al. 1992).
Hypertrophy in vitro is mostly associated with hyperhydricity. The swollen stems result from an increase in the size of stem mesophyll cells (Ziv 1991). Hyperplasia is swelling due to an increase in cell division rather than an increase in cell size, and may be due to infection or physical damage that leads to abnormal development of tissues or organs. There is little information on the effects of medium nutrients on any of these disorders. Hooked and upwardly curled young leaves are a symptom of Ca deficiency, but this symptom is rarely reported in the tissue culture literature (Epstein and Bloom 2005).
During our study of the effects of mineral nutrition on the growth and multiplication of pears (Reed et al. 2013), we documented a range of responses associated with certain mineral nutrient combinations and concentrations. In this study, we evaluated the effects of five Murashige and Skoog (1962) (MS) mineral stock solutions on the development of physiological disorders of shoot cultures of three species of pear.
Materials and Methods
Plant materials.
Genotypes tested were Pyrus dimorphophylla, Pyrus ussuriensis ‘Hang Pa Li,’ and Pyrus communis ‘Horner 51,’ ‘Old Home × Farmingdale 87’ (OH×F87), and ‘Winter Nelis.’ Shoot cultures were maintained in Magenta GA7 boxes (Magenta Corp., Chicago, IL) with 40 ml medium per box of NCGR-PYR medium, which contained MS (Murashige and Skoog 1962) salts with 0.5× KNO3, 4.4 μM N6-benzyladenine, and (per liter): 2.5 mg thiamine, 3 g agar (Phytotech agar A111, PhytoTechnology Labs, Shawnee Mission, KS), and 1.75 g Gelrite at pH 5.7 (Reed 1995). Shoots were subcultured every 3 wk (Reed et al. 1998). All cultures were grown at 25°C under a 16-h photoperiod under 80 μE/m2/s irradiance provided by a combination of cool- and warm-white fluorescent bulbs.
Experimental design.
The strategy was the same as noted in Reed et al. (2013); briefly, (1) a five-dimensional experimental design space defined by a specific MS salt or group of MS salts was created; (2) pear shoots were evaluated on treatment combinations represented as points within or on the surface of the five-dimensional design space; and (3) a prediction equation was generated for each response. Five mineral nutrient factors were created, based on MS salts, with each factor varied over a range of concentrations (×MS): 0.5× to 1.5× for NH4NO3 and KNO3, mesos (CaCl2·2H20, KH2PO4, and MgSO4), and 0.5× to 4× for micronutrients (B, Cu, Co, I, Mn, Mo, and Zn) and Fe-EDTA to form 46 treatment design points (Table 1). These 46 design points were separated into three groups and performed separately, each with a control (points 44–46) and internal replication. Boxes were assigned a random number for arrangement on the growth room shelf. Shoots were transferred to a medium of the same composition at 3-wk intervals and harvested after 9 wk.
Data.
The six responses measured for this study were rated as 1 = none, 2 = low, and 3 = high for the following responses: callus, shoot tip necrosis, hyperhydricity, hooked leaves, fasciation, and hypertrophy. Three plants from predetermined locations in each box were evaluated (two corners and one center on a diagonal from the label to avoid subjective selection), and the remaining plants were photographed.
Statistical analysis.
The responses for each design point were the means of three shoots from two boxes (n = 6); some points were replicated to include two additional boxes (n = 12). For each response, the highest-order polynomial model, where additional model terms were significant at the 0.05 level, was analyzed by analysis of variance (Niedz and Evens 2006, 2007; Evens and Niedz 2008). The software application Design-Expert® 8 (2010) was used for experimental design construction, model evaluation, and analysis.
Results
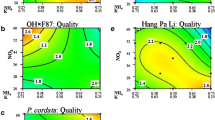
Physiological disorders were relatively common in shoots grown on standard MS medium, but they were also induced by a range of mineral nutrients. Summary data and p values indicating the driving factors or main interactions (mineral nutrients) for each response are presented for each genotype (Table 2). The models were significant for all genotypes for callus, four genotypes for STN, two genotypes for hyperhydricity, three genotypes for hooked leaves, one genotype for fasciation, and no genotypes for hypertrophy. All genotypes exhibited physiological disorders with some of the treatments (Fig. 1). Response models for each genotype, indicating the effect of the driving factors for each response, are shown in the figures.
Physiological disorders observed in pear shoots cultured on suboptimal media: (A) ‘Hang Pa Li’ (P. ussuriensis) shoot tip necrosis and leaf necrosis; (B) ‘Hang Pa Li’ hooked leaves and epinasty; (C) ‘Horner 51’ hooked leaves; (D) ‘Horner 51’ hypertrophy; (E) P. dimorphophylla hypertrophy and hooked leaves; (F) ‘Hang Pa Li’ hyperhydricity and hooked leaves; (G) ‘Hang Pa Li’ shoot tip necrosis, leaf necrosis, hooked leaves, and stem fasciation; (H) ‘Horner 51’ apex fasciation and hypertrophy.
Callus.
Callus production (Fig. 2) varied with genotype. ‘OH×F87,’ P. dimorphophylla, and ‘Winter Nelis’ produced the most callus tissue. In most cases, callus production was influenced by mesos, Fe, and KNO3 or NH4NO3 (Table 2). Increased callus formation was often observed with low concentrations of NH4NO3 for all of the pears tested, while little or no callus was present when NH4NO3 levels were high. Low amounts of the minors, mesos, iron, and KNO3 also contributed to callus formation while specific factors varied with the genotype (Fig. 2).
Shoot tip necrosis.
The three P. communis cultivars had the most STN (Fig. 3) on media with low mesos and the least STN on media with higher mesos. The effects of low iron and nitrogen were also significant (Table 2). The other species reacted quite differently. For P. dimorphophylla, high concentrations of NH4NO3, mesos, and Fe with low KNO3 and micros led to STN while STN was minimized when media with low NH4NO3 and KNO3, and high mesos were used (data not shown). P. ussuriensis ‘Hang Pa Li’ had significantly increased STN when tissues were cultured on media with low NH4NO3, KNO3, and mesos (Fig. 1A, G ) while STN decreased when media with higher KNO3 and lower micros concentrations were used.
Hyperhydricity.
Two pear genotypes exhibited significant hyperhydricity (Fig. 4), but the symptoms were not observed if media with high mesos and other factors at the 1× MS concentration were used (data not shown). High NH4NO3 and low amounts of the remaining factors induced hyperhydric plants of ‘Horner 51.’ Hyperhydricity in P. dimorphophylla was greatest if mesos were high and all other factors were low, but hyperhydricity was not evident with high nitrogen and mesos. For ‘Hang Pa Li,’ the model was not significant, but there was a significant interaction between NH4NO3 and mesos, and obvious symptoms were observed (Fig. 1F ). There was also significant hyperhydricity when micros were high and all other factors were low.
Hooked leaves.
In ‘Horner 51,’ hooked leaves (Fig. 4) were increased by low mesos and an interaction among high KNO3 with low micros and Fe (Fig. 1C ); no hooked leaves were seen when media contained normal MS Fe and high mesos. ‘Winter Nelis’ was only affected by low mesos, which produced the most hooked leaves, and this was alleviated at high mesos concentrations. P. dimorphophylla had a modest amount of hooked leaves, resulting from high micros and Fe combined with low amounts of the other factors (Fig. 1E ). Low micros with high mesos and moderate Fe gave the fewest hooked leaves (data not shown). The model was not significant for ‘Hang Pa Li,’ but the interaction between NH4NO3 and KNO3 was significant for hooked leaves. Low nitrogen produced the most hooked leaves, and it was common on standard MS medium (Fig. 1B ). A reduction in hooked leaves was seen with normal levels of MS nitrogen, Fe, and micros combined with high mesos (data not shown).
Fasciation.
The only significant fasciation noted was for P. dimorphophylla, with NH4NO3, mesos, and micros as significant factors (Table 2). Fasciation was very rare, but it did occur when micros and NH4NO3 were at moderate levels (design point 16). No fasciation was noted on standard MS, but it was seen occasionally in some treatments with ‘Hang Pa Li’ (Fig. 1G ) and ‘Horner 51’ (Fig. 1H ).
Hypertrophy.
‘Horner 51’ rarely exhibited hypertrophy (Fig. 1D and H ); however, it was induced by the combination of low mesos and Fe with moderate NH4NO3. Lower or higher NH4NO3 reduced hypertrophy. Hypertrophy was seen in P. dimorphophylla at one design point (design point 8; Table 1; Fig. 1E ) when micros were high and mesos were low.
Genotype effects.
Among the five genotypes, the frequency and type of physiological disorders varied (Fig. 1). The three P. communis cultivars that displayed disorders were often due to low mesos concentrations in the medium (Table 2). ‘OH×F87’ shoots displayed fewer disorders than the other two genotypes; only callus and STN were observed. ‘Horner 51’ exhibited callus, hyperhydricity, hooked leaves, and hypertrophy, while ‘Winter Nelis’ showed callus, STN, and hooked leaves. All the disorders were seen in P. dimorphophylla on various nutritional treatments, mostly relating to NH4NO3 (although hypertrophy was very rare and the model was not significant). ‘Hang Pa Li’ exhibited callus, STN, and hooked leaves. Nitrogen and Fe were significant factors for many of the P. dimorphophylla and P. ussuriensis disorders.
Discussion
Physiological disorders are often attributed to a range of causes, but the factors that produce disorders of one plant type often do not affect other cultivars or species. The objectives of this study were to determine the effects of mineral nutrition on the growth of pear shoot cultures in vitro (Reed et al. 2013) and to study the effects of minerals on physiological disorders of the micropropagated shoots. All models except those for hypertrophy indicated that mineral factors had significant effects on physiological responses (Table 2). Callus, STN, hyperhydricity, and hooked leaves were the most common physiological disorders noted in pears (Fig. 1).
For the pear shoots in this study, low NH4NO3 increased callus growth in all cultivars (Fig. 2). In most cases, high NH4NO3 and increased Fe with standard amounts of other nutrients led to reduced callus formation (data not shown). Callus production was also reduced or eliminated when the mesos nutrients were increased in a previous study (Reed et al. 2013). Callus growth on micropropagated shoots is one of the least understood growth responses. Some studies indicate a correlation between mineral nutrients and callus production when callus was the desired result. Individual micronutrients often stimulate callus production. Increased callus growth was observed with rose and pepper leaves when Cu concentrations were 10× greater than that used in standard MS salts (Kintzios et al. 2001). Increasing Co while decreasing Mn encouraged callus growth in pepper leaves. Callus was significantly stimulated in barley leaves by Mo at 2× the MS level and 5× KH2PO4 (Chauhan and Kothari 2004). Increased concentrations of NH4NO3 and Fe encouraged lush callus growth in citrus (Niedz and Evens 2007). There are obvious variations in species and tissue-specific responses with different patterns of callus induction among genera and between leaf and stem tissues.
STN is a major problem in pear tissue culture, and many studies attempted to reduce it by testing known media or adding Ca to the existing medium. For the P. communis cultivars, significant STN was observed when the mesos components were low, but other factors were also involved (Fig. 3). For P. ussuriensis ‘Hang Pa Li,’ STN was increased when Fe and micros were high and KNO3 was low (Fig. 3). For P. dimorphophylla, STN was complex with important interactions between NH4NO3 and KNO3, and between mesos and micros (Table 2). Collectively, these responses indicate that the problem of STN is genotype dependent and involves a range of factors in addition to Ca. Shoot tip necrosis was mostly eliminated by increasing mesos for P. communis cultivars (Wada et al. 2013). Grigoriadou et al. (2000) reduced STN for P. communis ‘Highland’ and ‘Williams’ by changing the medium salts from MS to woody plant medium (Lloyd and McCown 1980). Use of ½-strength MS salts with 1× MS Ca (3 mM) resulted in increased STN; the amount of STN was not influenced by pH or cytokinin concentration. Ca influences the uptake of other mineral nutrients and was implicated as a factor in STN of pear (Singha et al. 1990). STN was alleviated by increasing the Ca significantly to 6× or 10× MS (18 or 30 mM). STN in wild and cultivated pears was heavily influenced by the concentration of plant growth regulators in the medium, but it could be controlled in wild pear by using media that contained 3 mM Ca and in ‘Patharnakh’ with B (500 μM and 1,000 μM B). Some of the cultivars showed increased STN when media containing increasing Ca were used (Thakur and Kanwara 2011). STN was reduced in pistachio shoot cultures placed on filter paper bridges in MS medium with either high Ca concentrations (15 mM) or 100 to 1,000 μM B (Abousalim and Mantell 1994). In Musa, only increased Ca helped resolve STN; shortening the culture period or altering plant growth regulators, media salts, sucrose, or silver nitrate did not reduce STN (Martin et al. 2007).
For the pears in this study, hyperhydricity was often influenced by the nitrogen components and mesos, but there was a large genotype component. ‘Horner 51’ and ‘Hang Pa Li’ required high mesos to reduce hyperhydricity, while higher nitrogen was effective for P. dimorphophylla (Fig. 4). Hyperhydricity is a long-standing problem in commercial micropropagation and is often linked to microenvironment, water availability, micronutrient supply, and hormone balance (Hazarika 2006). We found an influence of micros interacting with other nutrients, but micros were only significant at very high or very low concentrations (Fig. 4). Use of mineral-rich media leads to more hyperhydricity than when minimal media are used (Paques 1991); reducing NH4, NO3, and CaCl2 may decrease hyperhydricity (Debergh et al. 1992; Ivanova and Van Staden 2009). In chestnut, media with reduced nitrogen levels and with a low NH4-to-NO3 ratio (0.2) reduced hyperhydricity (Piagnani and Eccher 1988). We found the opposite response for all three pear species studied. As the mineral concentrations decreased in the medium, more hyperhydricity was seen, and the nitrogen ratios that produced the problem were not consistent across the genotypes tested. In quince, increasing Ca decreased hyperhydricity (Singha et al. 1990), but carnation required increased Fe (0.2 mM) and Mg (3 mM) levels (Yadav et al. 2003). This finding is consistent with our results for increased mesos as a factor for decreased hyperhydricity in two of the three species.
A range of factors influenced hooked leaves in pears (Table 2; Fig. 4). Hooked leaves were seen in four of the five genotypes in this study (Fig. 1). Ca deficiency can cause hooked young leaves (Epstein and Bloom 2005). Higher mesos concentrations reduced the amount of hooked leaves in the P. communis cultivars, which would be expected if it were related to a Ca deficiency. However, the other two species’ responses required altered NH4NO3-to-KNO3 ratios (Fig. 4). Little information is published on hooked leaves of in vitro cultures with regard to mineral nutrition; however, from our experience, it is common.
In pear, the less common disorders of fasciation and hypertrophy were linked to abnormal nutrient levels and were only seen when several components were at very low or very high concentrations. It is likely that very unbalanced combinations of mineral nutrients contribute to these responses. It is difficult to generalize, as these responses were uncommon. Fasciation and hypertrophy in vitro are mostly recognized as a response to inappropriate levels of plant growth regulators. Walnut cultures grown on media containing thidiazuron produced fasciated and hypertrophic shoots (Bosela and Michler 2008). In Arabidopsis, several apical meristem genes were associated with fascinated mutants (Leyser et al. 1992). Environmental factors or plant growth regulators are known to cause fasciation and are linked to the CLAVATA genes (Iliev and Kitin 2011). Fasciation may also be caused by altered auxin transport, high cytokinin treatment, or a zinc deficiency. Anatomically, fasciation seems to result from accelerated growth in some sectors of shoot tissue after normal growth has stopped (Iliev and Kitin 2011).
This study demonstrates the utility of surface response studies for mineral nutrition research. Mineral nutrients have a large influence on many of the physiological responses of micropropagated shoots, and this is clearly the case for pear. It is important to recognize that micropropagation protocols resulting in hyperhydric plants or those with STN or other disorders may be due to an imbalance of mineral nutrients. Our earlier study (Reed et al. 2013) found that increasing the mesos components of MS medium to 1.5× or 2× reduced leaf spot and necrosis symptoms and greatly improved the overall quality of the five pear genotypes tested. In addition, a study of the mesos components indicated that increased levels improved shoot quality and eliminated many physiological disorders (Wada et al. 2013). In the current study, increasing the mesos components of MS medium reduced STN and hyperhydricity for P. communis cultivars; increasing the nitrogen compounds improved STN for the other two species. Callus formation was more complex but was often reduced with higher NH4NO3 and sometimes increased mesos concentrations. Hooked leaves, a symptom not often mentioned in the literature, was commonly observed with low mesos treatments for P. communis cultivars and low nitrogen for the other species. The current analysis demonstrated that many of the physiological disorders of pear are caused by the use of growth media that are too low in nitrogen or mesos components for proper growth. We were able to eliminate these disorders by increasing the mesos components and, in some cases, by altering the NH4NO3-to-KNO3 ratios compared to MS medium. These systematic studies provide clear data to establish the effects of mineral nutrients on these physiological abnormalities and aid in determining growth media that alleviate mineral imbalances for a range of pear genotypes.
References
Abousalim A.; Mantell S. H. A practical method for alleviating shoot-tip necrosis symptoms in in vitro shoot cultures of Pistacia vera cv. Mateur. J Hortic Sci 69: 357–365; 1994.
Bairu M. W.; Stirk W. A.; Van Staden J. Factors contributing to in vitro shoot-tip necrosis and their physiological interactions. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 98: 239–248; 2009.
Bosela M. J.; Michler C. H. Media effects on black walnut (Juglans nigra L.) shoot culture growth in vitro: evaluation of multiple nutrient formulations and cytokinin types. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol - Plant 44: 316–329; 2008.
Bottcher I.; Zohlauer K.; Goring H. Induction and reversion of vitrification of plants cultured in vitro. Physiol Plant 72: 560–564; 1988.
Chauhan M.; Kothari S. L. Optimization of nutrient levels in the medium increases the efficiency of callus induction and plant regeneration in recalcitrant Indian barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) in vitro. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol - Plant 40: 520–527; 2004.
Debergh P.; Aitken-Christie J.; Cohen D.; Grout B.; Von Arnold S.; Zimmerman R.; Ziv M. Reconsideration of the term ‘vitrification’ as used in micropropagation. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 30: 135–140; 1992.
Design-Expert. Stat-Ease, Inc., Minneapolis, MN; 2010
Epstein E.; Bloom A. (eds). Mineral nutrition of plants: principles and perspectives. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, pp 1–380; 2005.
Evens T. J.; Niedz R. P. ARS-Media: ion solution calculator. U.S. Horticultural Research Laboratory, Ft. Pierce; 2008.
Grigoriadou K.; Leventakis N.; Vasilakakis M. Effects of various culture conditions on proliferation and shoot tip necrosis in the pear cultivars ‘Williams’ and ‘Highland’ grown in vitro. Acta Hortic 520: 03–108; 2000.
Hamant O.; Traas J. The mechanics behind plant development. New Phytol 185: 369–385; 2010.
Hazarika B. N. Morpho-physiological disorders in in vitro culture. Scientia Hortic 108: 105–120; 2006.
Iliev I.; Kitin P. Origin, morphology, and anatomy of fasciation in plants cultured in vitro and in vivo. Plant Growth Regul 63: 115–129; 2011.
Ishida T.; Anno T.; Matsukawa S.; Nagano T. Hydraulic conductivity and diffusion coefficient in gels for plant tissue culture. Environ Cont Biol 38: 165–171; 2000.
Ivanova M.; Van Staden J. Nitrogen source, concentration, and NH4 +:NO3 - ratio influence shoot regeneration and hyperhydricity in tissue cultured Aloe polyphylla. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 99: 167–174; 2009.
Kintzios S.; Drossopoulos J. B.; Lymperopoulos C. Effect of vitamins and inorganic micronutrients on callus growth and somatic embryogenesis from leaves of chilli pepper. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 67: 55–62; 2001.
Kintzios S.; Stavropoulou E.; Skamneli S. Accumulation of selected macronutrients and carbohydrates in melon tissue cultures: association with pathways of in vitro dedifferentiation and differentiation (organogenesis, somatic embryogenesis). Plant Sci 167: 655–664; 2004.
Leyser H.; Ottoline M.; Furner I. J. Characterisation of three shoot apical meristem mutants of Arabidopsis thaliana. Development 116: 397–403; 1992.
Lloyd G.; McCown B. Commercially feasible micropropagation of mountain laurel, Kalmia latifolia, by use of shoot-tip culture. Comb Proceed Int Plant Propag Soc 30: 421–427; 1980.
Martin K. P.; Zhang C.-L.; Slater A.; Madassery J. Control of shoot necrosis and plant death during micropropagation of banana and plantains (Musa spp.). Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 88: 51–59; 2007.
Murashige T.; Skoog F. A revised medium for rapid growth and bio assays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15: 473–497; 1962.
Niedz R. P.; Evens T. J. A solution to the problem of ion confounding in experimental biology. Nat Methods 3: 417; 2006.
Niedz R. P.; Evens T. J. Regulating plant tissue growth by mineral nutrition. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol - Plant 43: 370–381; 2007.
Paques M. Vitrification and micropropagation: causes, remedies and prospects. Acta Hortic 289: 283–290; 1991.
Piagnani C.; Eccher T. Factors affecting the proliferation and rooting of chestnut in vitro. Acta Hortic 227: 384–386; 1988.
Podwyszynska M.; Goszczynska D. M. Effect of inhibitors of ethylene biosynthesis and action, as well as calcium and magnesium on rose shoot rooting, shoot-tip necrosis and leaf senescence in vitro. Acta Physiol Plant 20: 91–89; 1998.
Reed B. M. Screening Pyrus germplasm for in vitro rooting response. HortScience 30: 1292–1294; 1995.
Reed B. M.; DeNoma J.; Luo J.; Chang Y.; Towill L. Cryopreservation and long-term storage of pear germplasm. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol - Plant 34: 256–260; 1998.
Reed B. M.; Wada S.; DeNoma J.; Niedz R. P. Improving in vitro mineral nutrition for diverse pear germplasm. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol - Plant 49: 343–355; 2013.
Singha S.; Townsend E.; Oberly G. Relationship between calcium and agar on vitrification and shoot-tip necrosis of quince (Cydonia oblonga Mill.) shoots in vitro. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 23: 135–142; 1990.
Thakur A.; Kanwara J. S. Effect of phase of medium, growth regulators and nutrient supplementations on in vitro shoot-tip necrosis in pear. New Zealand J Crop Hort Sci 39: 131–140; 2011.
Wada S.; Niedz R. P.; DeNoma J.; Reed B. M. Mesos components (CaCl2, MgSO4, KH2PO4) are critical for improving pear micropropagation. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol - Plant 49: 356–365; 2013.
Yadav M. K.; Gaur A. K.; Garg G. K. Development of suitable protocol to overcome hyperhydricity in carnation during micropropagation. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 72: 153–156; 2003.
Ziv M. Quality of micropropagated plants—vitrification. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol - Plant 27: 64–69; 1991.
Acknowledgments
We thank the NCGR lab personnel for assistance with the collection of data for this study. This project was funded by a grant from the Oregon Association of Nurseries and the Oregon Department of Agriculture, and by the United States Department of Agriculture-Agricultural Research Service, CRIS project 5358-21000-0-38-00D.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Editor: John Finer
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reed, B.M., Wada, S., DeNoma, J. et al. Mineral nutrition influences physiological responses of pear in vitro . In Vitro Cell.Dev.Biol.-Plant 49, 699–709 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11627-013-9556-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11627-013-9556-2