Abstract
Phosphorus release from Microcystis aeruginosa and attached bacterium (Pseudomonas sp.) isolated from Lake Taihu was examined using a phosphorus isotope tracer in order to investigate the phosphorus transference between the two species. Our results reveal that the amount of phosphorus released form 32P-saturated M. aeruginosa is determined by its growth phase and most of phosphorus is assimilated by Pseudomonas finally while the amount of phosphorus released from 32P-saturated Pseudomonas is also determined by the growth phase of M. aeruginosa and most of them are assimilated by M. aeruginosa. The results suggest that phosphorus transference occurs between M. aeruginosa and its attached Pseudomonas . This process makes microenvironment of mucilage of M. aeruginosa attached bacteria maintain relative high amounts of phosphorus. Attached bacteria may be a temporary phosphorus bank to the growth of M. aeruginosa, and assimilation of phosphorus by M. aeruginosa becomes easy when M. aeruginosa is in lag growth phase. Thus, the phosphorus exchange between M. aeruginosa and attached Pseudomonas in microenvironment may be important to microfood web and cyanobacteria bloom.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Microcystis aeruginosa is the dominant cyanobacterium in Lake Taihu, a shallow hypereutrophic lake in eastern China with extensive cyanobacterial algal blooms in summer and autumn (Dokulil et al., 2000). M. aeruginosa forms large mucilaginous colonies, usually colonized by the great deal of bacteria. There is a mutualistic relationship between M. aeruginosa and attached bacteria (Whitton, 1973). This symbiotic relation may be favorable to Microcystis cells (Steppe et al., 1996). M. aeruginosa constitute a microhabitat where attached bacteria are sheltered from grazing by embedding in the mucilage. The microenvironment allows attached bacteria to associate with the primary producer of organic carbon for its growth. In this microenvironment, heterotrophic bacteria are important: (1) as contributors of CO2 and possibly sources of nitrogen, phosphorus and trace elements to M. aeruginosa; (2) as primary consumers of algal excretions; and (3) as decomposers. Some bacteria may promote blooms while others have algicidal and lysis effects and are involved in termination and decomposition of blooms (Caiola, 1991; Pellegrini et al., 1997; Lovejoy et al., 1998; Van Hannen et al., 1999; Manage et al., 2000; Manage et al., 2001). Thus, the metabolic relationship of Microcystis with attached bacteria is important for understanding bloom dynamics.
Phosphorus is the major limiting nutrient for primary producer, including M. aeruginosa in Lake Taihu (Dokulil et al., 2000). Pilot studies were conducted on the phosphorus metabolism of M. aeruginosa and its attached bacteria, respectively (Shi et al., 2003; Shi et al., 2004; Zou et al., 2005). The information of interaction of cyanobacterium with its attached bacterium for phosphorus transference was little. In this paper, a phosphorus isotope tracer was used to study phosphorus uptake and release from M. aeruginosa and its attached bacterium, Pseudomonas, to probe their interactions and phosphorus transformation.
Materials and methods
Organism and cultivation
Microcystis aeruginosa was obtained from Institute of Hydrobiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences. It was grown in the modified MA medium (pH = 8.6) in which inorganic phosphorus was replaced by β-Na2-glycerophosphate (Oh & Lee, 2000). Cultures were incubated at 25°C under illumination intensity of 2200 lx with a 14:10 h of light:dark cycle.
Pseudomonas sp. was isolated from the mucilage of Microcystis in Lake Taihu, China and grown in complex medium: glucose 6.0; NH4Cl 1.0; NaCl 2.0; MgSO4·7H2O 0.2; K2HPO4 1.0; KH2PO4 1.0; yeast extract 0.5 (all in grams per liter of deionized water). pH was adjusted to 7.2–7.5 before the complex medium was autoclaved.
Precultivation
This study was conducted with phosphorus-starved M. aeruginosa, 32P-saturated M. aeruginosa, phosphorus-starved Pseudomonas and 32P-saturated Pseudomonas. M. aeruginosa and Pseudomonas in exponential growth phase were harvested by centrifugation at 10,000g for 15 min respectively, washed with sterile deionized water and resuspended in MA medium without phosphorus. Phosphorus-starved cells were directly obtained after incubation for 3 days. Phosphorus-starved cells were collected by centrifugation and transferred to MA medium in which β-Na2-glycerophosphate was replaced with 12 mg l−1 Na2H32PO4, then were incubated for 3 days to obtain 32P-saturated cells of M. aeruginosa and Pseudomonas respectively.
Transference of phosphorus from 32P-saturated M. aeruginosa to Pseudomonas
Attachment of bacteria to M. aeruginosa mucilage made it difficult to measure 32P content in bacteria cells or in cyanobacteria cells. Considering this difficulty, a dialysis membrane bag was used to separate Pseudomonas from M. aeruginosa. However, low molecular weight substances, such as phosphate and small organic compounds, could move across the dialysis membrane.
Phosphorus-starved Pseudomonas cells were harvested by centrifugation at 10,000g for 15 min, and washed with sterile deionized water and resuspended in a 500 ml beaker containing 200 ml MA medium without phosphorus to 1.0 × 107 cell ml−1. 32P-saturated Microcystis cells were harvested by the same way except they were resuspended in the dialysis bag to 5.2 × 106 cell ml−1. This dialysis bag was put in the beaker so then M. aeruginosa and Pseudomonas cells were separated, while phosphate could migrate across the dialysis membrane. They were incubated at 25°C under a 14:10 h of light:dark cycle.
In order to probe the change of intracellular phosphorus, the cells of M. aeruginosa or Pseudomonas in certain volume were separated respectively via centrifugation at 10000 g for 15 min and rinsed several times with MA medium until rinse solution radioactivity was close to background. These cells were digested with 0.2 ml 60% HClO4 and 0.4 ml 30% H2O2 at 80°C for 60 min. Then, the digested liquids and the upper aqueous solution separated by centrifugation were respectively put into scintillation vials containing 5 ml Triton X-100 toluene scintillator to analyze the radioactivity with a Beckman LS9800 liquid scintillation counter. Actual phosphorus concentration was corrected using the radioactive decay rate. All samples had three replicates.
In order to measure the biomass of M. aeruginosa and Pseudomonas, their optical densities were measured with at 460 nm and 380 nm, respectively. Then, the amounts of 32P in M. aeruginosa or Pseudomonas were calculated.
Transference of phosphorus from 32P-saturated Pseudomonas to M. aeruginosa
The experimental procedures were same as described above except that phosphorus-starved M. aeruginosa was incubated in a 500 ml beaker, while 32P-saturated Pseudomonas was incubated in dialysis bag.
Results
Transference of phosphorus from 32P-saturated M. aeruginosa to Pseudomonas
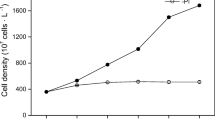
The transference of phosphorus from M. aeruginosa to Pseudomonas was investigated in a culture system of phosphorus-starved Pseudomonas and 32P-saturated M. aeruginosa which were separated by a dialysis membrane (Fig. 1a). The growth phases of M. aeruginosa comprised four distinct phases of the lag (0–1 day), exponential (1–4 day), stationary (4–6 day) and decline phases (6–12 day) while the growth phases of Pseudomonas was in the exponential phase. The total 32P in Pseudomonas always increased though the increase was slight for Pseudomonas in initial 4-days. Because of the growth of Pseudomonas and its incessant assimilation of 32P, the 32P content in Pseudomonas increased after M. aeruginosa was in the stationary phase. 32P content in Pseudomonas increased to 50% of the total 32P on the 12th day when M. aeruginosa was in the decline phase.
During the whole experiment period, the intracellular 32P content of M. aeruginosa decreased at all times. The 32P concentration in the aqueous solution remained relative steadily from the 1st day to the 9th day, then the sharp increase happened because M. aeruginosa in decline growth phase released a large amount of phosphorus to aqueous solution.
Transference of phosphorus from 32P-saturated Pseudomonas to M. aeruginosa
Not only phosphorus could move from M. aeruginosa to Pseudomonas, but also from Pseudomonas to M. aeruginosa. When phosphorus-starved M. aeruginosa was present, partitioning of 32P released from 32P-saturated Pseudomonas was observed (Fig. 1b). The growth of M. aeruginosa exhibited the lag phase (0–2 day), exponential phase (2–9 day) and decline phase (9–12 day) while Pseudomonas grew slightly at all times. Most of 32P released from Pseudomonas was assimilated by M. aeruginosa.
Intracellular 32P content of M. aeruginosa increased in the lag and exponential phases, but decreased in decline phase which decrease of 32P content in M. aeruginosa was due to the growth of Pseudomonas though this decrease was not rapid. 32P concentration in the aqueous solution increased in the first day and then remained relative steadily in the following days.
Discussion
In this experimental system, phosphorus was main factor for the growth of M. aeruginosa and Pseudomonas and the latter was also controlled by organic carbon. When the intracellular phosphorus content of M. aeruginosa was luxury, it grew by utilization of the intracellular phosphorus in its lag and exponential phases (Okada & Sudo, 1982), thus, only 20% of intracellular phosphorus was released form M. aeruginosa to aqueous solution and to Pseudomonas. However, M. aeruginosa released a lot of phosphorus in its stationary and decline phases while it could simultaneously provide Pseudomonas with organic carbon and trace elements (Sommaruga & Robarts, 1997; Worm, 1998; Brunberg, 1999). Thus, the growth of Pseudomonas was better and the assimilated phosphorus was more when M. aeruginosa was in decline phase than that in stationary phase.
After the amount of M. aeruginosa was low enough, its second growth became possible. M. aeruginosa could use phosphorus in Pseudomonas to grow because Pseudomonas had a geat deal of phosphorus which was assimilated from overripe M. aeruginosa formerly (Fig. 1b). Compared with the phosphorus transference form M. aeruginosa to Pseudomonas, phosphorus movement form Pseudomonas to M. aeruginosa was easy and a great deal of 32P was assimilated by M. aeruginosa in lag and exponential phases. When M. aeruginosa was in the decline phase, its intracellular 32P then turned back to Pseudomonas again. This process made soluble phosphorus in aqueous solution stable. Thus, phosphorus released form M. aeruginosa could store in attached bacteria and Pseudomonas might be a temporary phosphorus bank to M. aeruginosa in the microenvironment for its growth.
Conclusion
Phosphorus transference from Pseudomonas to M. aeruginosa occurs when M. aeruginosa is in grow phase while phosphorus transference from M. aeruginosa to Pseudomonas happens when M. aeruginosa is in decline phase. Pseudomonas may serve as a temporary phosphorus bank to M. aeruginosa in the microenvironment. Thus, phosphorus transference between cyanobacteria and their attached bacteria is decided by their growth phases and phosphorus amount and this exchange could keep an amount of phosphorus in the microenvironment of cyanobacteria and their attached bacteria which is important to microfood web and cyanobacteria bloom.
References
Brunberg, A. K., 1999. Contribution of bacteria in the mucilage of Microcystis spp. to benthic and pelagic bacterial production in a hypereutrophic lake. FEMS Microbiology Ecology 29: 13–22.
Caiola, M. G., 1991. Bdellovibrio-like bacteria in Microcystis aeruginosa. Algological Studies 64: 369–376.
Dokulil, M., W. Chen & Q. Cai, 2000. Anthropogenic impacts to large lakes in China: the Tai Hu example. Aquatic Ecosystem Health and Management 3: 81–94.
Lovejoy, C., J. P. Bowman & G. M. Hallegraeff, 1998. Algicidal effects of a novel marine Pseudoalteromonas isolate (Class Proteobacteria, Gamma Subdivision) on harmful algal bloom species of the genera Chattonella, Gymnodinium, and Heterosigma. Applied Environmental Microbiology 64: 2806–2813.
Manage, P. A., Z. Kawabata & S. Nakano, 2000. Algicidal effect of the bacterium Alcaligenes denitrificans on Microcystis spp.. Aquatic Microbial Ecology 22: 111–117.
Manage, P. A., Z. Kawabata & S. Nakano, 2001. Dynamics of cyanophage-like particles and algicidal bacteria causing Microcystis aeruginosa mortality. Limnology 2: 73–78.
Oh, H. M. & S. J. Lee, 2000. Microcystin production by Microcystis aeruginosa in a phosphorus-limited chemostat. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 66: 176–179.
Okada, M. & R. Sudo, 1982. Phosphorus uptake and growth of bule-green alga, Microcystis aeruginosa. Biotechnology and Bioengineering 24: 143–152.
Pellegrini, S., L. Allievi, B. Lolli & M. G. Caiola, 1997. Bdellovibrio isolation from the Lake Varese (Italy). Annali Di Microbiologia ED Enzimologa 47: 121–129.
Shi, X., L. Yang, X. Niu & L. Xiao, 2003. Intraintracellular phosphorus metabolism of Microcystis aeruginosa under various redox potential in darkness. Micobiological Research 158: 345–352.
Shi, X., L. Yang, F. Wang, L. Xiao, L. Jiang, Z. Kong, G. Gao & B. Qin, 2004. Growth and phosphate uptake kinetics of Microcystis aeruginosa under varying environmental conditions. Journal of Environmental Sciences 16: 88–92 (in Chinese).
Sommaruga, R. & R. D. Robarts, 1997. The significance of autotrophic and heterotrophic picoplankton in hypertrophic ecosystems. FEMS Microbiology Ecology 24: 187–200.
Steppe, T. F., J. B. Olson, H. W. Paerl, R. W. Litaker & J. Belnap, 1996. Consortial N2 fixation: a strategy for meeting nitrogen requirements of marine and terrestrial cyanobacterial mats. FEMS Microbiology Ecology 21: 149–156.
Van Hannen, E. J., G. Zwart & H. J. Laanbroek, 1999. Changes in bacterial and eukaryotic community structure after mass lysis of filamentous cyanobacteria associated with viruses. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 65: 795–801.
Whitton, B. A., 1973. Interactions with other organisms. In Carr, N. G. & B. A. Whitton (eds), The Biology of Blue-green Algae. Blackwell, Oxford: 415–433.
Worm, J., 1998. Dynamics of heterotrophic bacteria attached to Microcystis spp. (Cyanobacteria). Aquatic Microbial Ecology 14(1): 19–28.
Zou, D., L. Xiao, L. Yang & Y Wan, 2005. Effects of Phosphorus Sources of different forms on phosphorus metabolism of Microcystis aeruginosa and adhesive Pseudomonas sp.. Environmental Science 26(3): 118–121 (in Chinese).
Acknowledgements
We thank F. Wang (Modern Analysis Center, Nanjing University) for their technical assistances. This study was funded by Chinese Academy of Sciences (No. KZCX2-311), “973” Project (No. 2002CB412307) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 40371102, 40501078).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, L., Yang, L., Xiao, L. et al. Quantitative studies on phosphorus transference occuring between Microcystis aeruginosa and its attached bacterium (Pseudomonas sp.). Hydrobiologia 581, 161–165 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-006-0518-0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-006-0518-0