Abstract
Signaling by the melanocortin-4 receptor (MC4R) is important for mediation the effect of leptin on food intake and energy homeostasis, and is associated with obesity, energy homeostasis and control of feeding behavior. Presently, the bovine MC4R gene was characterized to detect genetic variation at this locus and to relate it to economic traits in Korean cattle (Hanwoo). Five single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) were identified in the coding region (G709A, C927T, C1069G, C1343A, and C1786T). G709A changed amino acid 166 of the MC4R protein from valine to methionine and C1069G changed amino acid 286 of the MC4R protein from leucine to valine. A SNP at C927T significantly influenced the Marbling score, SNP markers C1069G and C1343A significantly affected the Backfat thickness, and the SNP marker C1786T significantly influenced backfat and Marbling score. The MC4R gene may thus be a candidate gene for carcass traits with MC4R SNPs being potentially valuable as genetic markers for economic traits in Hanwoo.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
The Hanwoo (Bos taurus coreanae), is a cattle breed that is native to the Korean peninsula and the Japanese islands, which is considered to belong to the European cattle (Bos Taurus) breeds [1–3]. In Korea, consumer demands are driving efforts to increase meat production and produce higher quality meat [4]. Breeding and selection of founders with high potential for meat production/quality is incorporating molecular approaches, in particular the identification of selection markers [5]. Knowledge of genetic polymorphisms that are involved in different quantitative trait phenotypes of quantitative traits, and increased understanding of how these polymorphisms interact with the environment or with other genes affecting economic traits is essential [6]. In particular, the identification of genetic markers associated with such traits could contribute to an increased rate of genetic gain in farmed animals. The application of marker-assisted selection in the cattle is a promising strategy for genetic improvement of economic traits [7].
Melanocortin-4 receptor (MC4R) is a G-protein-coupled receptor with seven transmembrane domains that is highly expressed in the hypothalamus, a region of the brain intimately involved in appetite regulation [8]. MC4R signaling is important for mediating the effect of leptin on food intake and energy homeostasis [9]. It is associated with obesity, energy homeostasis and control of feeding behavior. In bovines, MC4R is located on chromosome 24; the gene has a length of 1,808 bp and one exon (GenBank accession No. NC_007325).
Many of the identified mutations in the MC4R gene are associated with obesity, energy expenditure, and serum triglyceride levels in human and animals. Several frameshift and nonsense mutations are associated with dominantly inherited obesity in humans [8, 10, 11]. In pigs, a functional mutation (Asp298Asn) in a highly conserved region has been detected in the MC4R peptide [11]. Single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) markers of the bovine MC4R gene have been detected [9, 12–14]. A SNP of C1069G was shown to be significantly associated with live weight (LW), carcass weight (CW), backfat thickness (BF), and Marbling score (MS) in Qinchuan cattle [15]. SNPs in the coding region of MC4R in Hanwoo have not been reported and were presently studied.
Materials and Methods
Animals and data collection
Ninety-four cattle consisted of 57 head of Korean cattle and 37 head of Angus cattle. The animals were collected from progeny test at two Korean stations (Korean Cattle Improvement Center, Agricultural Co-operative Federation; National Livestock Research Institute, Rural Development Administration). Genomic DNA was isolated from sperm and white blood cells that was used to genotype the MC4R genes.
The weight at slaughter was recorded as the carcass weight (CW) at slaughter age. Backfat thickness (BF) and longissimus muscle dorsi area (LMA) were measured at the 12th- and 13th- rib interface. Marbling score (MS) was evaluated on a cross section of the longissimus muscle at the 12th- to 13th-rib interface. MS is scored on a scale from 1 to 7 with 7 being associated with the most marbling. The estimated breeding value (EBV) based on measurements of performance, using phenotypic values on a number of its relatives. The overall means ± standard deviations of the analyzed traits are shown in Table 3.
SNP identification and genotyping
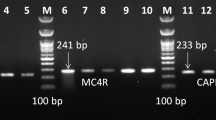
Four pairs of primers were designed based upon bovine MC4R gene sequences using Primer 3 software (http://www-genome.wi.mit.edu/cgi-bin/primer3-www.results.cgiv) (Table 1). Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) was performed in 20 μl volumes, each containing 50 ng of genomic DNA, 10× PCR buffer (100 mM Tris pH 8.9, 50 mM KCl, 15 mM MgCl, 0.01% gelatin, 0.1% Triton X-100, 10 mg/ml bovine serum albumin), 10 pmol of each primer, 40 μΜ of dNTPs and 0.5 unit Taq DNA polymerase (GeNet Bio, Korea). PCR conditions were 94°C for 4 min and 35 cycles of 30 s at 94°C, 30 s at 56.4°C, 30 s at 72°C, and a final step of 10 min at 72°C using a Peltier Thermal Cycler 200 (MJ Research, USA). DNA sequencing was performed on an ABI 3130 Genetic Analyzer (Applied Biosystems, USA). Searching sequence mutation was using the SeqMAN II software (DNA Star, USA).
Statistical analyses
Allele and genotype frequencies were calculated by a simple allele counting method. Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium was tested by comparing expected and observed genotype frequencies using a Chi-square test. The association between the genotypes of MC4R candidate gene and economic traits was evaluated with the least square method (GLM procedure of the SAS software package; SAS Institute, USA) using the following statistical linear model:
where Yijkl is the observation of the carcass traits, μ is the overall mean for each trait, YSi is the effect of ith year and season of calving, Pj is the fixed effect of jth parity, Mk is the fixed effect of Kth SNP genotype, and eijkl is the random residual effect [16].
Results and Discussion
The DNA samples from 94 unrelated cattle were amplified and sequenced for the bovine MC4R gene. Five polymorphic sites (SNPs) were identified by sequencing analysis of the bovine DNA. The four primer pairs of the MC4R gene were designed for the SNP genotyping of these SNPs on genomic DNA samples. Five SNPs (G709A, C927T, C1069G, C1343A, and C1786T) were detected in the exon 1 region (Fig. 1). C927T, C1343A, and C1786T were synonymous mutations, whereas G709A and C1069G were missense mutations. G709A displayed a change in amino acid 166 of the MC4R protein from valine (Val) to methionine (Met). C1069G exhibited a change of amino acid 286 of MC4R from leucine (Leu) to Val. Previous studies have detected several SNPs (C-293G, A-193T, T-192G, A-129G, T-84C, C927T, C1069G, Val145Ala, Ala172Thr) in the MC4R gene of cattle, and have linked the SNPs to growth traits [12–15, 17].
Estimated MCR4 allele and genotype frequencies for the Hanwoo and Angus populations are shown in Table 2. The G709A frequency for allele G was higher than that for allele A. Among Hanwoo and Angus, 45.5 and 82.4% displayed the GG phenotype, respectively, and 54.5 and 17.6%, respectively, displayed the GA genotype. The C1069G frequency for allele G was higher than that for the C allele in Hanwoo. Moreover, 19.3, 42.1, and 38.6% displayed the CC, CG, and GG genotype, respectively. Among Angus, 57.1, 40.5, and 2.4% displayed the CC, CG, and GG genotype, respectively.
The genotypes of the 94 individuals were compared with their EBV. EBV is an estimate of the ability of an individual to produce superior offspring. Therefore, EBV is a useful tool to quicken the progress of breeding in animal [18]. The overall means ± standard deviations of the analyzed traits are summarized in Table 3.
To investigate the effects of SNPs, the association of the MC4R genotypes was analyzed to determine the effects on variation in the economic traits in Hanwoo. The SNP marker of C927T significantly affected the MS. Hanwoo cattle with a CT genotype displayed a significantly higher MS than genotype CC (P < 0.05) (Table 4). In both SNP markers of C1069G and C1343A, there was a significant effect on the BF. Hanwoo with the CC genotype had a higher BF than genotype GG in SNP markers of C1069G (P < 0.05) (Table 5). Hanwoo with the CA genotype had a higher BF than genotype CC in the SNP markers of C1343A (P < 0.05) (Table 6). The SNP marker of C1786T significantly affected BF and MS. Hanwoo with the genotype CC had a higher BF than genotype CT, and genotype CT had a higher MS than genotype CC (P < 0.05) (Table 7).
SNP C1069G was a missense mutation that replaced Leu with Val at the position identical to amino acid 286 of bovine MC4R protein. It was significantly associated with BF. This result was similar to the previous report of a significant association of a SNP with LW, CW, BF and MS in Chinese (Qinchuan) cattle [15].
The present study identified SNPs in the coding region of the MC4R in Hanwoo. C927T, C1343A and C1786T were found to be synonymous mutations, whereas G709A (Val166Met) and C1069G (Leu286Val) were identified as missense mutations. Statistical analysis indicated that the polymorphisms in C927T, C1069G, and C1343A significantly affected MS. The results provide evidence that the MC4R gene is a candidate gene for carcass traits. Further studies with other populations are required.
References
Mannen H, Tsuji S, Loftus RT, Bradley DG (1998) Mitochondral DNA variation and evolution of Japanese black cattle (Bos taurus). Genet 150:1169–1175
Mannen H, Kohno M, Nagata Y, Tsuji S, Bradley DG, Yeo JS, Nyamsamba D, Zagdsuren Y, Yokohama M, Nomura K, Amano T (2004) Independent mitochondral origin and historical genetic differentiation in North Eastern Asian cattle. Mol Phylogenet Evol 32:539–544
Yum S, Suh JY, Woo S, Jeon HW, Kim KC, Suh DS (2004) Genetic relationship of Korean cattle (Hanwoo) based on nucleotide variation of mitochondrial D-loop region. Korean J Genet 26(3):297–307
Chung KimWT (2005) Association of SNP marker in IGF-I and MYF5 candidate genes with growth traits in Korean cattle. Asian Australas J Anim Sci 18(8):1061–1065
Han SH, Cho IC, Kim JH, Ko MS, Jeong HY, Oh HS, Lee SS (2009) A GHR polymorphism and its associations with carcass traits in Hanwoo cattle. Genes Genom 31(1):35–41
Cheong HS, Yoon DH, Kim LH, Park BL, Choi YH, Chung ER, Cho YM, Park EW, Cheong IC, Oh SJ, Yi SG, Park T, Shin HD (2006) Growth hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH) polymorphisms associated with carcass traits of meat in Korean cattle. BMC Genet 7:35–41
Choi JR, Oh JD, Cho KJ, Lee JH, Kong HS, Lee HK (2007) Identification and analysis of PIT1 polymorphisms and its association with growth and carcass traits in Korean cattles (Hanwoo). J Emb Trans 22(3):167–172
Yeo GS, Farooqi IS, Aminian S, Halsall DJ, Stanhope RG, O’Rahilly S (1998) A frameshift mutation in MC4R associated with dominantly inherited human obesity. Nat Genet 20:111–112
Zhang CL, Wang YH, Chen H, Lan XY, Lei CZ, Fang XT (2009) Association between variants in the 5′-untranslated region of the bovine MC4R gene and two growth traits in Nanyang cattle. Mol Biol Rep 36:1839–1843
Vaisse C, Clement K, Guy-Grand B, Froguel P (1998) A frameshift mutation in human MC4R is associated with a dominant form of obesity. Nat Genet 20:113–114
Kim KS, Larsen N, Short T, Plastow G, Rothschild MF (2000) A missense variant of the porcine melanocortin-4 receptor (MC4R) gene is associated with fatness, growth, and feed intake traits. Mamm Genome 11:131–135
Haegeman A, Coopman F, Jacobs K, Mattheeuws M, Van Zeveren A, Peelman L (2001) Bovine melanocortin receptor 4: cDNA sequence, polymorphisms and mapping. Anim Genet 32:189–192
Thue TD, Schmutz SM, Buchanan FC (2001) A SNP in the cattle MC4R gene is used to map MC4R to BTA 24. Anim Genet 32:390–391
Valle E, Habermann FA, Moore SS, Crews DH, Benkel BF (2004) Genomic localization and SNP discovery in the bovine melanocortin receptor 4 gene (MC4R). Anim Genet 35:351–352
Liu H, Tian W, Zan L, Wang H, Cui H (2010) Mutations of MC4R gene and its association with economic traits in Qinchuan cattle. Mol Biol Rep 37(1):535–540
Shin SC, Kang MJ, Chung ER (2007) Identification of a novel SNP associated with meat quality in C/EBPα gene of Korean cattle. Asian Australas J Anim Sci 20:466–470
Zhang CL, Chen H, Wang YH, Lan XY, Zhang L, Zhang AL et al (2006) Association of a missense mutation of the MC4R gene with growth traits in cattle. Arch Tierz 49:515–516
Ren J, Lu L, Liu X, Tao Z, Zhang C, Wang D, Shen J, Liu W, Tian Y, Zhu Z (2009) Paternity assessment: application on estimation of breeding value in body-weigh at first egg trait of egg-laying duck (Anas platyrhynchos). Mol Biol Rep 36:2175–2181
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a grant from the Next-Generation BioGreen 21 Program (No. PJ008196), Rural Development Administration, Republic of Korea and Technology Development Program for Agriculture and Forestry, Ministry for Food, Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries, Republic of Korea (109180-03-2-HD110).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Seong, J., Suh, D.S., Park, K.D. et al. Identification and analysis of MC4R polymorphisms and their association with economic traits of Korean cattle (Hanwoo). Mol Biol Rep 39, 3597–3601 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-011-1133-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-011-1133-3