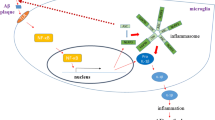
Abstract
Autophagy is a highly evolutionary conserved process that degrades cytosolic macromolecules or damaged organelles (e.g., mitochondria), as well as intracellular pathogens for energy and survival. Dysfunction of autophagy has been associated with the pathologies of Alzheimer’s disease (AD), including Aβ plaques and neurofibrillary tangles. Recently, the presence of sustained immune response in the brain has been considered a new core pathology in AD. Accumulating evidence suggests that autophagy activation may suppress inflammation response through degrading inflammasomes or pro-inflammatory cytokines and improving immune system function in both clinical trials and preclinical studies. This review provides an overview of updated information on autophagy and inflammation and their potential mediators in AD. In summary, we believe that understanding the relationship between autophagy and inflammation will provide insightful knowledge for future therapeutic implications in AD.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Not applicable.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
References
Arnaud L, Benech P, Greetham L et al (2021) The Alzheimer′s disease risk factor APOE4 drives pro-inflammation in human astrocytes via HDAC-dependent repression of TAGLN3. bioRxiv. https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.04.16.440108
Atagi Y, Liu CC, Painter MM et al (2015) Apolipoprotein E is a ligand for triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2 (TREM2). J Biol Chem 290(43):26043–26050. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M115.679043
Bao J, Zheng L, Zhang Q et al (2016) Deacetylation of TFEB promotes fibrillar Abeta degradation by upregulating lysosomal biogenesis in microglia. Protein Cell 7(6):417–433. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13238-016-0269-2
Bostancıklıoğlu M (2019) An update on the interactions between Alzheimer’s disease, autophagy and inflammation. Gene 705:157–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2019.04.040
Brandscheid C, Schuck F, Reinhardt S et al (2017) Altered gut microbiome composition and tryptic activity of the 5xFAD Alzheimer’s mouse model. J Alzheimers Dis 56(2):775–788. https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-160926
Cai B, Zhao J, Zhang Y et al (2021) USP5 attenuates NLRP3 inflammasome activation by promoting autophagic degradation of NLRP3. Autophagy. https://doi.org/10.1080/15548627.2021.1965426
Carosi JM, Sargeant TJ (2019) Rapamycin and Alzheimer disease: a double-edged sword? Autophagy 15(8):1460–1462. https://doi.org/10.1080/15548627.2019.1615823
Carvalho C, Santos MS, Oliveira CR et al (2015) Alzheimer’s disease and type 2 diabetes-related alterations in brain mitochondria, autophagy and synaptic markers. Biochim Biophys Acta 1852(8):1665–1675. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbadis.2015.05.001
Chandra S, Jana M, Pahan K (2018) Aspirin induces lysosomal biogenesis and attenuates amyloid plaque pathology in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease via PPARα. J Neurosci 38(30):6682–6699. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0054-18.2018
Chen JL, Luo C, Pu D et al (2019a) Metformin attenuates diabetes-induced tau hyperphosphorylation in vitro and in vivo by enhancing autophagic clearance. Exp Neurol 311:44–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2018.09.008
Chen JY, Zhu Q, Zhang S et al (2019b) Resveratrol in experimental Alzheimer’s disease models: a systematic review of preclinical studies. Pharmacol Res 150(null):104476. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2019b.104476
Costa LG, Cole TB, Coburn J et al (2017) Neurotoxicity of traffic-related air pollution. Neurotoxicology 59:133–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuro.2015.11.008
Cullen NC, Mälarstig AN, Stomrud E et al (2021) Accelerated inflammatory aging in Alzheimer’s disease and its relation to amyloid, tau, and cognition. Sci Rep 11(1):1965. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-81705-7
Deng H, Mi MT (2016) Resveratrol attenuates Abeta25-35 caused neurotoxicity by inducing autophagy through the TyrRS-PARP1-SIRT1 signaling pathway. Neurochem Res 41(9):2367–2379. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-016-1950-9
Deng G, Li C, Chen L et al (2022) BECN2 (beclin 2) negatively regulates inflammasome sensors through ATG9A-dependent but ATG16L1- and L C3-independent non-canonical autophagy. Autophagy 18(2):340–356. https://doi.org/10.1080/15548627.2021.1934270
Eikelenboom P, Hoozemans JJ, Veerhuis R et al (2012) Whether, when and how chronic inflammation increases the risk of developing late-onset Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Res Therapy 4(3):15. https://doi.org/10.1186/alzrt118
Fang EF (2019) Mitophagy and NAD(+) inhibit Alzheimer disease. Autophagy 15(6):1112–1114. https://doi.org/10.1080/15548627.2019.1596497
Farrall AJ, Wardlaw JM (2009) Blood-brain barrier: ageing and microvascular disease–systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurobiol Aging 30(3):337–352. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2007.07.015
Fedeli C, Filadi R, Rossi A et al (2019) PSEN2 (presenilin 2) mutants linked to familial Alzheimer disease impair autophagy by altering Ca(2+) homeostasis. Autophagy 15(12):2044–2062. https://doi.org/10.1080/15548627.2019.1596489
Feng Q, Luo Y, Zhang XN et al (2020) MAPT/Tau accumulation represses autophagy flux by disrupting IST1-regulated ESCRT-III complex formati on: a vicious cycle in Alzheimer neurodegeneration. Autophagy 16(4):641–658. https://doi.org/10.1080/15548627.2021.1934270
Gilardini Montani MS, Santarelli R, Falcinelli L et al (2018) EBV up-regulates PD-L1 on the surface of primary monocytes by increasing ROS and activating TLR signaling and STAT3. J Leukoc Biol 104(4):821–832. https://doi.org/10.1002/JLB.2A0118-029RR
Gong B, Pan Y, Vempati P et al (2013) Nicotinamide riboside restores cognition through an upregulation of proliferator-activated receptor-gamma coactivator 1alpha regulated beta-secretase 1 degradation and mitochondrial gene expression in Alzheimer’s mouse models. Neurobiol Aging 34(6):1581–1588. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2012.12.005
Gonzales MM, Garbarino VR, Pollet E et al (2022) Biological aging processes underlying cognitive decline and neurodegenerative disease. J Clin Investig 132(10):e158453. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI158453
Granato M, Santarelli R, Farina A et al (2014) Epstein-barr virus blocks the autophagic flux and appropriates the autophagic machinery to enhance viral replication. J Virol 88(21):12715–12726. https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.02199-14
Griciuc A, Serrano-Pozo A, Parrado AR et al (2013) Alzheimer’s disease risk gene CD33 inhibits microglial uptake of amyloid beta. Neuron 78(4):631–643. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2013.04.014
Griciuc A, Patel S, Federico AN et al (2019) TREM2 acts downstream of CD33 in modulating microglial pathology in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuron 103(5):820–835. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2019.06.010
Griciuc A, Federico AN, Natasan J et al (2020) Gene therapy for Alzheimer’s disease targeting CD33 reduces amyloid beta accumulation and neuroinflam mation. Hum Mol Genet 29(17):2920–2935. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddaa179
Guerreiro RJ, Gustafson DR, Hardy J (2012) The genetic architecture of Alzheimer’s disease: beyond APP. Psens and APOE Neurobiol Aging 33(3):437–456. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2010.03.025
Hara T, Nakamura K, Matsui M et al (2006) Suppression of basal autophagy in neural cells causes neurodegenerative disease in mice. Nature 441(7095):885–889. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature04724
Hebert LE, Weuve J, Scherr PA et al (2013) Alzheimer disease in the United States (2010–2050) estimated using the 2010 census. Neurology 80(19):1778–1783. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0b013e31828726f5
Heneka MT, Kummer MP, Stutz A et al (2013) NLRP3 is activated in Alzheimer’s disease and contributes to pathology in APP/PS1 mice. Nature 493(7434):674–678. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11729
Hill JM, Lukiw WJ (2015) Microbial-generated amyloids and Alzheimer’s disease (AD). Front Aging Neurosci 7:9. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2015.00009
Hong S, Stevens B (2017) TREM2: keeping microglia fit during good times and bad. Cell Metab 26(4):590–591. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2017.09.010
Horesh Y, Katsel P, Haroutunian V et al (2011) Gene expression signature is shared by patients with Alzheimer’s disease and schizophrenia at the superior temporal gyrus. Eur J Neurol 18(3):410–424. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-1331.2010.03166.x
Hou Y, Lautrup S, Cordonnier S et al (2018) NAD(+) supplementation normalizes key Alzheimer’s features and DNA damage responses in a new AD mouse model with introduced DNA repair deficiency. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 115(8):E1876–E1885. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1718819115
Hou Y, Wei Y, Lautrup S et al (2021) NAD+ supplementation reduces neuroinflammation and cell senescence in a transgenic mouse model of Alz heimer’s disease via cGAS-STING. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 118(37):e2011226118. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2011226118
Houtman J, Freitag K, Gimber N et al (2019) Beclin1-driven autophagy modulates the inflammatory response of microglia via NLRP3. EMBO J 38(4):e99430. https://doi.org/10.15252/embj.201899430
Inoue K, Rispoli J, Kaphzan H et al (2012) Macroautophagy deficiency mediates age-dependent neurodegeneration through a phospho-tau pathway. Mol Neurodegener 7:48. https://doi.org/10.1186/1750-1326-7-48
Irwin MR, Vitiello MV (2019) Implications of sleep disturbance and inflammation for Alzheimer’s disease dementia. Lancet Neurol 18(3):296–306. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(18)30450-2
Ismael S, Sakata K, McDonald MP et al (2021) ER stress associated TXNIP-NLRP3 inflammasome activation in hippocampus of human Alzheimer’s disease. Neurochem Int 148:105104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2021.105104
Itzhaki RF, Cosby SL, Wozniak MA (2008) Herpes simplex virus type 1 and Alzheimer’s disease: the autophagy connection. J Neurovirol 14(1):1–4. https://doi.org/10.1080/13550280701802543
Jendresen C, Arskog V, Daws MR et al (2017) The Alzheimer’s disease risk factors apolipoprotein E and TREM2 are linked in a receptor signaling pathway. J Neuroinflamm 14(1):59. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-017-0835-4
Jin MM, Wang F, Qi D et al (2018) A critical role of autophagy in regulating microglia polarization in neurodegeneration. Front Aging Neurosci 10:378. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2018.00378
Kang HT, Hwang ES (2009) Nicotinamide enhances mitochondria quality through autophagy activation in human cells. Aging Cell 8(4):426–438. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1474-9726.2009.00487.x
Karuppagounder SS, Pinto JT, Xu H et al (2009) Dietary supplementation with resveratrol reduces plaque pathology in a transgenic model of Alzheimer’ s disease. Neurochem Int 54(2):111–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2008.10.008
Kim S, Lee D, Song JC et al (2014) NDP52 associates with phosphorylated tau in brains of an Alzheimer disease mouse model. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 454(1):196–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.10.066
Kiyota T, Okuyama S, Swan RJ et al (2010) CNS expression of anti-inflammatory cytokine interleukin-4 ttenuates Alzheimer’s disease-like pathogenesis in APP+PS1 bigenic mice. FASEB J 24(8):3093–3102. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.10-155317
Ko JH, Yoon SO, Lee HJ et al (2017) Rapamycin regulates macrophage activation by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome-p38 MAPK-NFkappaB pathways in autophagy- and p62-dependent manners. Oncotarget 8(25):40817–40831. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.17256
Kokiko-Cochran ON, Godbout JP (2018) The inflammatory continuum of traumatic brain injury and Alzheimer’s disease. Front Immunol 9:672. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2018.00672
Lachance V, Wang Q, Sweet E et al (2019) Autophagy protein NRBF2 has reduced expression in Alzheimer’s brains and modulates memory and amyloid-beta homeostasis in mice. Mol Neurodegener 14(1):43. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13024-019-0342-4
Lagouge M, Argmann C, Gerhart-Hines Z et al (2006) Resveratrol improves mitochondrial function and protects against metabolic disease by activating SIRT1 and PGC-1alpha. Cell 127(6):1109–1122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2006.11.013
Lee M, McGeer E, McGeer PL (2015) Activated human microglia stimulate neuroblastoma cells to upregulate production of beta amyloid protein and tau: implications for Alzheimer’s disease pathogenesis. Neurobiol Aging 36(1):42–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2014.07.024
Lee JH, Wolfe DM, Darji S et al (2020) β2-adrenergic agonists rescue lysosome acidification and function in PSEN1 deficiency by reversing De fective ER-to-lysosome delivery of ClC-7. J Mol Biol 432(8):2633–2650. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2020.02.021
Li D, Wang C, Yao Y et al (2016) mTORC1 pathway disruption ameliorates brain inflammation following stroke via a shift in microglia phenotype from M1 type to M2 type. FASEB J 30(10):3388–3399. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.201600495R
Li JG, Chu J, Pratico D (2018) Downregulation of autophagy by 12/15Lipoxygenase worsens the phenotype of an Alzheimer’s disease mouse model with plaques, tangles, and memory impairments. Mol Psychiatry. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41380-018-0268-1
Li C, Zhao B, Lin C et al (2019) TREM2 inhibits inflammatory responses in mouse microglia by suppressing the PI3K/NF-kappaB signaling. Cell Biol Int 43(4):360–372. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbin.10975
Licastro F, Pedrini S, Caputo L et al (2000) Increased plasma levels of interleukin-1, interleukin-6 and alpha-1-antichymotrypsin in patients with Alzheimer’s disease: peripheral inflammation or signals from the brain? J Neuroimmunol 103(1):97–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0165-5728(99)00226-x
Lin L, Zheng LJ, Zhang LJ (2018) Neuroinflammation, gut microbiome, and Alzheimer’s disease. Mol Neurobiol 55(11):8243–8250. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-018-0983-2
Ling D, Song HJ, Garza D et al (2009) Abeta42-induced neurodegeneration via an age-dependent autophagic-lysosomal injury in Drosophila. PLoS ONE 4(1):e4201. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0004201
Liu D, Pitta M, Jiang H et al (2013) Nicotinamide forestalls pathology and cognitive decline in Alzheimer mice: evidence for improved neuronal bioenergetics and autophagy procession. Neurobiol Aging 34(6):1564–1580. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2012.11.020
Liu T, Tang Q, Liu K et al (2016) TRIM11 suppresses AIM2 inflammasome by degrading AIM2 via p62-dependent selective autophagy. Cell Rep 16(7):1988–2002. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2016.07.019
Long Z, Chen J, Zhao Y et al (2020) Dynamic changes of autophagic flux induced by Abeta in the brain of postmortem Alzheimer’s disease pa tients, animal models and cell models. Aging 12(11):10912–10930. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.103305
Lucin KM, O’Brien CE, Bieri G et al (2013) Microglial beclin 1 regulates retromer trafficking and phagocytosis and is impaired in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuron 79(5):873–886. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2013.06.046
Majumder S, Richardson A, Strong R et al (2011) Inducing autophagy by rapamycin before, but not after, the formation of plaques and tangles ameliorates cognitive deficits. PLoS ONE 6(9):e25416. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0025416
Manczak M, Kandimalla R, Yin X et al (2018) Hippocampal mutant APP and amyloid beta-induced cognitive decline, dendritic spine loss, defective autophagy, mitophagy and mitochondrial abnormalities in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Hum Mol Genet 27(8):1332–1342. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddy042
McGeer PL, Guo JP, Lee M et al (2018) Alzheimer’s disease can be spared by nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. J Alzheimers Dis 62(3):1219–1222. https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-170706
Mehto S, Chauhan S, Jena KK et al (2019a) IRGM restrains NLRP3 inflammasome activation by mediating its SQSTM1/p62-dependent selective autophagy. Autophagy 15(9):1645–1647. https://doi.org/10.1080/15548627.2019.1628544
Mehto S, Jena KK, Nath P et al (2019b) The Crohn’s disease risk factor IRGM limits NLRP3 inflammasome activation by impeding its assembly and by mediating its selective autophagy. Mol Cell 73(3):429–445. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2018.11.018
Moore AM, Mahoney E, Dumitrescu L et al (2020) APOE ε4-specific associations of VEGF gene family expression with cognitive aging and Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 87:18–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2019.10.021
Müller L, Power Guerra N, Stenzel J et al (2021) Long-term caloric restriction attenuates β-amyloid neuropathology and is accompanied by autophagy in APPswe/PS1delta9 mice. Nutrients 13(3):985. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13030985
Naseer MI, Bibi F, Alqahtani MH et al (2014) Role of gut microbiota in obesity, type 2 diabetes and Alzheimer’s disease. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets 13(2):305–311. https://doi.org/10.2174/18715273113126660147
Nixon RA, Wegiel J, Kumar A et al (2005) Extensive involvement of autophagy in Alzheimer disease: an immuno-electron microscopy study. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 64(2):113–122. https://doi.org/10.1093/jnen/64.2.113
Omata Y, Lim YM, Akao Y et al (2014) Age-induced reduction of autophagy-related gene expression is associated with onset of Alzheimer’s disease. Am J Neurodegener Dis 3(3):134–142
Orvedahl A, Alexander D, Talloczy Z et al (2007) HSV-1 ICP34.5 confers neurovirulence by targeting the Beclin 1 autophagy protein. Cell Host Microbe 1(1):23–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chom.2006.12.001
Parcon PA, Balasubramaniam M, Ayyadevara S et al (2018) Apolipoprotein E4 inhibits autophagy gene products through direct, specific binding to CLEAR motifs. Alzheimers Dement 14(2):230–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jalz.2017.07.754
Piras A, Collin L, Gruninger F et al (2016) Autophagic and lysosomal defects in human tauopathies: analysis of post-mortem brain from patients with familial Alzheimer disease, corticobasal degeneration and progressive supranuclear palsy. Acta Neuropathol Commun 4:22. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40478-016-0292-9
Pomilio C, Gorojod RM, Riudavets M et al (2020) Microglial autophagy is impaired by prolonged exposure to beta-amyloid peptides: evidence from experimental models and Alzheimer’s disease patients. Geroscience 42(2):613–632. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11357-020-00161-9
Price NL, Gomes AP, Ling AJ et al (2012) SIRT1 is required for AMPK activation and the beneficial effects of resveratrol on mitochondrial function. Cell Metab 15(5):675–690. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2012.04.003
Pyo JO, Nah J, Jung YK (2012) Molecules and their functions in autophagy. Exp Mol Med 44(2):73–80. https://doi.org/10.3858/emm.2012.44.2.029
Reddy PH, Oliver DM (2019) Amyloid beta and phosphorylated Tau-induced defective autophagy and mitophagy in Alzheimer’s disease. Cells 8(5):488. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8050488
Reddy PH, Yin X, Manczak M et al (2018) Mutant APP and amyloid beta-induced defective autophagy, mitophagy, mitochondrial structural and functional changes and synaptic damage in hippocampal neurons from Alzheimer’s disease. Hum Mol Genet 27(14):2502–2516. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddy154
Reinert LS, Lopusna K, Winther H et al (2016) Sensing of HSV-1 by the cGAS-STING pathway in microglia orchestrates antiviral defence in the CNS. Nat Commun 7:13348. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms13348
Ruganzu JB, Zheng Q, Wu X et al (2021) TREM2 overexpression rescues cognitive deficits in APP/PS1 transgenic mice by reducing neuroinflammat ion via the JAK/STAT/SOCS signaling pathway. Exp Neurol 336:113506. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2020.113506
Saitoh T, Fujita N, Jang MH et al (2008) Loss of the autophagy protein Atg16L1 enhances endotoxin-induced IL-1beta production. Nature 456(7219):264–268. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature07383
Salim SY, Kaplan GG, Madsen KL (2014) Air pollution effects on the gut microbiota: a link between exposure and inflammatory disease. Gut Microbes 5(2):215–219. https://doi.org/10.4161/gmic.27251
Salminen A, Kauppinen A, Suuronen T et al (2009) ER stress in Alzheimer’s disease: a novel neuronal trigger for inflammation and Alzheimer’s pathology. J Neuroinflammation 6:41. https://doi.org/10.1186/1742-2094-6-41
Schrank S, McDaid J, Briggs CA et al (2020) Human-induced neurons from Presenilin 1 mutant patients model aspects of Alzheimer’s disease pathology. Int J Mol Sci 21(3):1030. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21031030
Shao L, Dong C, Geng D et al (2022) Ginkgolide B inactivates the NLRP3 inflammasome by promoting autophagic degradation to improve learni ng and memory impairment in Alzheimer’s disease. Metab Brain Dis 37(2):329–341. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-021-00886-2
Sharma C, Kim SR (2021) Linking oxidative stress and proteinopathy in Alzheimer’s disease. Antioxidants 10(8):1231. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10081231
Shen L, Jia J (2016) An overview of genome-wide association studies in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci Bull 32(2):183–190. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12264-016-0011-3
Shi Y, Yamada K, Liddelow SA et al (2017) ApoE4 markedly exacerbates tau-mediated neurodegeneration in a mouse model of tauopathy. Nature 549(7673):523–527. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature24016
Singh AK, Kashyap MP, Tripathi VK et al (2017) Neuroprotection through rapamycin-induced activation of autophagy and PI3K/Akt1/mTOR/CREB signaling against amyloid-beta-induced oxidative stress, synaptic/neurotransmission dysfunction, and neurodegeneration in adult rats. Mol Neurobiol 54(8):5815–5828. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-016-0129-3
Sohn HY, Kim SI, Park JY et al (2021) ApoE4 attenuates autophagy via FoxO3a repression in the brain. Sci Rep 11(1):17604. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-97117-6
Sollberger G, Strittmatter GE, Garstkiewicz M et al (2014) Caspase-1: the inflammasome and beyond. Innate Immun 20(2):115–125. https://doi.org/10.1177/1753425913484374
Song H, Liu B, Huai W et al (2016) The E3 ubiquitin ligase TRIM31 attenuates NLRP3 inflammasome activation by promoting proteasomal degradation of NLRP3. Nat Commun 7:13727. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms13727
Spielman LJ, Little JP, Klegeris A (2014) Inflammation and insulin/IGF-1 resistance as the possible link between obesity and neurodegeneration. J Neuroimmunol 273(1–2):8–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneuroim.2014.06.004
Sun YX, Ji X, Mao X et al (2014) Differential activation of mTOR complex 1 signaling in human brain with mild to severe Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 38(2):437–444. https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-131124
Swaminathan G, Zhu W, Plowey ED (2016) BECN1/Beclin 1 sorts cell-surface APP/amyloid beta precursor protein for lysosomal degradation. Autophagy 12(12):2404–2419. https://doi.org/10.1080/15548627.2016.1234561
Tachibana M, Holm ML, Liu CC et al (2019) APOE4-mediated amyloid-beta pathology depends on its neuronal receptor LRP1. J Clin Investig 129(3):1272–1277. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI124853
Takeda S, Sato N, Ikimura K et al (2013) Increased blood–brain barrier vulnerability to systemic inflammation in an Alzheimer disease mouse model. Neurobiol Aging 34(8):2064–2070. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2013.02.010
Tang RH, Qi RQ, Liu HY (2019) Interleukin-4 affects microglial autophagic flux. Neural Regen Res 14(9):1594–1602. https://doi.org/10.4103/1673-5374.255975
Theuns J, Marjaux E, Vandenbulcke M et al (2006) Alzheimer dementia caused by a novel mutation located in the APP C-terminal intracytosolic fragment. Hum Mutat 27(9):888–896. https://doi.org/10.1002/humu.20402
Thevaranjan N, Puchta A, Schulz C et al (2017) Age-associated microbial dysbiosis promotes intestinal permeability, systemic inflammation, and macrophage dysfunction. Cell Host Microbe 21(4):455–466. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chom.2017.03.002
Tosatti JAG, Fontes A, Caramelli P et al (2022) Effects of resveratrol supplementation on the cognitive function of patients with Alzheimer’s disease: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Drugs Aging 39(4):285–295. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40266-022-00923-4
Uddin MS, Mamun AA, Labu ZK et al (2019) Autophagic dysfunction in Alzheimer’s disease: cellular and molecular mechanistic approaches to halt Alzheimer’s pathogenesis. J Cell Physiol 234(6):8094–8112. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.27588
Vagelatos NT, Eslick GD (2013) Type 2 diabetes as a risk factor for Alzheimer’s disease: the confounders, interactions, and neuropathology associated with this relationship. Epidemiol Rev 35:152–160. https://doi.org/10.1093/epirev/mxs012
Van Eldik LJ, Carrillo MC, Cole PE et al (2016) The roles of inflammation and immune mechanisms in Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement (n y) 2(2):99–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trci.2016.05.001
Vegeto E, Benedusi V, Maggi A (2008) Estrogen anti-inflammatory activity in brain: a therapeutic opportunity for menopause and neurodegenerative diseases. Front Neuroendocrinol 29(4):507–519. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yfrne.2008.04.001
Vingtdeux V, Giliberto L, Zhao H et al (2010) AMP-activated protein kinase signaling activation by resveratrol modulates amyloid-beta peptide metabolism. J Biol Chem 285(12):9100–9113. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M109.060061
Vogt NM, Kerby RL, Dill-McFarland KA et al (2017) Gut microbiome alterations in Alzheimer’s disease. Sci Rep 7(1):13537. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-13601-y
Wang H, Jiang T, Li W et al (2018) Resveratrol attenuates oxidative damage through activating mitophagy in an in vitro model of Alzheimer’s disease. Toxicol Lett 282:100–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxlet.2017.10.021
Wang X, Sun G, Feng T et al (2019) Sodium oligomannate therapeutically remodels gut microbiota and suppresses gut bacterial amino acids-shaped neuroinflammation to inhibit Alzheimer’s disease progression. Cell Res 29(10):787–803. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41422-019-0216-x
Wang H, Fu J, Xu X et al (2021) Rapamycin activates mitophagy and alleviates cognitive and synaptic plasticity deficits in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 76(10):1707–1713. https://doi.org/10.1093/gerona/glab142
Wang X, Zhu YT, Zhu Y et al (2022) Long-term running exercise alleviates cognitive dysfunction in APP/PSEN1 transgenic mice via enhancin g brain lysosomal function. Acta Pharmacol Sin 43(4):850–861. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-021-00720-6
Więckowska-Gacek A, Mietelska-Porowska A, Wydrych M et al (2021) Western diet as a trigger of Alzheimer’s disease: from metabolic syndrome and systemic inflammation to neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration. Ageing Res Rev 70:101397. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arr.2021.101397
Wolfe CM, Fitz NF, Nam KN et al (2018) The role of APOE and TREM2 in Alzheimer’s disease-current understanding and perspectives. Int J Mol Sci 20(1):81. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20010081
Xiao Q, Yan P, Ma X et al (2014) Enhancing astrocytic lysosome biogenesis facilitates Abeta clearance and attenuates amyloid plaque pathogenesis. J Neurosci 34(29):9607–9620. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3788-13.2014
Xiao Q, Yan P, Ma X et al (2015) Neuronal-targeted TFEB accelerates lysosomal degradation of APP, reducing abeta generation and amyloid plaque pathogenesis. J Neurosci 35(35):12137–12151. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0705-15.2015
Xu X, Sun Y, Cen X et al (2021) Metformin activates chaperone-mediated autophagy and improves disease pathologies in an Alzheimer dis ease mouse model. Protein Cell 12(10):769–787. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13238-021-00858-3
Yang SH (2019) Cellular and molecular mediators of neuroinflammation in Alzheimer disease. Int Neurourol J 23(Suppl 2):S54-62. https://doi.org/10.5213/inj.1938184.092
Yang Y, Zhang L (2020) The effects of caloric restriction and its mimetics in Alzheimer’s disease through autophagy pathways. Food Funct 11(2):1211–1224. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9fo02611h
Ye J, Jiang Z, Chen X et al (2017) The role of autophagy in pro-inflammatory responses of microglia activation via mitochondrial reactive oxygen species in vitro. J Neurochem 142(2):215–230. https://doi.org/10.1111/jnc.14042
Yoon SY, Kim DH (2016) Alzheimer’s disease genes and autophagy. Brain Res 1649(Pt B):201–209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2016.03.018
Yoshii SR, Mizushima N (2017) Monitoring and measuring autophagy. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18091865
Yu WH, Cuervo AM, Kumar A et al (2005) Macroautophagy–a novel Beta-amyloid peptide-generating pathway activated in Alzheimer’s disease. J Cell Biol 171(1):87–98. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200505082
Yuan Y, Chen Y, Peng T et al (2019) Mitochondrial ROS-induced lysosomal dysfunction impairs autophagic flux and contributes to M1 macrophage polarization in a diabetic condition. Clin Sci 133(15):1759–1777. https://doi.org/10.1042/CS20190672
Zhan X, Stamova B, Jin LW et al (2016) Gram-negative bacterial molecules associate with Alzheimer disease pathology. Neurology 87(22):2324–2332. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0000000000003391
Zhang Z, Yang X, Song YQ et al (2021) Autophagy in Alzheimer’s disease pathogenesis: Therapeutic potential and future perspectives. Ageing Res Rev 72(1):101464. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arr.2021.101464
Zhao H, Wang S, Li X (2022) DNA damage accumulation in aging brain and its links to Alzheimer’s disease progression. Genome Instab Dis. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42764-022-00069-y
Zheng H, Cheng B, Li Y et al (2018) TREM2 in Alzheimer’s disease: microglial survival and energy metabolism. Front Aging Neurosci 10:395. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2018.00395
Zhou Z, Zhu X, Yin R et al (2020) K63 ubiquitin chains target NLRP3 inflammasome for autophagic degradation in ox-LDL-stimulated THP-1 macrophages. Aging 12(2):1747–1759. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.102710
Acknowledgements
None.
Funding
The work was funded by Shanghai TCM special department (special disease) alliance project (HWZG (2021) No. 13).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XC and YW are co-first authors of the article. XC and YW participated in the conception of the study, wrote the paper, drew pictures and designed the framework of the paper. ZQ searched and assembled relevant literature. LH contributed to revision and final review of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical Approval
Not applicable.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Cheng, X., Wei, Y., Qian, Z. et al. Autophagy Balances Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s Disease. Cell Mol Neurobiol 43, 1537–1549 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-022-01269-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-022-01269-6