Abstract
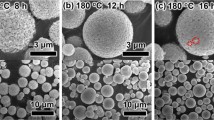
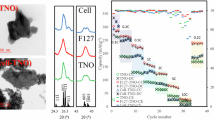
This study demonstrates a facile and efficient hydrothermal method to prepare spindle titanate (Li4Ti5O12 denoted as LTO) and/or carbon-LTO nanocomposites (C-LTO), in which the LTO or C-LTO microspheres have diameters of a few micrometers, composed of numerous nanosheets with thickness of ~30 nm and edge length of hundreds of nanometers. The morphology and size control of these nanoparticles could be achieved by varying experimental parameters including concentration of titanium butoxide, lithium hydroxide, and cetyltrimethylammonium bromide, as well as reaction temperature and time. These micro-nanostructures were characterized by several advanced techniques, such as transmission electron microscopy, scanning electron microscopy, X-ray diffraction, energy dispersive spectroscopic analysis, surface area, and electrochemical measurements. The LTO and C-LTO microstructures were examined in the charge–discharge capacity at a rate of 50 C, as well as the stability after 100 cycles at a rate of 10 C. The excellent capability may be attributed to good conductivity, large surface area, and stable assembly structure of such micro-nanostructures, which could be explored as a promising anode material for lithium-ion batteries.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liu C, Li F, Ma LP et al (2010) Advanced materials for energy storage. Adv Mater 22:E28–E62
Scrosati B (1995) Challenge of portable power. Nature 373:557–558
Bruce PG, Scrosati B, Tarascon JM (2008) Nanomaterials for rechargeable lithium batteries. Angew Chem Int Ed 47:2930–2946
Bruno S (2000) Recent advances in lithium ion battery materials. Electrochim Acta 45:2461–2466
Han Y, Wu X, Ma Y et al (2011) Porous SnO2 nanowire bundles for photocatalyst and li ion battery applications. CrystEngComm 13:3506–3510
Liu B, Wang X, Liu B et al (2013) Advanced rechargeable lithium-ion batteries based on bendable ZnCo2O4-urchins-on-carbon-fibers electrodes. Nano Res 6:525–534
Zaghib K, Simoneau M, Armand M et al (1999) Electrochemical study of Li4Ti5O12 as negative electrode for li-ion polymer rechargeable batteries. J Power Sources 81–82:300–305
Thackeray MM (1999) Spinel electrodes for lithium batteries. J Am Ceram Soc 82:3347–3354
Panero S, Reale P, Ronci F et al (2000) Structural and electrochemical study on Li(Li1/3Ti5/3)O4 anode material for lithium ion batteries. Ionics 6:461–465
Chen J, Yang L, Fang S et al (2012) Synthesis of hierarchical mesoporous nest-like Li4Ti5O12 for high-rate lithium ion batteries. J Power Sources 200:59–66
Kim DH, Ahn YS, Kim J (2005) Polyol-mediated synthesis of Li4Ti5O12 nanoparticle and its electrochemical properties. Electrochem Commun 7:1340–1344
Laumann A, Bremholm M, Hald P et al (2012) Rapid green continuous flow supercritical synthesis of high performance Li4Ti5O12 nanocrystals for li ion battery applications. J Electrochem Soc 159:A166–A171
Lee SS, Byun KT, Park JP et al (2007) Preparation of Li4Ti5O12 nanoparticles by a simple sonochemical method. Dalton Trans 37:4182–4184
Yuan T, Yu X, Cai R et al (2010) Synthesis of pristine and carbon-coated Li4Ti5O12 and their low-temperature electrochemical performance. J Power Sources 195:4997–5004
Wang XL, Han WQ, Chen H et al (2011) Amorphous hierarchical porous GeO x as high-capacity anodes for li ion batteries with very long cycling life. J Am Chem Soc 133:20692–20695
Zhao H, Li Y, Zhu Z et al (2008) Structural and electrochemical characteristics of Li4Ti5O12 as anode material for lithium-ion batteries. Electrochim Acta 53:7079–7083
Yi TF, Xie Y, Jiang LJ et al (2012) Advanced electrochemical properties of mo-doped Li4Ti5O12 anode material for power lithium ion battery. RSC Adv 2:3541–3547
Qi Y, Huang Y, Jia D et al (2009) Preparation and characterization of novel spinel Li4Ti5O12−x Br x anode material. Electrochim Acta 54:4772–4776
Huang S, Wen Z, Lin B et al (2008) The high-rate performance of the newly designed Li4Ti5O12/Cu composite anode for lithium ion batteries. J Alloys Compd 457:400–403
Wang YQ, Gu L, Guo YG et al (2012) Rutile-Tio2 nanocoating for a high-rate Li4Ti5O12 anode of a lithium-ion battery. J Am Chem Soc 134:7874–7879
Gao J, Ying J, Jiang C et al (2007) High-density spherical Li4Ti5O12/C anode material with good rate capability for lithium ion batteries. J Power Sources 166:255–259
Jung H-G, Kim J, Scrosati B et al (2011) Micron-sized, carbon-coated Li4Ti5O12 as high power anode material for advanced lithium batteries. J Power Sources 196:7763–7766
Xiang H, Tian B, Lian P et al (2011) Sol–gel synthesis and electrochemical performance of Li4Ti5O12/graphene composite anode for lithium-ion batteries. J Alloys Compd 509:7205–7209
Kang E, Jung YS, Kim GH et al (2011) Highly improved rate capability for a lithium-ion battery nano-Li4Ti5O12 negative electrode via carbon-coated mesoporous uniform pores with a simple self-assembly method. Advd Func Mater 21:4349–4357
Jung HG, Myung ST, Yoon CS et al (2011) Microscale spherical carbon-coated Li4Ti5O12 as ultra high power anode material for lithium batteries. Energy Environ Sci 4:1345–1351
Jiang X, Herricks T, Xia Y (2003) Monodispersed spherical colloids of titania: synthesis, characterization, and crystallization. Adv Mater 15:1205–1209
Wang P, Xie T, Peng L et al (2008) Water-assisted synthesis of anatase TiO2 nanocrystals: mechanism and sensing properties to oxygen at room temperature. J Phys Chem C 112:6648–6652
Cao AM, Hu JS, Liang HP et al (2005) Self-assembled vanadium pentoxide (V2O5) hollow microspheres from nanorods and their application in lithium-ion batteries. Angew Chem Int Ed 44:4391–4395
Wang X, Wu XL, Guo YG et al (2010) Synthesis and lithium storage properties of Co3O4 nanosheet-assembled multishelled hollow spheres. Adv Funct Mater 20:1680–1686
Yang S, Feng X, Müllen K (2011) Sandwich-like, graphene-based titania nanosheets with high surface area for fast lithium storage. Adv Mater 23:3575–3579
Aldon L, Kubiak P, Womes M et al (2004) Chemical and electrochemical li-insertion into the Li4Ti5O12 spinel. Chem Mater 16:5721–5725
Lee D, Shim HW, An J et al (2010) Synthesis of heterogeneous Li4Ti5O12 nanostructured anodes with long-term cycle stability. Nanoscale Res Lett 5:1585–1589
Ju BK, Dong JK, Kyung YC et al (2010) Research on carbon-coated Li4Ti5O12 material for lithium ion batteries. Phys Scripta, T139: 014026
Eklund PC, Holden JM, Jishi RA (1995) Vibrational modes of carbon nanotubes; spectroscopy and theory. Carbon 33:959–972
Chockla AM, Harris JT, Akhavan VA et al (2011) Silicon nanowire fabric as a lithium ion battery electrode material. J Am Chem Soc 133:20914–20921
Jung HG, Myung ST, Yoon CS et al (2011) Microscale spherical carbon-coated Li4Ti5O12 as ultra high power anode material for lithium batteries. Energy Environ Sci 4:1345–1351
Qi Y, Huang Y, Jia D et al (2009) Preparation and characterization of novel spinel Li4Ti5O12 anode materials. Electrochim Acta 54:4772–4776
Chen JS, Lou XW (2009) Anatase TiO2 nanosheet: an ideal host structure for fast and efficient lithium insertion/extraction. Electrochem Commun 11:2332–2335
He BL, Dong B, Li HL (2007) Preparation and electrochemical properties of ag-modified TiO2 nanotube anode material for lithium–ion battery. Electrochem Commun 9:425–430
Tang Y, Yang L, Fang S et al (2009) Li4Ti5O12 hollow microspheres assembled by nanosheets as an anode material for high-rate lithium ion batteries. Electrochim Acta 54:6244–6249
Yu SH, Pucci A, Herntrich T et al (2011) Surfactant-free nonaqueous synthesis of lithium titanium oxide (LTO) nanostructures for lithium ion battery applications. J Mater Chem 21:806–810
Shen L, Yuan C, Luo H et al (2010) Facile synthesis of hierarchically porous Li4Ti5O12 microspheres for high rate lithium ion batteries. J Mater Chem 20:6998–7004
Tian B, Xiang H, Zhang L et al (2010) Niobium doped lithium titanate as a high rate anode material for li-ion batteries. Electrochim Acta 55:5453–5458
Wang Y, Liu H, Wang K et al (2009) Synthesis and electrochemical performance of nano-sized Li4Ti5O12 with double surface modification of Ti(iii) and carbon. J Mater Chem 19:6789–6795
Chou SL, Wang JZ, Liu HK et al (2011) Rapid synthesis of Li4Ti5O12 microspheres as anode materials and its binder effect for lithium-ion battery. J Phys Chem C 115:16220–16227
Hu YS, Kienle L, Guo YG et al (2006) High lithium electroactivity of nanometer-sized rutile TiO2. Adv Mater 18:1421–1426
Matsumura Y, Wang S, Mondori J (1995) Mechanism leading to irreversible capacity loss in Li ion rechargeable batteries. J Electrochem Soc 142:2914–2918
Ding Z, Zhao L, Suo L et al (2011) Towards understanding the effects of carbon and nitrogen-doped carbon coating on the electrochemical performance of Li4Ti5O12 in lithium ion batteries: a combined experimental and theoretical study. Phys Chem Chem Phys 13:15127–15133
Wu ZS, Ren W, Wen L et al (2010) Graphene anchored with Co3O4 nanoparticles as anode of lithium ion batteries with enhanced reversible capacity and cyclic performance. ACS Nano 4:3187–3194
Wang D, Choi D, Li J et al (2009) Self-assembled TiO2–graphene hybrid nanostructures for enhanced li-ion insertion. ACS Nano 3:907–914
Hupalo M, Binz S, Tringides MC (2011) Strong metal adatom–substrate interaction of Gd and Fe with graphene. J Physs: Cond Matter 23:045005
Zhang LW, Fu HB, Zhu YF (2008) Efficient TiO2 photocatalysts from surface hybridization of TiO2 particles with graphite-like carbon. Adv Funct Mater 18:2180–2189
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Australia Research Council (ARC) through ARC Discovery Projects. The authors acknowledge access to the UNSW node of the Australian Microscopy & Microanalysis Research Facility (AMMRF).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
SPECIAL ISSUE: Advanced Materials for Clean Energy
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
About this article
Cite this article
Wen, R., Yue, J., Ma, Z. et al. Synthesis of Li4Ti5O12 nanostructural anode materials with high charge–discharge capability. Chin. Sci. Bull. 59, 2162–2174 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-014-0262-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-014-0262-1