Abstract
Little research has examined family emotional climate in the context of having a child with autism spectrum disorder (ASD). The goal of the current study was to determine how the emotional quality of family subsystems (parent–child and parent couple relationships, for both mothers and fathers) combine to create various classes of family emotional climate and to identify predictors of class membership in 148 families of children with ASD. The emotional quality of family subsystems was assessed using Five Minute Speech Samples from mothers and fathers. In total, 148 families of children with ASD (86% male) aged 6–13 years were included in analyses. About one-third of parents did not have a college degree and more than two-thirds were of non-Hispanic White origin. Latent class analysis revealed that 43% of the sample was characterized by high levels of warmth and low levels of criticism in both the parent–child and parent couple relationships; 12% of the sample was characterized by low warmth and high criticism in both sets of relationships; and the rest of the sample was divided among three additional classes of emotional climate characterized by different configurations of warmth and criticism across both sets of relationships. Parent level of broader autism phenotype and child emotional and behavioral problems were associated with emotional climate class membership. Implications for interventions are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
There is substantial evidence that the emotional quality of family subsystems, including the parent–child relationship and parent couple relationship, is a critical determinant of child development (Brock and Kochanska 2015; Kopala-Sibley et al. 2017). Expressed emotion is a research construct intended to capture the emotional quality of family subsystems through the Five Minute Speech Sample (FMSS), in which individuals speak about a family member and their dyadic relationship (Magaña et al. 1986). Two previously defined codes obtained from the FMSS include the level of criticism (i.e., dissatisfaction and/or negative comments) and warmth (i.e., interest, concern, and empathy), expressed about the family member and dyadic relationship. These two codes have been shown to mirror the emotional quality of observed family interactions (Weston et al. 2017). Research on the general (Labella et al. 2016), neurodevelopmental disability (Romero-Gonzalez et al. 2018), and autism spectrum disorder (ASD) populations (Baker et al. 2011; Smith et al. 2008) has used the FMSS to examine the emotional quality of the mother–child relationship. However, little FMSS research has assessed the emotional quality of other family dyads—such as the father–child and parent couple relationships—and virtually nothing is known about how emotional quality across family subsystems combines to create classes of family emotional climate. The goal of the current study was to identify classes of family emotional climate, and their predictors, in families of children with ASD.
Emotional Quality of Family Subsystems and ASD
In the United States, it is estimated that 1 in 59 children meet diagnostic criteria for ASD (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention 2018), a neurodevelopmental disability involving difficulties in social communication and restricted and repetitive interests and behaviors (American Psychiatric Association 2014). About 1 in 3 children with ASD also have intellectual disability (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention 2018) and about 1 in 2 have co-occurring emotional and behavioral problems such as anxiety and inattention (e.g., McStay et al. 2014).
This profile of child-related challenges may shape the emotional quality of family subsystems. As a group, parents of children with ASD are at risk for a high level of parenting stress (Estes et al. 2013) and poor psychological well-being, including depression and anxiety (Cohrs and Leslie 2017), relative to other parents. In non-ASD populations, high parenting stress and poor parental psychological well-being is associated with distant and critical parent–child interactions (Mackler et al. 2015). As a group, parents of children with ASD also report less satisfying parent couple relationships (Sim et al. 2016) and more couple conflicts (Hartley et al. 2017), and are at greater risk for separation/divorce (Baeza-Velasco et al. 2013; Hartley et al. 2010) than parents of children without ASD. Thus, parents of children with ASD may also be at risk for negative emotional quality parent couple relationships. Despite these group-level risks, there is variability among parents of children with ASD in these studies, with a subset of parents reporting more positive parent–child and parent couple relationship experiences.
In previous studies using the FMSS with parents of young and grown children with ASD, 12–18% of mothers expressed high criticism toward their son/daughter with ASD (Baker et al. 2011; Griffith et al. 2015), and 20–40% expressed high warmth (Griffith et al. 2015; Smith et al. 2008). It is not clear if the emotional quality of the father–child relationship differs from that of the mother–child relationship. Mothers of children with ASD have been found to report a higher level of parenting stress (Foody et al. 2015), and to take on more daily parenting responsibilities (Callander and Lindsay 2018), than fathers, which may put the mother–child relationship at greater risk for high criticism and low warmth.
Research on the general population has used the FMSS to examine emotional quality in the couple relationship (Favez et al. 2017; Iles et al. 2014). In these studies, women were more likely to express high criticism toward their partner than men (62% vs. 49%, respectively; Favez et al. 2017). There are no published FMSS studies of parent couple relationship quality in families of children with ASD. Given their group-level risk for unsatisfying, conflict-ridden, and shorter-term couple relationships (Sim et al. 2016; Hartley et al. 2010, 2017), many families of children with ASD may consist of one or both parents expressing low warmth and high criticism toward her/his partner.
Predictors of Family Emotional Climate
In addition to identifying various classes of family emotional climate evident in families of children with ASD, it is important to identify predictors of class membership to direct intervention. Longitudinal studies have shown positive bidirectional associations between the severity of child ASD symptoms and emotional and behavioral problems and levels of parenting stress (Rodriguez et al. 2019; Zaidman-Zait et al. 2014). Previous research also has demonstrated negative bidirectional associations between the severity of child ASD symptoms and emotional and behavioral problems and optimal parent psychological well-being (Yorke et al. 2018). In a transactional process, the challenging behavior of a child with ASD may alter the parent–child relationship in ways that elicit negative parent responses which, in turn, reinforce the challenging behavior of the child (Guralnick 2011). Families who have a child with more severe ASD symptoms and emotional and behavioral problems may thus be at risk for a negative (i.e., high criticism and low warmth) parent–child relationship.
The genetic etiology of ASD (Schaefer and Mendelsohn 2013) may also shape the emotional quality of family subsystems. Multiplex families involve having multiple family members affected by ASD or related conditions. Across studies, 15–21% of parents of children with ASD (compared to 4–8% of other parents) demonstrate the broader autism phenotype (BAP; Bora et al. 2017), involving cognitive rigidity, anxious personality traits, and social difficulties (Losh et al. 2008). Parent level of BAP has been found to be associated with lower couple relationship satisfaction (Pruitt et al. 2018), and thus may be associated with negative emotional quality in parent couple relationships. It is not yet known if parent level of BAP is associated with the emotional quality of the parent–child relationship. Approximately 20% of siblings of children with ASD are diagnosed with ASD (Messinger et al. 2015), and 10–32% have another type of neurodevelopmental disability or psychiatric condition (Jokiranta-Olkoniemi et al. 2016). Having multiple affected children is associated with a high level of parenting stress (Orsmond et al. 2007), and thus may be linked to a negative quality parent–child relationship.
Spillover Versus Divergence
Theory and empirical evidence indicate that the emotional quality of one family subsystem predicts the emotional quality of other family subsystems. Within family systems theory (Fine and Fincham 2013), the spillover hypothesis posits that tension, negative affect, and conflict generated in one family subsystem carries into other family subsystems (Almeida et al. 1999). For example, criticism in the parent–child relationship may lead to criticism in the parent couple relationship, and vice versa. There is evidence that spillover is most prominent under conditions of chronic stress or poor psychological resources (Almeida et al. 1999). Indeed, in a previous study based on the current sample, daily parenting stress co-varied with daily parent couple relationship quality at a within-parent level and was greatest if the child had a high severity of ASD symptoms and emotional and behavioral problems (citation removed for blind review). In the general population, however, there is evidence that spillover effects are not limited to a within-parent level. Instead, crossover effects have been found in which stress in one parent shapes the family relationships of the other parent (Falconier et al. 2015; Newland et al. 2015). As a result, high criticism and low warmth in the parent–child relationship of one parent may lead to high criticism and low warmth in the parent–child and/or parent couple relationship of the other parent. Thus, families reporting high child-related challenges (severe child ASD symptoms and/or emotional and behavioral problems) may be at risk for negative emotional quality across all family relationships (parent–child and parent couple relationships, in mothers and fathers).
On the other hand, the divergence hypothesis suggests that parents may compensate for one negative family subsystem by devoting additional time and energy into another (Erel and Burman 1995). Indeed, some parents of children with ASD have described forming a stronger couple relationship (e.g., deeper commitment and intimacy) as a result of child challenges (Hock et al. 2012). Alternatively, one parent may compensate for his/her partner’s negative parent–child relationship through her/his own positive parent–child relationship. Indeed, many families consist of one emotionally supportive parent and one emotionally detached or negative parent in the general population (Ryan et al. 2006).
Current Study
The first aim of the current study was to characterize and compare FMSS criticism and warmth in the mother–child, father–child, mother–spouse, and father–spouse relationships in 148 families of children with ASD (aged 6–13 years). Given evidence that mothers assume a disproportionate amount of daily parenting responsibilities in families of children with ASD (Callander and Lindsay 2018), and often report a higher level of parenting stress than fathers (Foody et al. 2015), mothers were hypothesized to express high criticism and low warmth in the parent–child relationship more often than fathers. Based on FMSS research on the general population (Favez et al. 2017), mothers of children with ASD were expected to express high criticism about the parent couple relationship more often than fathers.
The second aim of the study was to identify classes of family emotional climate using latent class analysis of the FMSS with these families of children with ASD. We hypothesized that some classes of families would be consistent with the spillover hypothesis (e.g., Almeida et al. 1999) and involve crossover effects (Falconier et al. 2015) of criticism and warmth across family relationships. We hypothesized that other classes of families would be consistent with the divergence hypothesis, exhibiting opposing emotional quality across family relationships.
The third aim of the study was to identify predictors of class membership. In line with the spillover hypothesis (e.g., Almeida et al. 1999) and crossover effects (Falconier et al. 2015), families undergoing high child-related challenges (i.e., higher severity of child ASD symptoms and emotional and behavioral problems) and multiplex families (i.e., having an additional child with a neurodevelopmental disability or psychiatric condition and parent level of BAP) were expected to be in a latent class involving low warmth and high criticism across all family relationships based on evidence of high parenting (Orsmond et al. 2007) and couple relationship distress (Pruitt et al. 2018).
Methods
Participants
The present study used data from 148 families who were participating in a longitudinal study of mother–father couples who had a child with ASD.Footnote 1 In 2 families, the parents were not married, but had lived together for more than 5 years. In 6 families, one parent was a step-parent who had been involved in the child’s life for at least 3 years. In 4 families, the child was adopted at least 4 years ago. Mothers had an average age of 39.52 years (SD = 5.60) and 28% (n = 42) did not have a college degree. Fathers had an average age of 41.57 years (SD = 6.25) and 38% (n = 56) did not have a college degree. The majority of parents identified as non-Hispanic White (n = 257, 87%). Remaining parents identified as African American (n = 2, 1%), Hispanic White (n = 25, 8%), American Indian (n = 2, 1%), Asian or Pacific Islander (n = 9, 3%), or multiple ethnicities (n = 4, 1%). Mean household income was $80,000–89,000. Overall, 36% (n = 53) of families had an additional child (or children) with a disability or psychiatric condition. The majority of target children with ASD were male (n = 127, 86%). On average, target children with ASD were 9.05 years old (SD = 2.26, range = 6–13), and 52 (35%) had intellectual disability.
Recruitment
Families were recruited through fliers posted at ASD clinics and in community settings (e.g., libraries), mailings to schools, and research registries. Original study inclusion criteria included being a parent of a child aged 5 to 12 years who was diagnosed with ASD and being part of a longstanding cohabiting couple relationship for at least 3 years in which both partners were willing to participate. Parents provided medical or educational records documenting the child’s ASD diagnosis and the diagnostic evaluation had to have included the Autism Diagnosis Observation Schedule (Lord et al. 2000, 2012). In addition, the Social Responsiveness Scale (SRS-2; Constantino and Gruber 2012) was used to verify current ASD symptoms; children had to have a SRS-2 Total T-score ≥ 60. For families who had more than one child with ASD (n = 10), the oldest child was the target child in the study as this is when parenting in the context of ASD began.
Procedures
Parents reported on family socio-demographics and independently completed questionnaires during a 2.5-h in person lab or home visit. All parents spoke English. Parents who preferred Spanish (n = 6) were given standardized questionnaires in both English and Spanish when available and a Spanish-speaking research staff member conducted their interview. Each parent was paid $50 at the completion of the visit.
Measures
FMSS Emotional Climate
The FMSS (Magaña et al. 1986) was conducted in person and individually with parents in separate rooms so they could not hear one another. Mothers and fathers were asked about their child with ASD and then their spouse/partner. In the FMSS, parents were given the prompt: “I’d like to hear your thoughts and feelings about (child’s name/spouse’s name), in your own words and without my interrupting with any questions or comments. When I ask you to begin, I’d like you to speak for 5 min, telling me what kind of person (child’s name/spouse’s name) is and how the two of you get along together. After you begin to speak, I prefer not to answer any questions until after the 5 min. Do you have any questions before we begin?” By eliciting open-ended responses based on the general FMSS prompt, rather than asking value-laden questions about the parent–child and parent couple relationships that can trigger socially desirable responses, the FMSS is intended to reduce response biases. Each FMSS was audio recorded and transcribed, and then coded by a trained FMSS rater who was blind to study questions. This rater has undergone formal FMSS training, coded more than a thousand FMSS, and was found to have high inter-rater reliability with 12 other FMSS trained raters (mean inter-rater agreement = 93% [range 80–100%]). FMSS ratings have been found to correlate with observed emotions and behaviors of parents within actual parent–child interactions (Weston et al. 2017), and have high reliability and construct validity with self-reported and observed measures of the quality of the parent–child relationship in diverse populations (Magaña et al. 1986; Van Humbeeck et al. 2002), including in parents of children with neurodevelopmental disabilities (Hastings et al. 2006) and ASD, specifically (Greenberg et al. 2006).
Criticism
Speech samples were rated as high, borderline, or low criticism as recommended by Magaña et al. (1986). High criticism involved making a negative opening remark, negatively describing the relationship, and/or making one or more critical comments (Magaña et al. 1986). Borderline criticism was coded if the parent made one or more statements of dissatisfaction. Low criticism was coded if the parent did not make any critical comments. Given the low number of speech samples coded as high criticism (3–5% toward the child, 7–12% toward partner), a dichotomous FMSS criticism rating was used in analyses in which the high and borderline categories were combined and coded 1 and low criticism was coded 0. The following is from a speech sample rated as ‘high criticism’:
Um, when [child’s name] is in the picture, which is always, there’s a lot of tension between everybody. He is very needy, and needs this and needs that, and he can’t do anything on his own. He’s afraid of everything… Um and I felt very angry with him, and frustrated and trapped that sometimes I don’t know what to do.
Warmth
In addition to those codes for criticism, speech samples also were rated as high, borderline, or low warmth as recommended by Vaughn and Leff (1976). High warmth was coded if parents expressed clear warmth based on tone, interest, and spontaneous sympathy, concern, and empathy. Borderline warmth was coded if parents expressed understanding, sympathy, and concern but only limited warmth of tone and/or a detached attitude. Low warmth was coded if parents expressed only a slight or no amount of understanding, sympathy, concern, enthusiasm, or interest. Due to the relatively low number of speech samples coded as low warmth (0–3% toward the child, 8–10% toward a partner) a dichotomous FMSS warmth rating was created by combining the low and borderline warmth categories and coded 0 versus high warmth, which was coded 1. The following excerpt is from a sample rated as ‘high warmth’:
[Child’s name] is, I think, a great person. He’s funny. He’s thirteen so he can be very moody sometimes, which is typical for thirteen year olds, and I realize that. We drive to school every day, so most of the time I really like driving in the car with him. We don’t always agree on the same music, but he’ll give mine a try and I’ll give his a try. He tells me funny things.
Family Socio-demographics
Socio-demographics were reported by parents and included in analyses as control variables if significantly associated with family emotional climate class membership. Target child age was coded in years and gender was coded as female = 1 and male = 0. Target child intellectual disability was based on medical or educational diagnosis of intellectual disability or if the child met criteria based on review of records reporting IQ and adaptive behavior; it was coded as intellectual disability = 1 and no intellectual disability = 0. Family size was the number of children in the family. Duration of the couple relationship was years in a committed relationship. Household income was coded 1–14, starting at ≤ $9999 = 1 and increasing by $10,000 to $20,000 intervals to ≥ $160,000 = 14.
Child-Related Challenges
Severity of child ASD symptoms was separately reported by each parent using the SRS-2, a 65-item questionnaire assessing autism symptoms in the past 6 months from ‘Not True’ = 1 to ‘Almost Always True’ = 4. The SRS-2 Total T-score was used and had high internal consistency (α = 0.88 for mothers and α = 0.86 for fathers). The severity of child emotional and behavioral problems was assessed by having parents separately rate the Child Behavior Check List (CBCL; Achenbach and Rescorla 2001) which had high internal consistency in our sample (α = 0.91 for mothers and α = 0.90 for fathers). The CBCL Total T-score has been shown to have good construct validity in ASD samples (Sikora et al. 2008).
Multiplex Families
The presence of an additional child or children with a neurodevelopmental disability, including ASD, or psychiatric disorder was reported on by parents and coded as yes = 1 or no = 0. Parents independently completed the Broad Autism Phenotype Questionnaire (BAPQ; Hurley et al. 2007) to assess their own level of BAP. The measure includes 36 statements rated from ‘very rarely’ = 1 to ‘very often’ = 6 (α = 0.93 for mothers and α = 0.91 for fathers).
Data Analysis
Descriptive statistics and histograms were used to examine the distribution of scores on measures and identify any outliers. Eighteen (6%) parents had missing items on the SRS-2, CBCL, or BAPQ. In all cases, more than 80% of items on the measure had been completed. A Little’s MCAR test statistic indicated that items were missing at random (p > .05) in all cases. Mean item score imputation for the individual was used to replace missing items to allow for the calculation of total scores. Thus, mothers and fathers in all 148 couples had scores on all study variables and were included in analyses.
Data analyses then proceeded in three stages, corresponding to the three study aims. First, phi coefficients were calculated to examine associations among mother and father warmth and criticism in the parent–child and parent couple relationships. McNemar’s tests were used to examine within-couple mother–father differences in these relationships.
Second, latent class analysis (Collins and Lanza 2010; Lanza et al. 2015) was used to identify subgroups of families characterized by distinct configurations of emotional climate. In this person-oriented approach, classes or subgroups are each composed of families that are similar to one another, based on their values on a set of dichotomous indicator variables. For this study, there were eight such variables: mother warmth in the parent–child relationship, father warmth in the parent–child relationship, mother warmth in the parent couple relationship, father warmth in the parent couple relationship, mother criticism in the parent–child relationship, father criticism in the parent–child relationship, mother criticism in the parent couple relationship, and father criticism in the parent couple relationship. The number of latent classes in the population is determined by which measurement model best represents the data, based on substantive theory and model fit criteria, namely relatively lower values on the Akaike information criterion (AIC) and sample-size adjusted Bayesian information criterion (BIC) and higher values on entropy (Celeux and Soromenho 1996). A model with fewer meaningful classes was preferred to a model with slightly better fit, but redundant or idiosyncratic small classes (Muthén 2004). In latent class analysis, each family has a greater than 0% chance but less than 100% chance of belonging to each class, but families are assigned to the class in which they had the highest probability of belonging (Johnson and Albert 2004).
Third, we examined the association between indicators of child-related challenges (SRS-2 and CBCL) and multiplex families (additional affected child and parent level of BAP) and family emotional climate class membership using one-way repeated measure analyses of variance (MANOVAs). We first examined whether family socio-demographics (child age, child gender, child intellectual disability status, family size, parent couple relationship duration, and household income) were associated with class membership. Any significant family socio-demographics were then controlled for in the analysis examining the association between indicators of child-related challenges and multiplex families and class membership. Pairwise comparisons were used to identify class differences.
Results
Table 1 displays the means, standard deviations, and range for study variables. Values of skewness and kurtosis indicated a relatively normal distribution for all continuous variables (skew range: − 0.49 to 0.77; kurtosis range: − 0.75 to 1.33). The target children with ASD had a mean SRS-2 Total T-score of 75.82 (SD = 10.30) as reported by mothers and 74.47 (SD = 10.52) as reported by fathers. The average CBCL Total T-score for the target child with ASD was 64.09 (SD = 8.51) as reported by mothers and 62.92 (SD = 8.85) as reported by fathers.
Mother Versus Father Warmth and Criticism
Overall, 47% of mothers and 51% of fathers expressed high warmth toward their child with ASD, and 47% and 48%, respectively, expressed high warmth toward their partners. In contrast, 23% of mothers and 14% of fathers expressed high criticism toward their child with ASD, and 30% and 19%, respectively, expressed high criticism toward their partners. Table 2 displays the small to modest associations between mothers’ and fathers’ FMSS criticism and warmth in the parent–child and parent couple relationships. When mothers expressed warmth toward their child with ASD, they were more likely to express warmth toward their partners (φ[148] = .34, p < .001); the same was true of criticism (φ[148] = .21, p = .012). Likewise, when fathers expressed warmth toward their child with ASD, they were more likely to express warmth toward their partners (φ[148] = .19, p < .021); the same was true of criticism (φ[148] = .21, p = .009). Not surprisingly, neither mothers nor fathers were likely to express both high warmth and high criticism in their relationships with their child with ASD or with each other (φ[148] = [− 0.40]–[− 0.56], p < .001). When one parent expressed high warmth or criticism of the child with ASD, the other parent was likely to do so as well (φ[148] = .22–.30, p < .01), and when one parent expressed high warmth or criticism of their partner, the emotion was often reciprocal (φ[148] = .29–.55, p < .001).
McNemar’s tests revealed that mothers were more likely to express high criticism in the parent–child relationship (χ2 = 5.28, p = .022) and parent couple relationship (χ2 = 5.63, p = .018) than fathers, within couples. There were no significant differences between the percentage of mothers versus father with high warmth in the parent–child relationship (χ2 = 0.43, p = .511) or in the parent couple relationship (χ2 = 0.00, p = 1.000), at a within-couple level.
Latent Class Classes of Family Emotional Climate
Table 3 summarizes the latent class analysis of family emotional climate, presenting fit statistics for models with two to six latent classes. There was a drop in AIC and sample size adjusted BIC with the addition of each class; however, the magnitude of change between the final two models was quite small (0.82 and 2.22, respectively) indicating that the six-class model was only weakly superior to the five-class model (Rafferty 1995). There was no improvement in entropy between the five- and six-class models (0.93 in both cases). Moreover, two of the classes in the six-class model included a small number of families (n = 6 and 9, respectively), raising concerns about outliers and replicability. Further, the final class in the six-class model made little sense conceptually. Thus, the five-class model was determined to be optimal based on fit, parsimony, and substantive meaning of the classes.
Table 4 presents the percentages of low and high warmth and criticism for mothers and fathers in each class. Figure 1 displays the average criticism and warmth ratings for each class. There was a Family Resilient class (Class 1; n = 63 [43% of the sample]) in which both parents in the family had low criticism and high warmth in both the parent–child and parent couple relationships. Consistent with the spillover hypothesis, there was a Family Distressed class (Class 2; n = 18 [12%]) in which both parents had high criticism and low warmth in both the parent–child and parent couple relationships. Three divergent classes of family emotional climate emerged. The Couple Distressed class (Class 3; n = 20 [14%]) consisted of families in which both parents had low criticism and high warmth in the parent–child relationship but high criticism and low warmth in the parent couple relationship. The Mother Distressed with Partner class (Class 4; n = 12 [8%]) involved mothers with low criticism and high warmth in the parent–child relationship but high criticism and low warmth in the parent couple relationship, whereas fathers had low criticism and a mixed pattern of warmth in both the parent–child and the parent couple relationships. In the Mother Low Warmth–Father Low Criticism class (Class 5; n = 35 [24%]), mothers had low warmth, paired with a mix of low or high criticism, in the parent–child and parent couple relationships, whereas fathers had low criticism and a mix of high or low warmth in the parent–child and parent couple relationships.
Predictors of Family Emotional Climate Class Membership
Table 5 displays the means and standard deviations for family socio-demographics and our key predictor variables by family class. A MANOVA indicated that family socio-demographics (child age, gender, and intellectual disability, parent couple relationship length, family size, and household income) were not significantly associated with class membership (F [24, 479] = 0.69, p = .863; Wilk’s Λ = 0.89). Thus, family socio-demographics were not controlled for when assessing the association between child-related challenges (SRS-2 and CBCL score) and multiplex families (additional affected children and parent level of BAP).
A one-way repeated measure MANOVA indicated a significant difference in our key predictor variables by family class (F (24, 465) = 2.46, p < .001; Wilk’s Λ = 0.66). Tests of between subject effects indicated that family classes differed on mothers’ ratings on the CBCL (F (4, 143) = 7.75, p < .001) and fathers’ ratings on the CBCL (F (4, 143) = 4.02, p = .004). Pairwise comparisons indicated that mothers’ ratings on the CBCL were lower in the Family Resilient class than in the Family Distressed, Couple Distressed, and Mother Low Warmth–Father Low Criticism classes. Fathers’ ratings on the CBCL were lower in the Family Resilient class than in the Family Distressed and Mother Low Warmth–Father Low Criticism classes. Family classes did not significantly differ on mothers’ or fathers’ rating on the SRS-2.
Tests of between subject effects indicated that family classes also significantly differed on mother level of BAP (F (4, 143) = 2.82, p = .027) and father level of BAP (F (4, 143) = 5.26, p = .001). Pairwise comparisons indicated that mother level of BAP was lower in the Family Resilient class than Mother Low Warmth–Father Low Criticism class. Father level of BAP was lower in the Family Resilient and Mother Low Warmth–Father Low Criticism classes than in the Family Distressed class. Having an additional child with a neurodevelopmental or psychiatric condition was not significantly associated with class membership.
Discussion
The emotional climate of families of children with ASD has only recently received research attention, yet may have critical implications for the development of children with ASD. It is clear from animal and human genetic and in utero neurobiological studies that the family environment does not cause ASD (Chaste and Leboyer 2012). It is critical for the field to continue to debunk myths that parenting can cause ASD. Yet, as is true in the general population (Brock and Kochanska 2015; Kopala-Sibley et al. 2017), family emotional climate is likely to be shaped by child-related factors and, in turn, to shape the functioning of children with ASD across time. The FMSS offers a reliable and valid way to assess the emotional quality of family relationships. However, to date, FMSS research on the ASD population has been limited to the investigation of the mother–child relationship (Baker et al. 2011; Griffith et al. 2015; Smith et al. 2008). The current study built on previous research by examining how the emotional quality of various family subsystems (parent–child and parent couple for mothers and fathers) combine to create classes of family emotional climate and identified predictors of class membership.
Our findings suggest that there are mother–father differences in the emotional quality of the parent–child and parent couple relationships in families of children with ASD. On average, mothers of children with ASD were more likely than fathers to express high criticism in the parent–child relationship. This difference may be related to previous findings that mothers report a higher level of parenting stress (Foody et al. 2015) and tend to take on more daily parenting responsibilities than fathers in families of children with ASD (Callander and Lindsay 2018). In the current study, we also found that mothers were more likely to express high criticism in the parent couple relationship than fathers. This difference, also found in non-ASD populations (Favez et al. 2017), may reflect broader gender differences in the experienced or expressed emotional quality of the couple relationship. Alternatively, there may be something unique about having a child with ASD that drives mothers to be more critical of their partner than fathers. Mothers’ higher average level of parenting stress may contribute to greater stress spillover between the parent–child and parent couple relationship compared to fathers, who have a lower average level of parenting stress.
We found that families of children with ASD fit into five different classes of family emotional climate. The largest class, 43% of all families, was Family Resilient, involving low criticism and high warmth across all family relationships. Thus, many families appear to be adapting well to child-related challenges associated with ASD. Only 12% of families were in the Family Distressed class involving high criticism and low warmth across family relationships. In line with the stress spillover hypothesis, stress may start in one family relationship and then carry into other family relationships (Almeida et al. 1999), and crossover from one parent to another (Falconier et al. 2015).
The remaining families exhibited opposing emotional quality across subsystems, in line with the divergence hypothesis (Erel and Burman 1995). Nearly 24% of families were in the Mother Low Warmth–Father Low Criticism class, 14% were in the Couple Distressed class, and 8% were in the Mother Distressed with Partner class. It appears that in many families of children with ASD, one or both parents prevent distress in one family relationship from carrying over into other relationships, and/or may compensate for one negative family subsystem by devoting resources to other family relationships.
In our sample, the severity of emotional and behavioral problems in the child with ASD predicted family emotional climate. The Family Resilient class was associated with a lower mother- and father-rated severity of child emotional and behavioral problems on the CBCL. The Family Distressed, Couple Distressed, and Mother Low Warmth–Father Low Criticism classes were associated with a higher mother- and father-rated severity of child emotional and behavioral problems. Thus, families undergoing more child-related challenges appear to be at greater risk for emotionally negative family relationships, and perhaps spillover between the parent–child and parent couple relationships. The emotional and behavioral problems of children with ASD have been found to be more strongly associated with parenting stress than children’s ASD symptoms (e.g., McStay et al. 2014). Efforts to reduce children’s emotional and behavioral problems may be most effective in improving family emotional climate.
Multiplex families were at risk for maladaptive classes of family emotional climate. Families in which mothers had a higher level of BAP were more likely to be in the Mother Low Warmth–Father Low Criticism class than the Family Resilient class. In contrast, families in which fathers had a higher level of BAP were most likely to be in the Family Distressed class. The effect of father level of BAP seems to take a toll on overall family emotional climate, whereas the effect of mother level of BAP is more localized, only affecting mothers’ family relationships. Families of children with ASD in which fathers exhibit a high level of BAP may derive the most benefit from family-wide interventions. Previous studies have shown that mothers and fathers who are high on BAP have different presentation of ASD-like traits (Klusek et al. 2014); specifically, fathers exhibited high aloof personality traits, whereas mothers exhibited high pragmatic language and social personality traits. In part, the different effect of father versus mother BAP may be due to the different constellation of BAP traits in fathers versus mothers. In contrast to our hypothesis, the presence of an additional child or children with a disability or psychiatric disorder did not predict family emotional climate class.
It is likely that other factors shape family emotional climate class membership, and may explain why some parents appear to be able to avoid spillover and crossover of a negative family subsystem into other family subsystems. For example, the Couple Distressed and Mother Distressed with Partner classes involve families with problems in the parent couple relationships but positive parent–child relationships. In these cases, adaptive co-parenting behaviors appear to negate spillover and crossover effects. Further, child or parent services, such as more therapist hours or a large support network, may increase parent emotional resources and help avoid spillover and crossover effects. Future research should examine these and other potential predictors of family emotional climate.
Study Strengths and Limitations and Future Research
The current study had several strengths. We investigated the parent–child and parent couple relationships in both mothers and fathers of children with ASD, providing a rich family-wide assessment of emotional climate. The study also employed a well-validated measure of the emotional quality of family relationships via the FMSS, which has been shown to mirror actual family interactions (Weston et al. 2017). As always, the current study had limitations. First, although the FMSS has been found to have robust associations with self-report measures assessing the global quality of the parent–child relationship (Sher-Censor 2015) and observed interactions (Weston et al. 2017), it is possible that the FMSS is biased toward reflecting recent as opposed to long-standing parent–child or parent couple relationship experiences. Second, the FMSS and ratings of parent BAP and child emotional and behavioral problems were all based on information from parents, perhaps inflating relations among constructs. Third, we did not include FMSS on a comparison group; thus, we do not know if mother–father differences and the classes of family emotional quality found in our sample differ from that of families of typically developing children or from families of children with other types of disabilities. Fourth, our sample of families of children with ASD was also fairly homogeneous in race/ethnicity and socioeconomic status and included mother–father co-residing parents. Although family socio-demographics were not associated with family emotional climate in our sample, factors such as household income, job security, and health insurance coverage may be important predictors of family emotional climate class in more diverse samples. Likewise, our finding that 43% of the sample was in the Family Resilient class may reflect the overall economic stability of the families in our sample. Finally, future longitudinal research is needed to determine how family emotional climate shifts across time and impacts the development of children with ASD.
Implication and Clinical Practice
Our findings indicate that the most common class of family emotional climate, occurring in 43% of the sample, was Family Resilient with high warmth and low criticism across family relationships. Thus, it is important to debunk myths that all families of children with ASD are vulnerable. Indeed, many families exhibited positive emotional quality across all family subsystems, and this climate is likely to foster adaptive functioning in children with ASD. The remaining 57% of families of children with ASD experienced various combinations of maladaptive family emotional climates. Interventions should be directed toward families in which a parent evidences high BAP and/or the child with ASD has a high severity of emotional and behavioral problems, as these factors were associated with maladaptive family emotional climate. Interventions should also engage the entire family, if possible, as parent–child and parent couple relationships were often connected at both a within- and across-parent level. Thinking about the various family relationships, parents should be guided in identifying and recognizing how child functioning can shape the family environment, and in turn, how the family environment can influence the child with ASD’s emotions and behaviors.
Notes
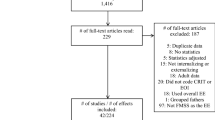
The original study included 187 families. However, this study included only those families in which both parents participated in the in-person portion of the second wave of data collection, when the FMSS was administered. The only difference between the families in the original study and the families in current analyses was that mothers in the original sample were more likely to be ethnically diverse (F = 4.19, p = .042).
References
Achenbach, T. M., & Rescorla, L. A. (2001). Manual for the ASEBA school-age forms & profiles. Burlington, VT: University of Vermont, Research Center for Children, Youth, & Families.
Almeida, D. M., Wethington, E., & Chandler, A. L. (1999). Daily transmission of tensions between marital dyads and parent-child dyads. Journal of Marriage and the Family, 61, 49–61. https://doi.org/10.2307/353882.
American Psychiatric Association. (2014). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (5th ed.). Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Publishing.
Baeza-Velasco, C., Michelon, C., Rattaz, C., Pernon, E., & Baghdadli, A. (2013). Separation of parents raising children with autism spectrum disorders. Journal of Developmental and Physical Disabilities, 25, 613–624. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10882-013-9338-0.
Baker, J. K., Smith, L. E., Greenberg, J. S., Seltzer, M. M., & Taylor, J. L. (2011). Change in maternal criticism and behavior problems in adolescents and adults with autism across a 7-year period. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 120, 465–475. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0021900.
Bora, E., Aydın, A., Saraç, T., Kadak, M. T., & Köse, S. (2017). Heterogeneity of subclinical autistic traits among parents of children with autism spectrum disorder: Identifying the broader autism phenotype with a data-driven method. Autism Research, 10, 321–326. https://doi.org/10.1002/aur.1661.
Brock, R. L., & Kochanska, G. (2015). Decline in the quality of family relationships predicts escalation in children’s internalizing symptoms from middle to late childhood. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 43, 1295–1308. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10802-015-0008-9.
Callander, E. J., & Lindsay, D. B. (2018). The impact of childhood autism spectrum disorder on parent’s labour force participation: Can parents be expected to be able to re-join the labour force? Autism, 22, 542–548. https://doi.org/10.1177/1362361316688331.
Celeux, G., & Soromenho, G. (1996). An entropy criterion for assessing the number of clusters in a mixture model. Journal of Classification, 13, 195–212. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01246098.
Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2018). Autism spectrum disorder. Retrieved May 4, 2018, from https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/autism/addm.html.
Chaste, P., & Leboyer, M. (2012). Autism risk factors: Genes, environment, and gene-environment interactions. Dialogues in Clinical Neuroscience, 14, 281–292.
Cohrs, A. C., & Leslie, D. L. (2017). Depression in parents of children diagnosed with autism spectrum disorder: A claims-based analysis. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 47, 1416–1422. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-017-3063-y.
Collins, L. M., & Lanza, S. T. (2010). Latent class and latent transition analysis: With applications in the social, behavioral, and health sciences (Vol. 718). New York: Wiley.
Constantino, J. N., & Gruber, C. P. (2012). Social Responsiveness Scale, Second Edition (SRS-2). Torrance, CA: Western Psychological Services.
Erel, O., & Burman, B. (1995). Interrelatedness of marital relations and parent-child relations: A meta-analytic review. Psychological Bulletin, 118, 108–132. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-2909.118.1.108.
Estes, A., Olson, E., Sullivan, K., Greenson, J., Winter, J., Dawson, G., et al. (2013). Parenting-related stress and psychological distress in mothers of toddlers with autism spectrum disorders. Brain and Development, 35, 133–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.braindev.2012.10.004.
Falconier, M. K., Nussbeck, F., Bodenmann, G., Schneider, H., & Bradbury, T. (2015). Stress from daily hassles in couples: Its effects on intradyadic stress, relationship satisfaction, and physical and psychological well-being. Journal of Marital and Family Therapy, 41, 221–235. https://doi.org/10.1111/jmft.12073.
Favez, N., Cairo Notari, S., Antonini, T., & Charvoz, L. (2017). Attachment and couple satisfaction as predictors of expressed emotion in women facing breast cancer and their partners in the immediate post-surgery period. British Journal of Health Psychology, 22, 169–185. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjhp.12223.
Fine, M. A., & Fincham, F. D. (2013). Handbook of family theories: A content-based approach. New York: Routledge.
Foody, C., James, J. E., & Leader, G. (2015). Parenting stress, salivary biomarkers, and ambulatory blood pressure: A comparison between mothers and fathers of children with autism spectrum disorders. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 45, 1084–1095. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-014-2263-y.
Greenberg, J. S., Seltzer, M. M., Hong, J., & Orsmond, G. I. (2006). Bidirectional effects of emotion and behavior problems and symptoms in adolescents and adults with autism. American Journal on Mental Retardation, 111, 229–249. https://doi.org/10.1352/0895-8017(2006)111%5b229:BEOEEA%5d2.0.CO;2.
Griffith, G. M., Hastings, R. P., Petalas, M. A., & Lloyd, T. J. (2015). Mothers’ expressed emotion towards children with autism spectrum disorder and their siblings. Journal of Intellectual Disability Research, 59, 580–587. https://doi.org/10.1111/jir.12178.
Guralnick, M. J. (2011). Why early intervention works: A systems perspective. Infants and Young Children, 24, 6. https://doi.org/10.1097/IYC.0b013e3182002cfe.
Hartley, S. L., Barker, E. T., Seltzer, M. M., Floyd, F., Greenberg, J., Orsmond, G., et al. (2010). The relative risk and timing of divorce in families of children with an autism spectrum disorder. Journal of Family Psychology, 24, 449–457. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0019847.
Hartley, S. L., Papp, L. M., Mihaila, I., Bussanich, P. M., Goetz, G., & Hickey, E. J. (2017). Couple conflict in parents of children with versus without autism: Self-reported and observed findings. Journal of Child and Family Studies, 26, 2152–2165. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10826-017-0737-1.
Hastings, R. P., Daley, D., Burns, C., & Beck, A. (2006). Maternal distress and expressed emotion: Cross-sectional and longitudinal relationships with behavior problems of children with intellectual disabilities. American Journal on Mental Retardation, 111, 48–61. https://doi.org/10.1352/0895-8017(2006)111%5b48:MDAEEC%5d2.0.CO;2.
Hock, R. M., Timm, T. M., & Ramisch, J. L. (2012). Parenting children with autism spectrum disorders: A crucible for couple relationships. Child and Family Social Work, 17, 406–415. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2206.2011.00794.x.
Hurley, R. S., Losh, M., Parlier, M., Reznick, J. S., & Piven, J. (2007). The Broad Autism Phenotype Questionnnaire. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 37, 1679–1690. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-006-0299-3.
Iles, J., Spiby, H., & Slade, P. (2014). Modification and preliminary use of the five-minute speech sample in the postpartum: Associations with postnatal depression and posttraumatic stress. Archives of Women’s Mental Health, 17, 389–402. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00737-014-0414-y.
Johnson, V. E., & Albert, J. H. (2004). Ordinal regression models. In D. Kaplan (Ed.), Handbook of quantitative methodology for the social sciences (pp. 345–368). Newbury Park, CA: Sage.
Jokiranta-Olkoniemi, E., Cheslack-Postava, K., & Sucksdorff, D. (2016). Risk of psychiatric and neurodevelopmental disorders among siblings of probands with autism spectrum disorders. JAMA Psychiatry, 73, 622–629. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2016.0495.
Klusek, J., Losh, M., & Martin, G. E. (2014). Sex differences and within-family associations in the broad autism phenotype. Autism, 18, 106–116. https://doi.org/10.1177/1362361312464529.
Kopala-Sibley, D. C., Dougherty, L. R., Dyson, M. W., Laptook, R. S., Olino, T. M., Bufferd, S. J., et al. (2017). Early childhood cortisol reactivity moderates the effects of parent–child relationship quality on the development of children’s temperament in early childhood. Developmental Science, 20, e12378. https://doi.org/10.1111/desc.12378.
Labella, M. H., Narayan, A. J., & Masten, A. S. (2016). Emotional climate in families experiencing homelessness: Associations with child affect and socioemotional adjustment in school. Social Development, 25, 304–321. https://doi.org/10.1111/sode.12154.
Lanza, S. T., Dziak, J. J., Huang, L., Wagner, A., & Collins, L. M. (2015). PROC LCA & PROC LTA users’ guide (version 1.3.2). University Park: The Methodology Center, Penn State.
Lord, C., DiLavore, P. C., Gotham, K., Guthrie, W., Luyster, R. J., Risi, S., et al. (2012). Autism diagnostic observation schedule: ADOS-2. Los Angeles: Western Psychological Services.
Lord, C., Risi, S., Lambrecht, L., Cook, E. J., Leventhal, B. L., DiLavore, P. C., et al. (2000). The autism diagnostic observation schedule-generic: A standard measure of social and communication deficits associated with the spectrum of autism. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 30, 205–223. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1005592401947.
Losh, M., Childress, D., Lam, K., & Piven, J. (2008). Defining key features of the broad autism phenotype: A comparison across parents of multiple- and single-incidence autism families. American Journal of Medical Genetics Part B: Neuropsychiatric Genetics, 147, 424–433. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajmg.b.30612.
Mackler, J. S., Kelleher, R. T., Shanahan, L., Calkins, S. D., Keane, S. P., & O’Brien, M. (2015). Parenting stress, parental reactions, and externalizing behavior from ages 4 to 10. Journal of Marriage and Family, 77, 388–406. https://doi.org/10.1111/jomf.12163.
Magaña, A. B., Goldstein, M. J., Karno, M., Miklowitz, D. J., Jenkins, J., & Falloon, I. R. H. (1986). A brief method for assessing expressed emotion in relatives of psychiatric patients. Psychiatry Research, 17, 203–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/0165-1781(86)90049-1.
McStay, R. L., Dissanayake, C., Scheeren, A., Koot, H. M., & Begeer, S. (2014). Parenting stress and autism: The role of age, autism severity, quality of life and problem behaviour of children and adolescents with autism. Autism, 18, 502–510. https://doi.org/10.1177/1362361313485163.
Messinger, D. S., Young, G. S., Webb, S. J., Ozonoff, S., Bryson, S. E., Carter, A., et al. (2015). Early sex differences are not autism-specific: A Baby Siblings Research Consortium (BSRC) study. Molecular Autism, 6, 32. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13229-015-0027-y.
Muthén, B. (2004). Latent variable analysis: Growth mixture modeling and related techniques for longitudinal data. In D. Kaplan (Ed.), Handbook of quantitative methodology for the social sciences (pp. 345–368). Newbury Park, CA: Sage.
Newland, R. P., Ciciolla, L., & Crnic, K. A. (2015). Crossover effects among parental hostility and parent–child relationships during the preschool period. Journal of Child and Family Studies, 24, 2107–2119. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10826-014-0012-7.
Orsmond, G. I., Lin, L. Y., & Seltzer, M. M. (2007). Mothers of adolescents and adults with autism: Parenting multiple children with disabilities. Intellectual and Developmental Disabilities, 45, 257–270. https://doi.org/10.1352/1934-9556(2007)45%5b257:MOAAAW%5d2.0.CO;2.
Pruitt, M. M., Rhoden, M., & Ekas, N. V. (2018). Relationship between the broad autism phenotype, social relationships and mental health for mothers of children with autism spectrum disorder. Autism, 22, 171–180. https://doi.org/10.1177/1362361316669621.
Rafferty, A. E. (1995). Bayesian model selection in social research. Sociological Methodology, 25, 111–163.
Rodriguez, G., Hartley, S. L., & Bolt, D. (2019). Transactional relations between parenting stress and child autism symptoms and behavior problems. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-018-3845-x.
Romero-Gonzalez, M., Chandler, S., & Simonoff, E. (2018). The relationship of parental expressed emotion to co-occurring psychopathology in individuals with autism spectrum disorder: A systematic review. Research in Developmental Disabilities, 72, 152–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ridd.2017.10.022.
Ryan, R. M., Martin, A., & Brooks-Gunn, J. (2006). Is one good parent good enough? Patterns of mother and father parenting and child cognitive outcomes at 24 and 36 months. Parenting, 6, 211–228. https://doi.org/10.1207/s15327922par0602&3_5.
Schaefer, G. B., & Mendelsohn, N. J. (2013). Clinical genetics evaluation in identifying the etiology of autism spectrum disorders: 2013 guideline revisions. Genetics in Medicine, 15, 399. https://doi.org/10.1038/gim.2013.32.
Sher-Censor, E. (2015). Five minute speech sample in developmental research: A review. Developmental Review, 36, 127–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dr.2015.01.005.
Sikora, D. M., Hall, T. A., Hartley, S. L., Gerrard-Morris, A. E., & Cagle, S. (2008). Does parent report of behavior differ across ADOS-G classifications: Analysis of scores from the CBCL and GARS. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 38, 440–448. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-007-0407-z.
Sim, A., Cordier, R., Vaz, S., & Falkmer, T. (2016). Relationship satisfaction in couples raising a child with autism spectrum disorder: A systematic review of the literature. Research in Autism Spectrum Disorders, 31, 30–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rasd.2016.07.004.
Smith, L. E., Greenberg, J. S., Seltzer, M. M., & Hong, J. (2008). Symptoms and behavior problems of adolescents and adults with autism: Effects of mother-child relationship quality, warmth, and praise. American Journal on Mental Retardation, 113, 387–402. https://doi.org/10.1352/2008.113:387-402.
Van Humbeeck, G., Van Audenhove, C., De Hert, M., Pieters, G., & Storms, G. (2002). Expressed emotion: A review of assessment instruments. Clinical Psychology Review, 22, 321–341. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0272-7358(01)00098-8.
Vaughn, C., & Leff, J. (1976). The measurement of expressed emotion in the families of psychiatric patients. British Journal of Clinical Psychology, 15, 157–165. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.2044-8260.1976.tb00021.x.
Weston, S., Hawes, D. J., & Pasalich, D. S. (2017). The five minute speech sample as a measure of parent–child dynamics: Evidence from observational research. Journal of Child and Family Studies, 26, 118–136. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10826-016-0549-8.
Yorke, I., White, P., Weston, A., Rafla, M., Charman, T., & Simonoff, E. (2018). The association between emotional and behavioral problems in children with autism spectrum disorder and psychological distress in their parents: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-018-3605-y.
Zaidman-Zait, A., Mirenda, P., Duku, E., Szatmari, P., Georgiades, S., Volden, J., et al. (2014). Examination of bidirectional relationships between parent stress and two types of problem behavior in children with autism spectrum disorder. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 44, 1908–1917. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-014-2064-3.
Funding
This research was supported by a Grant from the National Institute of Mental Health (Hartley; R01 MH099190) and National Institute of Child Health and Development (Messing; U54 HD090256).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
EJH conceived of the study discussed in this paper, participated in its design and coordination, conducted statistical analysis, interpreted the analysis, and drafted the manuscript. RLN participated and consulted in conducting statistical analysis, assisted with the interpretation of findings, and helped to draft the manuscript. SLH conceived of the larger ongoing study from which data were taken, helped to draft the manuscript, and assisted with the interpretation of findings. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained by all participating families in this study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hickey, E.J., Nix, R.L. & Hartley, S.L. Family Emotional Climate and Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder. J Autism Dev Disord 49, 3244–3256 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-019-04037-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-019-04037-6