One new δ-valerolactone (1) and one new natural phenolic glycoside 2, together with four known compounds 3–6, were isolated from the fruits of Ligustrum lucidum. Their structures were elucidated on the basis of spectral data. The chemical transformation from 2 to 3 was observed. The immunomodulatory activities of the compounds were also evaluated.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
The fruits of Ligustrum lucidum Ait. (Oleaceae) are known as Nuzhenzi, and it is commonly used in Chinese medicine to supplement “kidneys”, nourish “yin,” strengthen liver, and clear vision [1]. It was also reported to possess antioxidant, antiinflammatory, immunomodulatory, and hepatoprotective activities [2]. Chemical studies have found volatile components, triterpenes, flavonoids, secoiridoid glucosides, and phenolic compounds from this material [3]. Herein we describe the isolation and structural identification of one new compound 1 and one new natural product 2 together with four known compounds 3–6 from the fruits of this medicinal material.
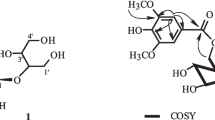
Compound 1 was isolated as a white powder. UV: λmax 216 nm. [α] 20D –131.7° (c 0.20, MeOH). Its molecular formula was determined to be C10H14O4 on the basis of HR-ESI-MS [M + Na]+ at m/z 221.0794 (calcd: 221.0790), indicating four degrees of unsaturation. In the 1H NMR spectrum (Table 1), one methyl (δ 1.78), one methoxyl (3.60), three methylenes (1.76 and 2.03, 2.44 and 2.57, 4.13 and 4.35), and one methine (3.28), as well as one olefinic proton (6.83), were observed. The 13C NMR and DEPT spectrum (Table 1) gave 10 carbon signals, which were attributed to one methyl, one methoxyl, three methylenes, one methine, two olefinic carbons (δ 140.5 and 130.2), and two carbonyl groups (165.8 and 171.6). In the 1H–1H COSY spectrum, correlations from H-6 (4.13 and 4.35) to H-5 (1.76 and 2.03) and from H-4 (3.28) to H-5 (1.76 and 2.03) and H-9 (2.44 and 2.57) suggested the presence of the CH2CH2CHCH2 moiety. The methoxyl (3.60) and H-9 (2.44 and 2.57) displayed HMBC correlations to C-10 (171.6), which established the CH2COOCH3 moiety, and the correlation from H-8 (1.78) to C-3 (130.2) indicated that the moiety =CHCH3 was connected to C-3. The additional correlations from H-6 to C-2 (165.8) and C-4 (28.9) were also observed. From the above data, the structure of 1 was determined as (3-ethylidene-2-oxotetrahydropyran-4-yl)-acetic acid methyl ester.
Compound 2 was obtained as a white amorphous powder. [α] 20D –85.1° (c 0.07, MeOH). Its HR-ESI-MS showed a [M + Na]+ ion peak at m/z 365.1212 (calcd 365.1186), which established the molecular formula as C16H22O8. In the 1H NMR spectrum, the AA’BB’ spin systems at δ 7.04 (2H, d, J = 8.7 Hz) and 6.67 (2H, d, J = 8.7 Hz) indicated that 2 had a para-substituted aromatic ring. The 13C NMR and DEPT spectra revealed 16 carbon signals attributable to one methyl, three methylenes, nine methines, and three quaternary carbons. The 1H NMR and 13C NMR data also provided evidence for the presence of a sugar moiety. By comparison with the spectroscopic data in the literature [4], compound 2 was elucidated as β-D-glucopyranoside,2-(4-hydroxyphenetyl) 6-acetate. This compound was isolated for the first time from nature.

The known compounds, salidroside (3) [5], ligustroside (4) [6], nuezhenoside (5) [7], and nuezhenoside G13 (6) [8], were identified by spectral data and comparison with those reported in previous literature.
To our surprise, compound 2 (6′-acetylated product of salidroside) can slowly transform to compound 3 (salidroside) in DMSO-d6 over 6 months at room temperature. This indicated that compound 3 might be the hydrolysate of compound 2.
The immunomodulatory activities of the compounds were tested by MTT method [9]. The proliferation ratio of mouse splenic lymphocytes treated with compound 2 was 34.65 ± 0.44% (x ± s, n = 3) at a concentration of 1 μg/mL. Other compounds did not show remarkable activity.
Experimental
1H, 13C NMR, and 2D NMR spectra were recorded on a JEOLJNM-ECP600 MHz NMR spectrometer with TMS as an internal standard. MS spectral data were obtained on a Micromass Q-TOF spectrometer for ESI-MS. Silica gel (200–300 mesh) for column chromatography and GF254 for TLC were obtained from the Qingdao Marine Chemical Factory, Qingdao, China.
Plant Material. The plant material was collected from Zhejiang Province, China, in October 2005 and identified by Prof. Feng-Qin Zhou, Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine. The voucher was deposited in the Key Laboratory of Marine Drugs, Ocean University of China, Qingdao.
Extraction and Separation of Metabolites. The fruits of L. lucidum (2.0 kg) were extracted three times with EtOH at room temperature. After removal of the solvent in vacuo, the residue (115.0 g) was suspended in water and extracted with EtOAc. The EtOAc extract (15.0 g) was subjected to silica gel column chromatography (CHCl3–MeOH), Sephadex LH-20 column chromatography (CHCl3–MeOH 1:1), and preparative HPLC to afford compounds 1 (5.0 mg), 2 (25.0 mg), 3 (10.0 mg), 4 (5.0 mg), 5 (18.0 mg), and 6 (22.0 mg).
References
Z. D. He, P. P. H. But, T. W. D. Chan, H. Dong, H. X. Xu., C. P. Lau, and H. D. Sun, Chem. Pharm. Bull., 49, 780 (2001).
Y. Zhang, W. P. Lai, P. C. Leung, C. F. Wu, X. S. Yao, and M. S. Wang, Biol. Pharm. Bull., 29, 291 (2006).
L. R. Qiu and L. Li, J. Chin. Med. Mater., 30, 891 (2007).
H. L. Yu, J. H. Xu, Y. X. Wang, W. Y. Lu, and G. Q. Lin, J. Combinat. Chem., 10, 79 (2008).
L. Y. Zhou, X. H. Zhang, and C. X. Chen, Nat. Prod. Res. Dev., 16, 410 (2004).
Z. D. He, H. Dong, H. X. Xu, W.C. Ye, H. D. Sun, and PPH But, Phytochemistry, 56, 327 (2001).
Y. Takenaka, T. Tanahashi, M. Shitaku, T. Sakai, N. Nagakura, and Parida, Phytochemistry, 55, 275 (2000).
Y. Fukuyama, K. Koshino, T. Hasegawa, T. Yamada, and K. Nakagawa, Planta Med., 53, 427 (1987).
N. W. Roehm, G. H. Rodgers, S. M. Hatfield, and A. L. Glasebrook, J. Immunol. Methods, 142, 257 (1991).
Acknowledgment
This work was financially supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 30572314), the Program for New Century Excellent Talents in Universities of the Ministry of Education of China (No. NCET-05-0600), the Basic Research Program of Science and Technology, Ministry of Science and Technology of China (2007FY210500), and the Science and Technology Program of Shandong Province, China (No. 03BS109).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Published in Khimiya Prirodnykh Soedinenii, No. 5, pp. 595–596, September–October, 2010.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, X., Wang, CY., Shao, CL. et al. Chemical constituents from the fruits of Ligustrum lucidum . Chem Nat Compd 46, 701–703 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10600-010-9719-x
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10600-010-9719-x