Abstract
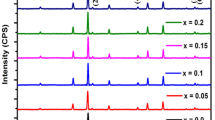
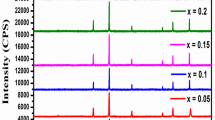
In this study, Co–Cu–Zn–Cr nano ferrites with a composition of Co0.5Cu0.25Zn0.25Fe2-xCrxO4 (x = 0.0, 0.05, 0.1, 0.15, 0.2, and 0.25) are prepared by sol–gel auto combustion method. These doped nanocrystalline ferrites’ characteristics were examined using X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM), and vibratory sample magnetometer (VSM). Such analytical characterizations were done for the structural and magnetic investigations. The crystallographic structure was identified using X-ray diffraction, which showed that a single-phase cubic spinel structure has been formed. According to the Debye–Scherrer equation, the synthesized samples’ average crystallite diameters ranged from 55.32 to 33.41 nm. Field emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM) was used to study the surface morphology of the particles, revealing aggregated grains with a sponge-like structure. Functional groups were detected using Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy; peaks at about 393.21–582.71 cm−1 and 392.74–381.50 cm−1 indicated specific chemical properties. Magnetic characteristics at room temperature were investigated using a vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM), revealing some magnetic parameters. Hysteresis curves demonstrate reduced coercivity (263.98 to 126.62 Oe) and saturation magnetization (43.72 to 63.29 emu/g) upon metal ion replacement in the Co–Cu–Zn nano ferrites.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data can be obtained from the corresponding author on request.
References
A. Ramakrishna, N. Murali, T.W. Mammo, K. Samatha, V. Veeraiah, Structural and DC electrical resistivity, magnetic properties of Co0.5M0.5Fe2O4 (M=Ni, Zn, and Mg) ferrite nanoparticles. Physica B B 534, 134–140 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2018.01.033
K. Chandramouli, B. Suryanarayana, P.V.S.K.P. Varma, V. Raghavendra, K.A. Emmanuel, P. Taddesse, N. Murali, T.W. Mammo, D. Parajuli, Effect of Cr3+ substitution on dc electrical resistivity and magnetic properties of Cu0.7Co0.3Fe2–xCrxO4 ferrite nanoparticles prepared by sol-gel auto combustion method. Results Phys. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinp.2021.104117
R.Y. Mudi, V.B.G. Tiruveedhi, D. Kothandan, P.S.V. Shanmukhi, T.W. Mammo, N. Murali, Structural investigation, magnetic and DC electrical resistivity properties of Co0.5–xNixZn0.5Fe2O4 nano ferrites. Inorg. Chem. Commun.. Chem. Commun. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inoche.2023.111958
Y. Zhao, Y. Sun, H. Hou, Core-shell structure nanoprecipitates in Fe–xCu–3.0Mn-1.5Ni–15Al alloys: a phase field study. Prog. Nat. Sci.: Mater. Int. 32(3), 358–368 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnsc.2022.04.001
Q. Guo, H. Hou, Y. Pan, X. Pei, Z. Song, P.K. Liaw, Y. Zhao, Hardening-softening of Al0.3CoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy under nanoindentation. Mater. Des. 231, 112050 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2023.112050
K.L.V. Nagasree, B. Suryanarayana, V. Raghavendra, S. Uppugalla, T.W. Mammo, D. Kavyasri, N. Murali, M.K. Raju, D. Parajuli, K. Samatha, Influence of Mg2+ and Ce3+ substituted on synthesis, structural, morphological, electrical, and magnetic properties of Cobalt nano ferrites. Inorg. Chem. Commun.. Chem. Commun. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inoche.2023.110405
W. Yang, X. Jiang, X. Tian, H. Hou, Y. Zhao, Phase-field simulation of nano-α′ precipitates under irradiation and dislocations. J. Market. Res. 22, 1307–1321 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2022.11.165
K. Sakthipandi, N. Lenin, R.R. Kanna, A.S. Afroze, M. Sivabharathy, PVA-doped NiNdxFe2-xO4 nanoferrites: tuning of dielectric and magnetic properties. J. Magn. Magn. Mater.Magn. Magn. Mater. 485, 105–111 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2019.04.074
T.W. Mammo, N. Murali, Y.M. Sileshi, T. Arunamani, Studies of structural, morphological, electrical, and magnetic properties of Mg-substituted Co-ferrite materials synthesized using sol-gel autocombustion method. Physica B B 523, 24–30 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2017.08.013
L. Shao, S. Zhang, L. Hu, Y. Wu, Y. Huang, P. Le, S. Dai, W. Li, N. Xue, F. Xu, L. Zhu, Influence of heat treatment condition on the microstructure, microhardness and corrosion resistance of Ag–Sn–In–Ni–Te alloy wire. Materials 17(11), 2785 (2024). https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17112785
R. Wang, H. Huang, K. Li, J. Yang, Z. Wu, H. Kong, Design and evolution of Fe–Si–Al soft magnetic composites doped with carbonyl iron powders: overcoming the restrictive relation between permeability and core loss. Ceram. Int. 50(10), 17861–17872 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2024.02.274
A. Hossain, A.R. Gilev, P. Yanda, V.A. Cherepanov, A.S. Volegov, K. Sakthipandi, A. Sundaresan, Optical, magnetic and magneto-transport properties of Nd1-xAxMn0.5Fe0.5O3-δ (A= Ca, Sr, Ba; x= 0, 0.25). J. Alloys Compd. 847, 156297 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.156297
K. Sakthipandi, K. Kannagi, A. Hossain, Effect of lanthanum doping on the structural, electrical, and magnetic properties of Mn0.5Cu0.5LaxFe2–xO4 nanoferrites. Ceram. Int. 46(11), 19634–19638 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.04.255
L. Xie, X. Cen, H. Lu, G. Yin, M. Yin, A hierarchical feature-logit-based knowledge distillation scheme for internal defect detection of magnetic tiles. Adv. Eng. Inform. 61, 102526 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aei.2024.102526
M. Wang, C. Jiang, S. Zhang, X. Song, Y. Tang, H. Cheng, Reversible calcium alloying enables a practical room-temperature rechargeable calcium-ion battery with a high discharge voltage. Nat. Chem. 10(6), 667–672 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41557-018-0045-4
A. Ahlawat, V.G. Sathe, V.R. Reddy, A. Gupta, Mossbauer, Raman and X-ray diffraction studies of superparamagnetic NiFe2O4 nanoparticles prepared by sol–gel auto-combustion method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater.Magn. Magn. Mater. 323(15), 2049–2054 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2011.03.017
S.K.R. Kurucheti, G. Ranganath, A. Nagaraj, S.H. Jose, Corrosion rate and surface hardness optimization in wire electrical discharge machining of AISI A2 tool steel in various conductive states and mediums. Mater. Res. Expr. 8(7), 076001 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/ac0eb8
A.B.A. Hammad, H.S. Magar, A.M. Mansour, R.Y. Hassan, A.M.E. Nahrawy, Construction and characterization of nano-oval BaTi0.7Fe0.3O3@NiFe2O4 nanocomposites as an effective platform for the determination of H2O2. Sci. Rep. 13(1), 9048 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-36076-6
A.M. Mansour, A.M. Fathi, A.B. Abou, A.M. Hammad, El. Nahrawy, Microstructures, optical and electrochemical properties of advanced Fe0.8Se0.14Si0.06MoO4 nanocrystalline for energy storage applications. Phys. Scr. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1088/1402-4896/acc9ea
T.W. Mammo, N. Murali, Y.M. Sileshi, T. Arunamani, Effect of Ce-substitution on structural, morphological, magnetic and DC electrical resistivity of Co-ferrite materials. Physica B B 531, 164–170 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2017.12.049
T.W. Mammo, C.V. Kumari, S.J. Margarette, A. Ramakrishna, R. Vemuri, Y.B. Shankar Rao, K.L. Vijaya Prasad, Y. Ramakrishna, N. Murali, Synthesis, structural, dielectric and magnetic properties of cobalt ferrite nanomaterial prepared by sol-gel autocombustion technique. Physica B B 581, 411769 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2019.411769
K.M. Batoo, M.-S. Abd El-sadek, Electrical and magnetic transport properties of Ni–Cu–Mg ferrite nanoparticles prepared by sol–gel method. J. Alloys Compd. 566, 112–119 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2013.02.129
P. Kaur, S. Singh, V. Babbar, V. Kumar, K.B. Tikoo, A. Kaushik, S. Singhal, Aggrandized catalytic performance of transition metal doped strontium hexagonal ferrites for the treatment of malevolent organic pollutants. J. Alloy. Compd. 856, 158026 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.158026
A.M. Abouelnaga, A.M. Mansour, A.B. AbouHammad, A.M. El Nahrawy, Optimizing magnetic, dielectric, and antimicrobial performance in chitosan-PEG-Fe2O3@ NiO nanomagnetic composites. Int. J. Biol. Macromol.Macromol. 260, 129545 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.129545
A.B. AbouHammad, B.A. Hemdan, A.M. Mansour, A.M. El Nahrawy, Improved antimicrobial and antibiofilm efficacy of adaptable BaTi2Fe4O11−(x)NiFe2O4 nanoceramics: investigating microstructural and spectroscopic analysis. SN Appl. Sci. 5(12), 317 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-023-05547-w
A.M. Mansour, M. Morsy, A.M. El Nahrawy, A.B. AbouHammad, Humidity sensing using Zn(1.6–x)Na0.4CuxTiO4 spinel nanostructures. Sci. Rep. 14(1), 562 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-50888-6
P. Kulandaivelu, K. Sakthipandi, P.S. Kumar, V. Rajendran, Mechanical properties of bulk and nanostructured La0.61Sr0.39MnO3 perovskite manganite materials. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 74(2), 205–214 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2012.09.008
A. Subalakshmi, B. Kavitha, N. Srinivasan, M. Rajarajan, A. Suganthi, An affordable efficient SrWO4 decorated Bi2O3 nanocomposite: Photocatalytic activity for the degradation of methylene blue under visible light irradiation. Mater. Today: Proc. 48, 409–419 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.11.167
K. Sakthipandi, B.G. Babu, G. Rajkumar, A. Hossian, M.S. Raghavan, M.R. Kumar, Investigation of magnetic phase transitions in Ni0.5Cu0.25Zn0.25Fe2xLaxO4 nanoferrites using magnetic and in-situ ultrasonic measurements. Physica B B 645, 414280 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2022.414280
K.M. Batoo, D. Salah, G. Kumar, A. Kumar, M. Singh, M. Abd El-Sadek, F.A. Mir, A. Imran, D.A. Jameel, Hyperfine interaction and tuning of magnetic anisotropy of Cu doped CoFe2O4 ferrite nanoparticles. J. Magnetism Magn. Mater. 411, 91–97 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2016.03.058
M. Madhu, A.V. Rao, D. Parajuli, S.Y. Mulushoa, N. Murali, Cr3+ substitution influence on structural, magnetic and electrical properties of the Ni0.3Zn0.5Co0.2Fe2-xCrxO4 (0.00≤ x≤ 0.20) nanosized spinel ferrites. Inorg. Chem. Commun.. Chem. Commun. 143, 109818 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inoche.2022.109818
H. Bhargava, N. Lakshmi, V. Sebastian, V.R. Reddy, K. Venugopalan, A. Gupta, Investigation of the large magnetic moment in nano-sized Cu0.25Co0.25Zn0.5Fe2O4. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 42(24), 245003 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1088/0022-3727/42/24/245003
N. Chaibakhsh, Z. Moradi-Shoeili, Enzyme mimetic activities of spinel substituted nanoferrites (MFe2O4): a review of synthesis, mechanism and potential applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 99, 1424–1447 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2019.02.086
V.S. Shinde, V. Vinayak, S. P. Jadhav, N.D. Shinde, A.V. Humbe, K.M. Jadhav, Structure, Morphology, Cation distribution and magnetic properties of Cr3+-substituted CoFe2O4 nanoparticles. J. Supercond. Novel Magn.Supercond. Novel Magn. 32, 945–955 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-018-4778-5
X. Li, P. Yu, X. Niu, H. Yamaguchi, D. Li, Non-contact manipulation of nonmagnetic materials by using a uniform magnetic field: experiment and simulation. J. Magn. Magn. Mater.Magn. Magn. Mater. 497, 165957 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2019.165957
A.I. Ivanets, V. Srivastava, M.Y. Roshchina, M. Sillanpää, V.G. Prozorovich, V.V. Pankov, Magnesium ferrite nanoparticles as a magnetic sorbent for the removal of Mn2+, Co2+, Ni2+ and Cu2+ from aqueous solution. Ceram. Int. 44(8), 9097–9104 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.02.117
M.A. Munir, M.Y. Naz, S. Shukrullah, M.T. Ansar, M.U. Farooq, M. Irfan, S.N.F. Mursal, S. Legutko, J. Petru, M. Pagác, Enhancement of magnetic and dielectric properties of Ni0.25Cu0.25Zn0.50Fe2O4 magnetic nanoparticles through non-thermal microwave plasma treatment for high-frequency and energy storage applications. Materials 15, 6890 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15196890
W.A. Farooq, M. SajjadUl Hasan, M.I. Khan, A.R. Ashraf, M. Abdul Qayyum, N. Yaqub, M.A. Almutairi, M. Atif, A. Hanif, Structural, optical and electrical properties of Cu0.6CoxZn0.4-xFe2O4 (x = 0.0, 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4) soft ferrites. Molecules (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26051399
T.J.B. Holland, S.A.T. Redfern, Unit cell refinement from powder diffraction data: the use of regression diagnostics. Mineral. Mag. 61(404), 65–77 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1180/minmag.1997.061.404.07
F. Barkat, M. Afzal, B.S. Khan, A. Saeed, M. Bashir, A. Mukhtar, T. Mehmood, K. Wu, Formation mechanism and lattice parameter investigation for copper-substituted cobalt ferrites from zingiber officinale and elettaria cardamom seed extracts using biogenic route. Materials 15, 4374 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15134374
A.A. Al-Juaid, M.A. Gabal, Effects of co-substitution of Al3+ and Cr3+ on structural and magnetic properties of nano-crystalline CoFe2O4 synthesized by the sucrose technique. J. Mater. Res. Technol. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2021.06.023
A.M. Abu-Dief, W.S. Mohamed, α-Bi2O3 nanorods: synthesis, characterization and UV-photocatalytic activity. Mater. Res Exp. 4(3), 035039 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/aa6712
E.M.M. Ibrahim, A.M. Abu-Dief, A. Elshafaie, A.M. Ahmed, Electrical, thermoelectrical and magnetic properties of approximately 20-nm Ni–Co–O nanoparticles and investigation of their conduction phenomena. Mater. Chem. Phys. 192, 41–47 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2017.01.054
E.M.M. Ibrahim, L.H. Abdel-Rahman, A.M. Abu-Dief, A. Elshafaie, S.K. Hamdan, A.M. Ahmed, Electric, thermoelectric and magnetic characterization of γ-Fe2O3 and Co3O4 nanoparticles synthesized by facile thermal decomposition of metal-Schiff base complexes. Mater. Res. Bull. 99, 103–108 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2017.11.002
E.M.M. Ibrahim, L.H. Abdel-Rahman, A.M. Abu-Dief, A. Elshafaie, S.K. Hamdan, A.M. Ahmed, The synthesis of CuO and NiO nanoparticles by facile thermal decomposition of metal-Schiff base complexes and an examination of their electric, thermoelectric and magnetic Properties. Mater. Res. Bull. 107, 492–497 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2018.08.020
L.H. Abdel Rahman, A.M. Abu-Dief, R.M. El-Khatib, S.M. Abdel-Fatah, A.M. Adam, E.M.M. Ibrahim, Sonochemical synthesis, structural inspection and semiconductor behavior of three new nano sized Cu (II), Co (II) and Ni (II) chelates based on tri-dentate NOO imine ligand as precursors for metal oxides. Appl. Organomet. Chem.Organomet. Chem. 32(3), e4174 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1002/aoc.4174
S. Singhal, S. Bhukal, Effect of chromium substitution on the structural, magnetic and electrical properties of nano crystalline Co0.6Zn0.4Cu0.2CrxFe1.8-xO4 Ferrite. Solid State Phenom. 202, 173–192 (2013). https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/SSP.202.173
K. Chandramouli, P.A. Rao, B. Suryanarayana, V. Raghavendra, S.J. Mercy, D. Parajuli, P. Taddesse, S.Y. Mulushoa, T.W. Mammo, N. Murali, Effect of Cu substitution on magnetic and DC electrical resistivity properties of Ni–Zn nanoferrites. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-06127-7
K. Chandramouli, V. Raghavendra, P.P. Varma, B. Suryanarayana, T.W. Mammo, D. Parajuli, P. Taddesse, and Murali, N, Influence of Cr3+-substituted Co0.7Cu0.3Fe2-xCrxO4 nano ferrite on structural, morphological, dc electrical resistivity and magnetic properties. Appl. Phys. A 127, 596 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-021-04750-z
R. Jasrotia, S. Kour, P. Puri, A.D. Jara, B. Singh, C. Bhardwaj, V.P. Singh, R. Kumar, Structural and magnetic investigation of Al3+ and Cr3+ substituted Ni–Co–Cu nanoferrites for potential applications. Solid State Sci. 110, 106445 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solidstatesciences.2020.106445
H.R. Daruvuri, K. Chandu, N. Murali, D. Parajuli, M.P. Dasari, Effect on structural, dc electrical resistivity, and magnetic properties by the substitution of Zn2+ on Co-Cu nano ferrite. Inorg. Chem. Commun.. Chem. Commun. 143, 109794 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inoche.2022.109794
K.M. Batoo, Structural and electrical properties of Cu doped NiFe2O4 nanoparticles prepared through modified citrate gel method. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 72(12), 1400–1407 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2011.08.005
P. Himakar, N. Murali, D. Parajuli, V. Veeraiah, K. Samatha, T.W. Mammo, K.M. Batoo, M. Hadi, E.H. Raslan, S.F. Adil, Magnetic and DC Electrical Properties of Cu Doped Co–Zn Nanoferrites. J. Electron. Mater. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-021-08760-8
S. Qamar, M.N. Akhtar, K.M. Batoo, E.H. Raslan, Structural and magnetic features of Ce doped Co–Cu–Zn spinel nanoferrites prepared using sol gel self-ignition method. Ceram. Int. 46(10), 14481–14487 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.02.246
W.S. Mohamed, N.M.A. Hadia, M. Alzaid, A.M. Abu-Dief, Impact of Cu2+ cations substitution on structural, morphological, optical and magnetic properties of Co1-xCuxFe2O4 nanoparticles synthesized by a facile hydrothermal approach. Solid State Sci. 125, 106841 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solidstatesciences.2022.106841
W.S. Mohamed, A.M. Abu-Dief, Impact of rare earth europium (RE-Eu3+) ions substitution on microstructural, optical and magnetic properties of CoFe2−xEuxO4 nanosystems. Ceram. Int. 46(10), 16196–16209 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.03.175
W.S. Mohamed, M. Alzaid, M.S.M. Abdelbaky, Z. Amghouz, S. García-Granda, A.M. Abu-Dief, Impact of Co2+ substitution on microstructure and magnetic properties of CoxZn1-xFe2O4 nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 9(11), 1602 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9111602
A.M. Abu-Dief, M.S. Abdelbaky, D. Martínez-Blanco, Z. Amghouz, S. García-Granda, Effect of chromium substitution on the structural and magnetic properties of nanocrystalline zinc ferrite. Mater. Chem. Phys. Chem. Phys. 174, 164–171 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2016.02.065
G.K. Sarveena, R.K. Arun Kumar, K.M. Kotnala, M.S. Batoo, Investigation of structural, magnetic and Mössbauer properties of Co2+ and Cu2+ substituted Ni–Zn nanoferrites. Ceram. Int. 42(4), 4993–5000 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2015.12.012
B. Suryanarayana, P.P. Varma, P.S.V. Shanmukhi, M.G. Kiran, N. Murali, T.W. Mammo, V. Raghavendra, D. Parajuli, K.M. Batoo, S. Hussain, Comparison of the effect of Cr3+ substituted Co–Cu and Cu–Co nano ferrites on structural, magnetic, DC electrical resistivity, and dielectric properties. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 35, 93 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-11808-6
M.N. Akhtar, M.A. Khan, Effect of rare earth doping on the structural and magnetic features of nanocrystalline spinel ferrites prepared via sol-gel route. J. Magnetism Magn. Mater. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2018.03.069
R.H. Kadam, R.B. Borade, M.L. Mane, D.R. Mane, K.M. Batoo, S.E. Shirsath, Structural, mechanical, dielectric properties and magnetic interactions in Dy3+-substituted Co–Cu–Zn nanoferrites. RSC Adv. 10(47), 27911–27922 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1039/D0RA05274D
P.S. Jadhav, K.K. Patankar, V. Puri, Structural, electrical and magnetic properties of Ni–Co–Cu–Mn ferrite thick films. Mater. Res. Bull. 75, 162–166 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2015.11.034
Y. Vijapure, Synthesis and properties of Ho3+ Doped Co–Cr–Fe ferrite nanoparticles prepared by sol-gel chemical route. Int. J. Res. Appl. Sci. Biotechnol. 9(1), 203–206 (2022)
R.R. Akurati, N.K. Jaladi, S.R. Kurapati, G. Kapusetti, M. Choppadandi, P. Mandal, Preparation, characterization and study of magnetic induction heating of Co–Cu nanoparticles. Mater. Today Commun. 34, 104964 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2022.104964
R.S. Yadav, I. Kuřitka, J. Havlica, M. Hnatko, C. Alexander, J. Masilko, L. Kalina, M. Hajdúchová, J. Rusnak, V. Enev, Structural, magnetic, elastic, dielectric and electrical properties of hot-press sintered Co1−xZnxFe2O4 (x=0.0, 0.5) spinel ferrite nanoparticles. J. Magnetism Magn. Mater. 447, 48–57 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2017.09.033
M.P. Ghosh, S. Mukherjee, Microstructural, magnetic, and hyperfine characterizations of Cu-doped cobalt ferrite nanoparticles. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 102(12), 7509–7520 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1111/jace.16687
S. Rasheed, H.S. Aziz, R.A. Khan, A.M. Khan, A. Rahim, J. Nisar, S.M. Shah, F. Iqbal, A.R. Khan, Effect of Li–Cu doping on structural, electrical and magnetic properties of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles. Ceram. Int. 42(2), 3666–3672 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2015.11.034
C. Komali, N. Murali, K. Rajkumar, A. Ramakrishna, S. Yonatan Mulushoa, D. Parajuli, P.N.V.V.L. Pramila Rani, S. Ampolu, K. Chandra Mouli, Y. Ramakrishna, Probing the dc electrical resistivity and magnetic properties of mixed metal oxides Cr3+ substituted Mg–Zn ferrites. Chem. Papers 77(1), 109–117 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-022-02466-9
M.A. Abdo, A.A. El-Daly, Sm-substituted copper-cobalt ferrite nanoparticles: Preparation and assessment of structural, magnetic and photocatalytic properties for wastewater treatment applications. J. Alloy. Compd. 883, 160796 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.160796
E.E. Ateia, F.S. Soliman, Modification of Co/Cu nanoferrites properties via Gd3+/ Er3+doping. Appl. Phys. A 123, 312 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-017-0948-8
T.B. Taha, A.A. Barzinjy, F.H.S. Hussain, T. Nurtayeva, Nanotechnology and computer science: trends and advances, memories - materials, devices. Circuits Syst. 2, 100011 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memori.2022.100011
H.B. Omietimi, S.A. Afolalu, J.F. Kayode, S.I. Monye, S.L. Lawal, M.E. Emetere, An overview of nanotechnology and its application. E3S Web Conf. 391, 01079 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1051/e3sconf/202339101079
J. Mathew, J. Joy, S.C. George, Potential applications of nanotechnology in transportation: a review. J. King Saud Univ. Sci 31, 586–594 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksus.2018.03.015
Funding
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study’s conception and design. J. Kishore Babu, Sk. Erfan, N. Revathi, K. Vagdevi, G. Srinivas Reddy, and M. V. N. V. Sharma prepared material, collected data, and analysed. J. Kishore Babu wrote the first draft of the manuscript, and all authors commented on previous versions. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare they have no competing interests.
Ethical approval
The authors certify that they have no financial or personal interests that compete with or appear to influence the research presented in this publication. There are no human or animal participants in this study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Babu, J.K., Erfan, S., Revathi, N. et al. Enhanced magnetic properties of Co0.5Cu0.25Zn0.25Fe2-xCrxO4 nano ferrites. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 35, 1441 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-024-13217-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-024-13217-9