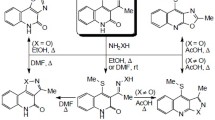
3-Chloroquinoline-2,4-diones react with ethanolamine to form 3-(3-hydroxyethylamino)quinoline-2,4-diones. These compounds afford, depending on substituents in positions 1 and 3, four different products from their reaction with isothiocyanic acid: 3-(2-hydroxyethyl)-2-thioxo-3,3a-dihydro-1H-imidazo[4,5-c]quinolin-4(5H)-ones, 9b-hydroxy-3-(2-hydroxyethyl)-2-thioxo-3,3a,5,9b-tetrahydro-1Himidazo[4,5-c]quinolin-4(2H)-ones, 3-(2-hydroxyethyl)-2-thioxo-2,3-dihydro-1H-imidazo[4,5-c]quinolin-4(5H)-ones, or 1′-methyl-7a-phenyl-5-thioxo-3,5,6,7a-tetrahydro-2H-spiro[imidazo[5,1-b]oxazole-7,3′-indolin]-2′-one.
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
The chemistry of quinolinediones, and in particular, 3-aminoquinoline-2,4-diones have been of interest to our group for a long time.1 In the literature, two derivatives of 3-aminoquinoline-2,4-diones are mentioned in connection with their biological activity. 3-Amino-3-(4-fluorophenyl)- 1H-quinoline-2,4-dione is effective against oxidative stressrelated diseases2 and inhibits cisplatin-induced hearing loss through suppression of reactive oxygen species.3,4 A similar effect is exhibited by 3-amino-6-fluoro- 3-(4-fluorophenyl)-1H-quinoline-2,4-dione.4 Therefore, we tried to prepare some 3-aminoquinoline-2,4-dione derivatives with the 3-amino group fixed in a fused ring structure. 3-Aminoquinoline-2,4(1H,3H)-diones were prepared in our laboratory from 3-chloroquinoline-2,4-diones and ammonia or primary amines.1a We found, that these compounds undergo molecular rearrangements when reacting with isocyanic acid that is formed from urea in boiling acetic acid. Through this synthetic route, 2,6-dihydroimidazo[1,5-c]- quinolone-2,4-diones and rearranged 3,3a-dihydro-5Himidazo[ 4,5-c]quinazoline-3,5-diones, 3-(3-acylureido)-2,3- dihydro-1H-indol-2-ones, and 4-alkylidene-1′H-spiro- [imidazolidine-5,3′-indole]-2,2′-diones were prepared.1b,c
Later we found that the preferable source of isocyanic acid is sodium cyanate and that an acceptable source of isothiocyanic acid is potassium thiocyanate, both in acetic acid solution. Under these conditions, we prepared new heterocycles, e. g., spiro-linked imidazoline-2-thiones and thioxo derivatives of imidazo[1,5-c]quinazolin-5-ones and imidazo[4,5-c]quinolin-4-ones.1g
In an effort to discover an influence of other substituents in the molecule of the amine, we chose ethanolamine as an easily accessible and inexpensive reagent. In our last paper,1h we described its reaction with 3-chloroquinoline- 2,4-diones 1. According to expectations, 3-(2-hydroxyethylamino) quinoline-2,4-diones 2 were obtained and their reaction with isocyanic acid afforded mainly 5-hydroxy- 1-(2-hydroxyethyl)-1H-spiro[imidazolidine-4,3′-indole]-2,2′- diones 3, but also 3-(2-hydroxyethyl)-3,3a-dihydro-2Himidazo[ 4,5-c]quinoline-2,4-(5H)-diones 4 (Scheme 1).

Scheme 1
In this paper, the analogous reaction of compounds 2 with isothiocyanic acid is described. The starting compounds 2a–f were reacted with isothiocyanic acid generated in situ from potassium thiocyanate in acetic acid. The composition of products from this reaction was different from that with isocyanic acid and comprised three different N-hydroxyethyl-substituted 2-thioxo-1H-imidazo- [4,5-c]quinolin-4-ones 5a,c,d,f, 6a,b,d,e,f, and 7b,e, and, in one case, a product of molecular rearrangement 8c with spiro[imidazo[5,1-b]oxazole-7,3′-indolin]-2′-one structure (Scheme 1, Table 1). It is noteworthy that the respective noncyclized thioureas derived of compounds 2 were never isolated.
It can be expected, that compounds 3 and 5 can probably arise from hydroxyethyl derivative 2 by known Marckwald synthesis.5 However, no strong acid is present in the reaction mixture. Therefore, we offer another interpretation, based on the formation of isocyanic or isothiocyanic acids during the reaction. With moderately strong isocyanic acid (pKa 3.7),6 arising from the isomerization of weak cyanic acid (pKa 5.4),7 compounds 2a,b,d–f react to form1h compounds 3a,b and 4d–f. However, isothiocyanic acid is a very strong acid (pKa –1.3)7,8 and arises from the isomerization of weak thiocyanic acid (pKa 5.4).7 Its reaction with 3-aminoquinoline-2,4(1H,3H)-diones 2 afforded not only compounds 5a,c,d,f which are thio analogs of products 4, obtained by the reaction with isocyanic acid, but also new structures containing sulfur atom, such as dealkylated products 7b,e, due to the influence of strong isothiocyanic acid.
The explanation of the origin of the obtained compounds was based on the NMR spectroscopy. Yellow or orange compounds 5a,c,d,f were produced in moderate yield from compounds 2a,c,d,f through the reaction with HNCS. The signals of NCH2 protons resonate more downfield than the signals of OCH2 protons. It was surprising, however, the location was proved by 2D NMR (mainly HSQC and HSQC–TOCSY). Protons are situated on the periphery of a molecule and their resonance can be relatively easily influenced by different neighbouring groups.
When compound 5a was kept for one month in DMSO-d6 the NMR spectrum indicated conversion into compound 6a, the product of a nucleophilic attack on compound 5a by H2O, with a yield of about 65%. Typical 13C chemical shifts in the spectra of this condensation product agree with those in oxa analog of compound 6a, except that it has a different alkyl substituent at N-3 atom.1i On the other hand, compounds 6 can also be an antecedent of compounds 5.1g Indeed, yellow compounds 5a,f were prepared in high yields through the dehydration of colorless 6a,f upon treatment with P2O5 (Scheme 2). However, the same treatment of compound 6e does not result in compound 5e, instead, colorless compound 9e was isolated with 39% yield (Scheme 2). It is likely that this new compound must originate from C-debenzylation and subsequent S-benzylation with benzyl cation.

Scheme 2
In the first-order positive-ion ESI-MS spectra of compounds 5a,c,d,f, we observed three singly charged signals, which we assigned to [M+H]+, [M+Na]+, and [M+K]+. In the first-order negative-ion ESI-MS spectra of compounds 6, singly charged signals assigned to [M–H]–, [M+Cl]–, and [2M–H]– were detected. Moreover, singly charged ion with m/z 150 in the mass spectra of compounds 6a,b and m/z 212 in the mass spectra of compounds 6d,e,f were observed in the negative ionization mode. We assigned these ions to 1-[2-(methylamino)phenyl]ethanolate and 1-[2-(phehylamino)phenyl]ethanolate, respectively. We propose that these ions are products of in-source fragmentation of deprotonated molecular ion [M–H]–.
The only product of molecular rearrangement is compound 8c, having two aliphatic quaternary carbons, unlike its isomer 5c. In agreement with our preceding results, this compound must originate from the molecular rearrangement of compound 6c (Scheme 3). In three cases (Table 1), the corresponding isatins were isolated in addition to the main product, which is indicative of the extensive degradation of the starting compound 2 by isothiocyanic acid. Compounds 7b,e (Scheme 3) arise from the debenzylation of starting compounds 2b,e, bearing a benzyl group at position 3. Such reaction, resulting from the presence of strongly acidic isothiocyanic acid, has been observed before.1a

Scheme 3
In conclusion, we would like to emphasize that our results provide new information about the behavior of reactive quinoline-2,4-dione systems. 3-(2-Hydroxyethylamino) quinolinediones, prepared from 3-chloroquinolinedione and ethanolamine, react with isothiocyanic acid to form four different heterocyclic structures: three related imidazo[4,5-c]quinolin-4-ones and spiro[imidazo[5,1-b]- oxazole-7,3′-indolin]-2′-one, a new tetracyclic spiro system that has not been previously described. Unfortunately, the latter compound arises in only one case and our experiments on the preparation of other similar spiro compounds were so far unsuccessful. This study also demonstrated a new example of benzyl group migration from carbon to sulfur atom. An important result is also dehydration of 9b-hydroxy-2-thioxo-4H-imidazo[4,5-c]- quinolin-4-ones to 2-thioxo-4H-imidazo[4,5-c]quinolin- 4-ones enabling preparation of these compounds as the only product by the two-step reaction from starting 3-aminoquinoline-2,4-diones. The prepared compounds are suitable for biological testing as well as further synthetic elaboration.
Experimental
IR spectra were recorded on a Smart OMNI-Transmission Nicolet iS10 spectrophotometer in KBr pellets. 1H, 13C, and 15N NMR spectra were recorded on a Bruker Avance III HD 500 spectrometer (500, 125, and 50 MHz, respectively) in DMSO-d6; the 1H and 13C chemical shifts are given with respect to internal standard TMS; for 15N spectra, MeNO2 was used as external standard in a coaxial capillary; signal assignments were carried out using APT and 2D experiments (gradient-selected (gs) 1H–1H COSY, gs-1H–1H TOCSY, gs-1H–13C HMQC, gs-1H–13C HMQC-RELAY, gs-1H–13C HMBC, gs-1H–15N HMBC, and HSQC-TOCSY).9,10,11 Mass spectra were recorded on a Bruker Daltonics amaZon X ion-trap mass spectrometer, equipped with an ESI source; individual samples were injected into the ESI source as MeOH–H2O solutions (concentration 500 ng/ml) via a syringe pump with a constant flow rate of 3 ml/min; m/z range 50–1500, electrospray voltage ±4.2 kV, drying gas temperature 220°C, drying gas flow rate 6.0 dm3/min, nebulizer pressure 55.16 kPa, capillary exit voltage 140 V; N2 was used as both nebulizing and drying gas. Elemental analysis was carried out on a Thermo Fisher Scientific Flash EA 1112 elemental analyzer. Melting points were determined using a Kofler block. TLC was performed using Macherey-Nagel Alugram® SIL G/UV254 foil plates; elution with PhH– AcOEt, 4:1, CHCl3–EtOH, 9:1, or CHCl3–AcOEt, 7:3. Column chromatography was carried out on Merck silica gel (grade 60, 70–230 mesh); elution with CHCl3, then CHCl3–EtOH, 99:1→8:2, or PhH, then PhH–AcOEt, 99:1→8:2.
Compounds 2a–f were prepared from the respective compounds 1a–f and ethanolamine.1a
Reaction of compounds 2a–f with HNCS (General method). KSCN (0.874 g, 9 mmol) was added to a solution of compound 2a–f (1.5 mmol) in AcOH (4.5 ml), and the mixture was stirred for 3 h at 50°C. The course of the reaction was monitored by TLC. After cooling, the mixture was poured onto crushed ice (20 ml) and extracted with CHCl3 (5×15 ml) and then with AcOEt (5×15 ml). The combined extracts were dried with anhydrous Na2SO4 and evaporated to dryness. The residue was separated by column chromatography.
3a-Butyl-3-(2-hydroxyethyl)-5-methyl-2-thioxo-2,3,3a,5- tetrahydro-4H-imidazo[4,5-c]quinolin-4-one (5a) was prepared from compound 2a. Yield 0.137 g (24%). Orange solid. Mp 135–137°C (PhH–cyclohexane). IR spectrum, ν, cm–1: 3376, 2961, 2932, 2875, 1690, 1661, 1609, 1589, 1471, 1439, 1389, 1334, 1287, 1255, 1230, 1211, 1178, 1160, 1110, 1072, 1050, 990, 967, 775, 758, 730, 699, 683, 671, 608, 520. 1H NMR spectrum, δ, ppm (J, Hz): 0.68 (3Н, t, J = 7.3, 4-CH3 Bu); 0.66–0.76 (2Н, m, 2-CH2 Bu); 1.02–1.13 (2Н, m, 3-CH2 Bu); 1.81–1.90 (1H, m) and 2.33– 2.41 (1H, m, 1-CH2 Bu); 3.32 (3H, s, 5-CH3); 3.78–3.88 (3H, m, CH2O, NCH2); 4.03–4.10 (1H, m, NCH2); 4.90 (1H, br. s, OH); 7.32–7.37 (1Н, m, H-7); 7.43–7.47 (1Н, m, H-9); 7.74–7.79 (1Н, m, H-8); 7.90–7.94 (1Н, m, H-6). 13C NMR spectrum, δ, ppm: 13.6 (C-4 Bu); 21.1 (C-3 Bu); 24.2 (C-2 Bu); 29.9 (5-CH3); 36.5 (C-1 Bu); 47.2 (NCH2); 56.8 (CH2O); 81.2 (C-3a); 116.0 (C-5a); 116.8 (C-9); 124.1 (C-7); 125.8 (C-6); 135.7 (C-8); 141.7 (C-9a); 166.6 (C-4); 183.8 (C-9b); 194.5 (C-2). Mass spectrum, m/z (Irel, %): 685 [2M+Na]+ (5), 370 [M+K]+ (10), 354 [M+Na]+ (100), 351 [2M+Ca]2+ (9), 332 [M+H]+ (12). Found, %: C 61.45; H 6.60; N 12.79; S 9.64. C17H21N3O2S. Calculated, %: C 61.61; H 6.39; N 12.68; S 9.67.
3-(2-Hydroxyethyl)-5-methyl-3a-phenyl-2-thioxo-2,3,3a,5- tetrahydro-4H-imidazo[4,5-c]quinolin-4-one (5c) was prepared from compound 2c. Yield 0.058 g (11%). Yellow solid. Mp 170–177°C (PhH–hexane). IR spectrum, ν, cm–1: 3556, 3056, 2937, 2897, 1678, 1608, 1588, 1491, 1468, 1447, 1400, 1361, 1326, 1284, 1222, 1168, 1143, 1123, 1050, 1001, 968, 952, 934, 809, 760, 724, 695, 664, 610, 571, 529. 1H NMR spectrum, δ, ppm (J, Hz): 3.17–3.29 (1H, m) and 3.62–3.74 (1H, m, CH2O); 3.44 (3H, s, 5-CH3); 3.47–3.59 (1H, m) and 3.68–3.80 (1H, m, NCH2); 4.73 (1H, t, J = 5.7, OH); 6.98–7.02 (2Н, m, H-2,6 Ph); 7.23–7.28 (1Н, m, H-7); 7.36–7.43 (4Н, m, H-9, H-3,4,5 Ph); 7.62–7.66 (1Н, m, H-8); 7.82–7.92 (1Н, m, H-6). 13C NMR spectrum, δ, ppm: 30.4 (5-CH3); 47.4 (NCH2); 56.2 (CH2O); 83.4 (C-3a); 116.7 (C-5a); 116.8 (C-9); 124.1 (C-7); 125.9 (C-2,6 Ph); 126.1 (C-6); 130.1 (C-3,5 Ph); 130.4 (C-4 Ph); 131.6 (C-1 Ph); 135.5 (C-8); 141.2 (C-9a); 165.0 (C-4); 183.1 (C-9b); 195.0 (C-2). Mass spectrum, m/z (Irel, %): 725 [2M+Na]+ (9), 390 [M+K]+ (7), 374 [M+Na]+ (100), 371 [2M+Ca]2+ (8), 352 [M+H]+ (17). Found, %: C 64.86; H 4.91; N 11.77; S 9.00. C19H17N3O2S. Calculated, %: C 64.94; H 4.88; N 11.96; S 9.12.
3a-Butyl-3-(2-hydroxyethyl)-5-phenyl-2-thioxo-2,3,3a,5- tetrahydro-4H-imidazo[4,5-c]quinolin-4-one (5d) was prepared from compound 2d. Yield 0.177 g (30%). Yellow solid. Mp 161–166°C (PhH–hexane). IR spectrum, ν, cm–1: 3454, 3066, 2962, 2929, 2871, 1689, 1608, 1590, 1490, 1467, 1432, 1385, 1340, 1322, 1281, 1245, 1225, 1164, 1108, 1066, 1033, 1004, 962, 859, 777, 754, 733, 696, 633, 610, 582, 516. 1H NMR spectrum, δ, ppm (J, Hz): 0.78 (3Н, t, J = 7.3, 4-CH3 Bu); 0.75–0.85 (2Н, m, 2-CH2 Bu); 1.07–1.23 (2Н, m, 3-CH2 Bu); 2.15–2.27 (1H, m) and 2.48– 2.55 (1H, m, 1-CH2 Bu); 3.73–3.88 (3H, m, CH2O, NCH2); 4.05–4.11 (1H, m, NCH2); 4.83 (1H, t, J = 5.3, OH); 6.39– 6.44 (1Н, m, H-9); 7.27–7.34 (3H, m, H-7, H-2,6 Ph); 7.47– 7.64 (4H, m, H-8, H-3,4,5 Ph); 7.96–8.01 (1Н, m, H-6). 13C NMR spectrum, δ, ppm: 13.6 (C-4 Bu); 21.1 (C-3 Bu); 24.4 (C-2 Bu); 36.4 (C-1 Bu); 47.2 (NCH2); 56.8 (CH2O); 81.5 (C-3a); 115.7 (C-9); 117.3 (C-5a); 124.1 (C-7); 125.9 (C-6); 129.4 (C-2,6 Ph); 129.9 (C-4 Ph); 130.3 (C-3,5 Ph); 130.4 (C-1 Ph); 136.8 (C-8); 142.8 (C-9a); 166.9 (C-4); 183.7 (C-9b); 194.9 (C-2). Mass spectrum, m/z (Irel, %): 809 [2M+Na]+ (5), 432 [M+K]+ (11), 416 [M+Na]+ (100), 413 [2M+Ca]2+ (11), 394 [M+H]+ (15). Found, %: C 67.05; H 6.10; N 10.65; S 8.02. C22H23N3O2S. Calculated, %: C 67.15; H 5.89; N 10.68; S 8.15.
3-(2-Hydroxyethyl)-3a,5-diphenyl-2-thioxo-2,3,3a,5- tetrahydro-4H-imidazo[4,5-c]quinolin-4-one (5f) was prepared from compound 2f. Yield 0.192 g (31%). Orange solid. Mp 178–180°C (PhH–cyclohexane). IR spectrum, ν, cm–1: 3451, 3061, 2361, 1702, 1608, 1587, 1492, 1466, 1449, 1394, 1359, 1309, 1289, 1246, 1229, 1165, 1140, 1060, 1037, 1003, 953, 771, 733, 721, 703, 694, 671, 611, 594, 568, 516. 1H NMR spectrum, δ, ppm (J, Hz): 3.10– 3.19 (1H, m) and 3.59–3.66 (1H, m, CH2O); 3.49–3.58 (1H, m) and 3.79–3.86 (1H, m, NCH2); 4.68 (1H, t, J = 5.7, OH); 6.29–6.34 (1Н, m, H-9); 7.17–7.26 (3H, m, H-7, H-2,6 3a-Ph); 7.39–7.69 (9H, m, H-8, H 5-Ph, H-3,4,5 3a-Ph); 7.97–8.02 (1Н, m, H-6). 13C NMR spectrum, δ, ppm: 47.3 (NCH2); 56.1 (CH2O); 83.6 (C-3a); 116.6 (C-5a); 117.4 (C-9); 124.4 (C-7); 126.1 (C-2,6 3a-Ph); 126.3 (C-6); 128.9 (C-2,6 5-Ph); 130.1 (C-4 5-Ph); 130.3 (C-3,5 3a,5-Ph); 130.5 (C-4 3a-Ph); 131.5 (C-1 5-Ph); 135.1 (C-8); 136.8 (C-1 3a-Ph); 142.3 (C-9a); 165.2 (C-4); 182.9 (C-9b); 195.0 (C-2). Mass spectrum, m/z (Irel, %): 849 [2M+Na]+ (8), 452 [M+K]+ (8), 436 [M+Na]+ (100), 433 [2M+Ca]2+ (21), 414 [M+H]+ (16). Found, %: C 69.81; H 4.75; N 10.18; S 7.74. C24H19N3O2S. Calculated, %: C 69.71; H 4.63; N 10.16; S 7.75.
3a-Butyl-9b-hydroxy-3-(2-hydroxyethyl)-5-methyl-2-thioxo- 1,2,3,3a,5,9b-hexahydro-4H-imidazo[4,5-c]quinolin- 4-one (6a) was prepared from compound 2a. Yield 0.096 g (16%). Colorless solid. Mp 203–217°C (AcOEt). IR spectrum, ν, cm–1: 3418, 3226, 2958, 2933, 2871, 1662, 1605, 1478, 1436, 1365, 1303, 1255, 1205, 1170, 1122, 1054, 1005, 989, 956, 939, 910, 865, 843, 757, 721, 691, 623, 590, 518, 490. 1H NMR spectrum, δ, ppm (J, Hz): 0.68 (3Н, t, J = 7.3, 4-CH3 Bu); 0.70–0.76 (1H, m) and 0.92–1.01 (1H, m, 2-CH2 Bu); 1.07–1.15 (2Н, m, 3-CH2 Bu); 1.95 (2H, m, 1-CH2 Bu); 3.29 (3H, s, 5-CH3); 3.57–3.65 (2H, m, CH2O); 3.83–3.90 (2H, m, NCH2); 4.60 (1H, t, J = 6.4, OH); 6.87 (1H, s, 9b-OH); 7.12–7.20 (2H, m, H-6,8); 7.38–7.43 (1H, m, H-7); 7.72–7.79 (1H, m, H-9); 9.14 (1H, s, NH). 13C NMR spectrum, δ, ppm: 13.5 (C-4 Bu); 22.5 (C-3 Bu); 24.1 (C-2 Bu); 29.4 (5-CH3); 31.3 (C-1 Bu); 46.4 (NCH2); 59.0 (CH2O); 72.3 (C-3a); 84.7 (C-9b); 114.5 (C-6); 123.3 (C-8); 123.7 (C-9a); 126.3 (C-9); 130.0 (C-7); 136.2 (C-5a); 168.6 (C-4); 181.3 (C-2). 15N NMR spectrum, δ, ppm (J, Hz): –237.9 (d, 1J = 95.6, 1-NH); –252.6 (N-5); –253.3 (N-3). Mass spectrum, m/z (Irel, %): 721.2 [2M+Na]+ (5), 388 [M+K]+ (11), 372 [M+Na]+ (100), 369 [2M+Ca]2+ (26), 350 [M+H]+ (6). Mass spectrum, m/z (Irel, %): 697 [2M–H]– (66), 384 [M+35Cl]– (23), 348 [M–H]– (100), 150 (86). Found, %: C 58.36; H 6.74; N 11.86; S 8.98. C17H23N3O3S. Calculated, %: C 58.43; H 6.63; N 12.02; S 9.18.
3a-Benzyl-9b-hydroxy-3-(2-hydroxyethyl)-5-methyl- 2-thioxo-1,2,3,3a,5,9b-hexahydro-4H-imidazo[4,5-c]- quinolin-4-one (6b) was prepared from compound 2b. Yield 0.046 g (8%). Colorless solid. Mp 205–215°C (PhH– cyclohexane). IR spectrum, ν, cm–1: 3244, 2937, 2887, 1662, 1606, 1477, 1410, 1369, 1304, 1249, 1197, 1132, 1075, 1034, 1016, 961, 944, 896, 832, 790, 756, 740, 701, 621, 596, 550, 526, 456. 1H NMR spectrum, δ, ppm (J, Hz): 3.18 (1H, d, J = 16.0) and 3.36 (1H, d, J = 16.0, CH2Ph); 3.35 (3Н, s, 5-CH3); 3.65–3.81 (2H, s, CH2O); 4.04–4.08 (2H, m, NCH2); 4.65 (1H, t, J = 6.3, OH); 6.54– 6.56 (1H, m, H-6); 6.81–6.93 (5H, m, H Ph); 6.97–7.02 (1H, m, H-8); 7.07–7.12 (1H, m, H-7); 7.15 (1H, s, 9b-OH); 7.64–7.67 (1H, m, H-9); 9.19 (1H, s, NH). 13C NMR spectrum, δ, ppm: 29.0 (5-CH3); 36.2 (CH2Ph); 46.9 (NCH2); 59.2 (CH2O); 72.9 (C-3a); 84.7 (C-9b); 113.6 (C-6); 122.6 (C-8); 123.0 (C-9a); 126.1 (C-9); 126.7 (C-4 Ph); 126.8 (C-3,5 Ph); 129.2 (C-7); 130.0 (C-2,6 Ph); 132.2 (C-1 Ph); 135.6 (C-5a); 168.1 (C-4); 181.8 (C-2). 15N NMR spectrum, δ, ppm (J, Hz): –237.9 (d, 1J = 95.6, 1-NH); –250.3 (N-5); –254.0 (N-3). Mass spectrum, m/z (Irel, %): 789 [2M+Na]+ (10), 422 [M+K]+ (13), 406 [M+Na]+ (100), 403 [2M+Ca]2+ (15), 384 [M+H]+ (4). Mass spectrum, m/z (Irel, %): 765 [2M–H]– (47), 418 [M+35Cl]– (9), 382 [M–H]– (100), 150 (57). Found, %: C 62.83; H 5.51; N 10.84; S 8.53. C20H21N3O3S. Calculated, %: C 62.64; H 5.52; N 10.96; S 8.36.
3a-Butyl-9b-hydroxy-3-(2-hydroxyethyl)-5-phenyl-2-thioxo- 1,2,3,3a,5,9b-hexahydro-4H-imidazo[4,5-c]quinolin- 4-one (6d) was prepared from compound 2d. Yield 0.055 g (9%). White solid. Mp 220–226°C (PhH). IR spectrum, ν, cm–1: 3283, 3169, 2958, 2932, 2872, 1654, 1606, 1596, 1464, 1430, 1398, 1356, 1304, 1257, 1207, 1127, 1070, 1051, 1006, 966, 945, 857, 754, 720, 699, 681, 649, 628, 586, 511. 1H NMR spectrum, δ, ppm (J, Hz): 0.78 (3Н, t, J = 7.0, 4-CH3 Bu); 1.12–1.31 (4H, m, 2,3-CH2 Bu); 1.99– 2.12 (2H, m, 1-CH2 Bu); 3.59–3.67 (2H, m, CH2O); 3.75– 3.81 (1H, m) and 3.86–3.93 (1H, m, NCH2); 4.60 (1H, t, J = 6.2, OH); 6.14–6.17 (1H, m, H-6); 7.00 (1H, s, 9b-OH); 7.11–7.24 (4H, m, H-7,8, H-2,6 Ph); 7.50–7.54 (1H, m, H-4 Ph); 7.57–7.62 (2Н, m, H-3,5 Ph); 7.81–7.84 (1H, m, H-9); 9.28 (1H, s, NH). 13C NMR spectrum, δ, ppm: 13.5 (C-4 Bu); 22.5 (C-3 Bu); 24.3 (C-2 Bu); 31.7 (C-1 Bu); 46.6 (NCH2); 59.0 (CH2O); 72.5 (C-3a); 85.1 (C-9b); 115.5 (C-6); 123.4 (C-8,9a); 126.8 (C-9); 128.3 (C-2,6 Ph); 128.7 (C-4 Ph); 129.6 (C-7); 130.2 (C-3,5); 137.1 (C-5a); 137.4 (C-1 Ph); 168.9 (C-4); 181.5 (C-2). 15N NMR spectrum, δ, ppm (J, Hz): –231.0 (N-5); –237.7 (d, 1J = 96.0, 1-NH); –254.6 (N-3). Mass spectrum, m/z (Irel, %): 845 [2M+Na]+ (7), 450 [M+K]+ (20), 434 [M+Na]+ (100), 431 [2M+Ca]2+ (12), 412 [M+H]+ (3). Mass spectrum, m/z (Irel, %): 821 [2M–H]– (21), 446 [M+35Cl]– (27), 410 [M–H]– (29), 212 (100). Found, %: C 64.14; H 6.28; N 9.98; S 7.85. C22H25N3O3S. Calculated, %: C 64.21; H 6.12; N 10.21; S 7.79.
3a-Benzyl-9b-hydroxy-3-(2-hydroxyethyl)-5-phenyl- 2-thioxo-1,2,3,3a,5,9b-hexahydro-4H-imidazo[4,5-c]- quinolin-4-one (6e) was prepared from compound 2e. Yield 0.180 g (27%). Colorless solid. Mp 243–247°C (AcOEt). IR spectrum, ν, cm–1: 3387, 3192, 2933, 1652, 1598, 1491, 1475, 1432, 1397, 1358, 1303, 1239, 1199, 1134, 1067, 1038, 970, 854, 811, 755, 744, 717, 701, 608, 545, 524. 1H NMR spectrum, δ, ppm (J, Hz): 3.28 (1H, d, J = 16.0) and 3.54 (1H, d, J = 16.0, CH2Ph); 3.63–3.69 (1H, m) and 3.71–3.77 (1H, m, CH2O); 3.97–4.06 (2H, m, NCH2); 4.67 (1H, t, J = 6.3, OH); 5.59–5.64 (1H, m, H-6); 6.70–6.85 (2H, m, H Ph); 6.90–7.15 (7H, m, H-7,8, H Ph); 7.38 (1H, s, 9b-OH); 7.38–7.53 (3H, m, H Ph); 7.75–7.80 (1H, m, H-9); 9.39 (1H, s, NH). 13C NMR spectrum, δ, ppm: 36.3 (CH2Ph); 46.9 (NCH2); 59.2 (CH2O); 73.3 (C-3a); 85.1 (C-9b); 115.1 (C-6); 123.0 (C-8); 123.1 (C-9a); 126.5 (C-9); 127.1 (C-4 5-Ph); 127.3 (C-3,5 5-Ph); 128.6 (C-3,5 CH2Ph); 129.1 (C-4 CH2Ph); 130.0 (C-7); 130.8 (C-2,6 CH2Ph); 132.4 (C-1 CH2Ph); 136.8 (C-5a); 137.1 (C-1 5-Ph); 167.9 (C-4); 181.8 (C-2). Mass spectrum, m/z (Irel, %): 913 [2M+Na]+ (8), 484 [M+K]+ (27), 468 [M+Na]+ (100), 465 [2M+Ca]2+ (7), 446 [M+H]+ (10). Mass spectrum, m/z (Irel, %): 889 [2M–H]– (21), 480 [M+35Cl]– (43), 444 [M–H]– (22), 212 (100). Found, %: C 67.36; H 5.28; N 9.24; S 7.27. C25H23N3O3S. Calculated, %: C 67.40; H 5.20; N 9.43; S 7.20.
9b-Hydroxy-3-(2-hydroxyethyl)-3a,5-diphenyl-2-thioxo- 1,2,3,3a,5,9b-hexahydro-4H-imidazo[4,5-c]quinolin-4-one (6f) was prepared from compound 2f. Yield 0.149 g (23%). Colorless solid. Mp 228–235°C (AcOEt). IR spectrum, ν, cm–1: 3230, 2957, 1685, 1661, 1605, 1594, 1491, 1464, 1431, 1390, 1341, 1307, 1260, 1195, 1140, 1077, 996, 945, 930, 863, 832, 759, 735, 704, 691, 630, 606, 589, 574, 532, 513. 1H NMR spectrum, δ, ppm (J, Hz): 3.27–3.40 (1H, m, NCH2); 3.60–3.74 (2H, m, NCH2, OCH2); 3.87–3.99 (2H, m, OCH2); 4.55 (1H, t, J = 5.7, OH); 6.29–6.33 (1H, m, H-6); 7.00 (1H, s, 9b-OH); 7.07–7.13 (1H, m, H-8); 7.20– 7.26 (1H, m, H-7); 7.27–7.50 (7H, m, H-2,6 5-Ph, H-2,3,4,5,6 3a-Ph); 7.53–7.58 (1H, m, H-4 5-Ph); 7.61–7.69 (2Н, m, H-9, H-3,5 5-Ph); 9.55 (1H, s, NH). 13C NMR spectrum, δ, ppm: 48.7 (NCH2); 58.4 (CH2O); 79.0 (C-3a); 86.5 (C-9b); 116.2 (C-6); 122.5 (C-9a); 123.5 (C-8); 128.0 (C-9); 128.2 (C-2,6 3a-Ph); 128.8 (C-3,5 3a-Ph, C-2,6 5-Ph); 129.9 (C-7); 130.3 (C-3,5 5-Ph); 131.8 (C-1 3a-Ph); 137.4 (C-5a); 137.6 (C-1 5-Ph); 168.0 (C-4); 184.5 (C-2). Mass spectrum, m/z (Irel, %): 885 [2M+Na]+ (4), 470 [M+K]+ (15), 454 [M+Na]+ (100), 451 [2M+Ca]2+ (9), 432 [M+H]+ (5). Mass spectrum, m/z (Irel, %): 861 [2M–H]– (4), 466 [M+35Cl]– (20), 430 [M–H]– (59), 212 (100). Found, %: C 66.64; H 4.93; N 9.53; S 7.68. C24H21N3O3S. Calculated, %: C 66.80; H 4.91; N 9.74; S 7.43.
3-(2-Hydroxyethyl)-5-methyl-2-thioxo-1,2,3,5-tetrahydro- 4H-imidazo[4,5-c]quinolin-4-one (7b) was prepared from compound 2b. Yield 0.033 g (8%). Yellowish solid. Mp 295–310°C (cyclohexane–AcOEt). IR spectrum, ν, cm–1: 3347, 3074, 2925, 2842, 2730, 1670, 1635, 1587, 1524, 1483, 1427, 1393, 1358, 1327, 1261, 1211, 1164, 1115, 1074, 1063, 1043, 1009, 969, 884, 863, 768, 754, 733, 677, 626, 585, 520. 1H NMR spectrum, δ, ppm (J, Hz): 3.66 (3H, s, CH3); 3.71 (2H, t, J = 6.6, CH2O); 4.56 (2H, t, J = 6.6, NCH2); 4.84 (1H, br. s, OH); 7.31–7.36 (1H, m, H-8); 7.52–7.62 (1H, m, H-6,7); 8.05–8.09 (1H, m, H-9); 13.75 (1H, s, NH). 13C NMR spectrum, δ, ppm: 28.9 (CH3); 46.3 (NCH2); 58.4 (CH2O); 110.0 (C-3a); 115.7 (C-6); 117.7 (C-9a); 122.0 (C-8); 122.5 (C-9); 129.4 (C-7); 131.5 (C-9b); 136.8 (C-5a); 153.2 (C-2); 167.1 (C-4). 15N NMR spectrum, δ, ppm (J, Hz): –220.3 (N-3); –223.1 (d, 1J = 97.5, 1-NH); –240.0 (N-5). Mass spectrum, m/z (Irel, %): 573 [2M+Na]+ (73), 432.5 [3M+Ca]2+ (11), 314 [M+K]+ (9), 298 [M+Na]+ (100), 276 [M+H]+ (21). Mass spectrum, m/z (Irel, %): 571 [2M–2H+Na]– (12), 274 [M–H]– (100). Found, %: C 56.48; H 4.66; N 15.01; S 11.84. C13H13N3O2S. Calculated, %: C 56.71; H 4.76; N 15.26; S 11.65.
3-(2-Hydroxyethyl)-5-phenyl-2-thioxo-1,2,3,5-tetrahydro- 4H-imidazo[4,5-c]quinolin-4-one (7e) was prepared from compound 2e. Yield 0.040 g (8%). Colorless solid. Mp 275– 290°C (AcOEt). IR spectrum, ν, cm–1: 3426, 3056, 2924, 2740, 1668, 1634, 1591, 1569, 1521, 1480, 1463, 1434, 1394, 1341, 1324, 1267, 1238, 1210, 1164, 1121, 1072, 1029, 989, 860, 786, 753, 732, 699, 683, 608, 563, 515. 1H NMR spectrum, δ, ppm (J, Hz): 3.71 (2H, td, J = 6.7, J = 5.7, CH2O); 4.56 (2H, t, J = 6.7, NCH2); 4.88 (1H, t, J = 5.7, OH); 6.56–6.61 (1H, m, H-6); 7.31–7.45 (4H, m, H-7,8, H-2,6 Ph); 7.55–7.68 (3H, m, H-3,4,5 Ph); 8.16–8.20 (1H, m, H-9); 13.95 (1H, s, NH). 13C NMR spectrum, δ, ppm: 46.4 (NCH2); 58.5 (CH2O); 110.1 (C-3a); 116.5 (C-6); 117.9 (C-9a); 122.1 (C-9); 122.8 (C-8); 129.0 (C-4 Ph); 129.3 (C-7); 129.4 (C-2,6 Ph); 130.1 (C-3,5 Ph); 132.4 (C-9b); 137.2 (C-5a); 138.3 (C-1 Ph); 152.5 (C-2); 167.4 (C-4). 15N NMR spectrum, δ, ppm (J, Hz): –219.1 (N-5); –220.3 (N-3); –223.9 (d, 1J = 96.6, 1-NH). Mass spectrum, m/z (Irel, %): 697 [2M+Na]+ (14), 376 [M+K]+ (11), 360 [M+Na]+ (100), 338 [M+H]+ (16). Mass spectrum, m/z (Irel, %): 336 [M–H]– (100). Found, %: C 63.95; H 4.50; N 11.98; S 9.27. C18H15N3O2S. Calculated, %: C 64.08; H 4.48; N 12.45; S 9.50.
1′-Methyl-7a-phenyl-5-thioxo-2,3,5,6-tetrahydro-7aHspiro[ imidazo[5,1-b]oxazole-7,3′-indolin]-2′-one (8c) was prepared from compound 2c. Yield 0.258 g (49%). White solid. Mp 221–224°C (hexane–AcOEt). IR spectrum, ν, cm–1: 3289, 3058, 3033, 2968, 2901, 1710, 1612, 1472, 1356, 1293, 1260, 1233, 1193, 1154, 1127, 1093, 1072, 1052, 1024, 1005, 991, 948, 915, 857, 784, 753, 703, 687, 653, 623, 588, 532. 1H NMR spectrum, δ, ppm: 2.67 (3H, s, CH3); 3.22–3.30 (1H, m, 2-CH2); 3.40–3.46 and 3.86–3.93 (2H, m, 3-CH2); 4.51–4.56 (2H, m, 2-CH2); 6.94–7.01 (3Н, m, H-7′, H Ph); 7.14–7.18 (1H, m, H-5′); 7.20–7.32 (3H, m, H Ph); 7.43–7.48 (1H, m, H-6′); 7.53–7.56 (1H, m, H-4′); 9.98 (1H, s, NH). 13C NMR spectrum, δ, ppm: 25.8 (CH3); 47.9 (C-3); 62.8 (C-2); 71.7 (C-7); 102.9 (C-7a); 108.6 (C-7′); 121.6 (C-3a′); 122.4 (C-5′); 126.0 (C-2,6); 127.7 (C-3,5); 127.9 (C-4′); 129.0 (C-4 Ph); 130.8 (C-6′); 134.2 (C-1 Ph); 144.2 (C-7′); 172.0 (C-2′); 191.9 (C-5). 15N NMR spectrum, δ, ppm (J, Hz): 244.7 (N-4); –246.9 (d, 1J = 96.6, 6-NH); –252.0 (N-1′). Mass spectrum, m/z (Irel, %): 352 [M+H]+ (100). Mass spectrum, m/z (Irel, %): 350 [M–H]– (100). Found, %: C 65.12; H 5.01; N 11.72; S 9.28. C19H17N3O2S. Calculated, %: C 64.94; H 4.88; N 11.96; S 9.12.
Conversion of compounds 6a,e,f to compounds 5a,f and 9e. P2O5 (43 mg, 0.30 mmol) was added portionwise to a stirred solution of compound 6a,e,f (0.20 mmol) in CHCl3 (4.0 ml) at room temperature. After 45 min, the yellow solution was filtered through a short column of silica gel. The filtrate was evaporated to dryness, and the residue was crystallized. From compounds 6a,f, compounds 5a (yield 0.047 g (59%)) and 5f (yield 0.060 g (73%)) were obtained, identical to those prepared from compounds 2a,f, respectively. From compound 6e, compound 9e (yield 0.033 g (39%)) was obtained besides compound 7e (yield 3.4 mg (5%)).
2-(Benzylsulfanyl)-3-(2-hydroxyethyl)-5-phenyl-3,5- dihydro-4H-imidazo[4,5-c]quinolin-4-one (9e). Colorless solid. Mp 182–186°C (hexane–benzene). IR spectrum, ν, cm–1: 3317, 3061, 3031, 2962, 1670, 1575, 1492, 1456, 1430, 1359, 1309, 1247, 1223, 1163, 1128, 1056, 1036, 947, 852, 757, 702, 681, 666, 607, 563, 546. 1H NMR spectrum, δ, ppm (J, Hz): 3.64–3.69 (2H, m, CH2O); 4.32–4.36 (2H, m, NCH2); 4.64 (2H, s, SCH2); 4.96 (1H, t, J = 6.9, OH); 6.55–6.59 (1Н, m, H-6); 7.24–7.37 (7H, m, H-7,8, H-2,3,4,5,6 5-Ph); 7.47–7.51 (2H, m, H-2,6 CH2Ph); 7.58– 7.62 (1H, m, H-4 CH2Ph); 7.62–7.66 (2H, m, H-3,5 CH2Ph); 8.23–8.27 (1H, m, H-9). 13C NMR spectrum, δ, ppm: 36.5 (SCH2); 48.0 (NCH2); 60.1 (CH2O); 116.0 (C-9a); 116.3 (C-6); 121.1 (C-3a); 121.8 (C-9); 122.6 (C-8); 127.5 (C-4 5-Ph); 128.2 (C-7); 128.5 (C-2,6 5-Ph); 128.8 (C-4 CH2Ph); 129.0 (C-2,6 CH2Ph); 129.6 (C-3,5 5-Ph); 130.0 (C-3,5 CH2Ph); 137.4 (C-1 CH2Ph); 137.6 (C-1 5-Ph); 138.4 (C-5a); 143.9 (C-9b); 152.5 (C-2); 154.1 (C-4). 15N NMR spectrum, δ, ppm: –137.2 (N-1); –217.6 (N-3); –220.9 (N-5). Mass spectrum, m/z (Irel, %): 877 [2M+Na]+ (5), 466 [M+K]+ (8), 450 [M+Na]+ (63), 428 [M+H]+ (100). Mass spectrum, m/z (Irel, %): 426 [M–H]– (100). Found, %: C 70.46; H 5.09; N 9.56; S 7.47. C25H21N3O2S. Calculated, %: C 70.24; H 4.95; N 9.83; S 7.50.
Supplementary information file containing 1H, 13C, and 1H–15N HMBC NMR spectra of the synthesized compounds is available at the journal website at http://springerlink.bibliotecabuap.elogim.com/journal/10593.
References
(a) Kafka, S.; Klásek, A.; Polis, J.; Košmrlj, J. Heterocycles2002, 57, 1659. (b) Klásek, A.; Kořistek, K.; Lyčka, A.; Holčapek, M. Tetrahedron2003, 59, 1283. (c) Klásek, A.; Kořistek, K.; Lyčka, A.; Holčapek, M. Tetrahedron2003, 59, 5279. (d) Klásek, A.; Lyčka, A.; Holčapek, M. Tetrahedron2007, 63, 7059. (e) Klásek, A.; Lyčka, A.; Holčapek, M.; Hoza, I. Helv. Chim. Acta2008, 91, 354. (f) Prucková, Z.; Klásek, A.; Lyčka, A.; Mikšík, I.; Růžička, A. Tetrahedron2009, 65, 9103. (g) Mrkvička, V.; Lyčka, A.; Rudolf, O.; Klásek, A. Tetrahedron2010, 66, 8441. (h) Klásek, A.; Křemen, F.; Křemenová, H.; Lyčka, A.; Rouchal, M. Tetrahedron2017, 73, 1583. (i) Klásek, A.; Lyčka, A.; Holčapek, M.; Kovář, M.; Hoza, I. J. Heterocycl. Chem. 2006, 43, 1251.
Shin, Y. S.; Song, S. J. Kang, S. U.; Hwang, H. S.; Choi, J. W.; Lee, B. H.; Jung, Y.-S.; Kim, C.-H. Neurosciences2013, 232, 1.
Cifuentes-Pagano, M. E.; Meijles, D. N.; Pagano, P. J. Curr. Pharm. Design2015, 21, 6023.
Mittal, R.; Debs, L. H.; Nguyen, D.; Patel, A. P.; Grati, M.; Mittal, J.;Yan, D.; Eshraghi, A. A.; Liu, X. Z. J. Cell. Physiol.2017, 232, 2710.
Marckwald, W. Ber. Dtsh. Chem. Ges.1892, 25, 2354.
Borduas, N.; Place, B.; Wentworth, G. R. F.; Abbatt, P. D.; Murphy, J. G. Atmos. Chem. Phys.2016, 16, 703.
Ermans, A.-M.; Bourdoux, P. In Environmental Goitrogenesis; Gaitan, E., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, 1989, p. 15.
Chiang, Y.; Kresge, A. J. Can. J. Chem.2000, 78, 1627.
Berger, S.; Braun, S. 200 and More NMR Experiments: A Practical Course; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, 2004, 3rd ed.
Claridge, T. D. W. High-Resolution NMR Techniques in Organic Chemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, 2016, 3rd ed.
Marek, R.; Lyčka, A.; Kolehmainen, E.; Sievanen, E.; Toušek, J. Curr. Org. Chem.2007, 11, 1154.
A. K. and M. R. thank for financial support from the internal grant of TBU in Zlín (No. IGA/FT/2019/010), funded from the resources of specific university research. The authors thank Mrs. H. Geržová (Faculty of Technology, Tomas Bata University in Zlín) for technical help.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Published in Khimiya Geterotsiklicheskikh Soedinenii, 2020, 56(5), 566–571
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 3060 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Klásek, A., Lyčka, A., Rouchal, M. et al. Reaction of 1-substituted 3-(2-hydroxyethylamino)quinoline-2,4(1H,3H)-diones with isothiocyanic acid. Chem Heterocycl Comp 56, 566–571 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10593-020-02701-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10593-020-02701-9