Abstract
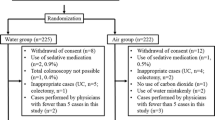
INTRODUCTION: Insufflation of air is a cause of discomfort during and after colonoscopy. Although this can be minimized by good technique, the use of carbon dioxide insufflation may provide further benefits. Carbon dioxide is rapidly absorbed and excreted through the lungs. We hypothesized that carbon dioxide would alleviate postcolonoscopy discomfort. METHODS: After they had provided informed consent, patients presenting for colonoscopy were randomized into two groups: those in whom air was used for colonoscopy and those in whom carbon dioxide was used. Pain during and ten minutes after colonoscopy was measured on a ten-point analog scale. Data are mean and 95 percent confidence limits. RESULTS: There were 124 patients in the air group and 123 in the carbon dioxide group. Age, body mass index, indication, diagnosis, and number of procedures were similar for the two groups. There were no differences between the groups in the amounts of sedation or analgesia used, the percentage of examinations that were complete (air, 98.4 percent; carbon dioxide, 95.2 percent), or patient satisfaction (on a scale of 1 to 10: air, 9.4; carbon dioxide, 9.5). Although there were more females in the carbon dioxide group (69 vs. 51), hysterectomy rates were the same. Pain scores (mean ± 95 percent confidence interval; scale of 1 to 10) immediately after the examination were 4.3 ± 0.3 for air and 3.6 ± 0.3 for carbon dioxide (no significant difference). Pain scores 10 minutes later were 2.1 ± 0.2 for air and 0.9 ± 0.2 for carbon dioxide (P < 0.05, Student’s t-test). CONCLUSION: Because there was significantly less abdominal pain ten minutes after colonoscopy in the group in whom carbon dioxide was used, carbon dioxide should be considered as an insufflating gas for colonoscopy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
JM Church (1994) ArticleTitleComplete colonoscopy: how often? And if not, why not? Am J Gastroenterol 89 556–560
LJ Brandt SJ Boley R Sammartano (1986) ArticleTitleCarbon dioxide and room air insufflation of the colon. Effects on colonic blood flow and intraluminal pressure in the dog Gastrointestinal Endosc 32 324–329
BH Rogers (1980) ArticleTitleCarbon dioxide for colonoscopy Gastroenterology 78 1659–1660
BH Rogers (1974) ArticleTitleThe safety of carbon dioxide insufflation during colonoscopic electrosurgical polypectomy Gastrointest Endosc 20 115–117
AM Hussein CI Bartram CB Williams (1984) ArticleTitleCarbon dioxide insufflation for more comfortable colonoscopy Gastrointestinal Endosc 30 68–70
K Phaosawasdi W Cooley J Wheeler P Rice (1986) ArticleTitleCarbon dioxide-insufflated colonoscopy Gastrointestinal Endosc 32 330–333
GW Stevenson JA Wilson J Wilkinson G Norman RL Goodacre (1992) ArticleTitlePain following colonoscopy Gastrointestinal Endosc 38 564–567
M Bretthauer E Thiis-Evensen G Huppertz-Haus et al. (2002) ArticleTitleNORCCAP Gut 50 604–607
FW Jackson (2001) ArticleTitleCO2 is easy [letter] Am J Gastroenterol 96 3035–607
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
Church, J., Delaney, C. Randomized, Controlled Trial of Carbon Dioxide Insufflation During Colonoscopy. Dis Colon Rectum 46, 322–326 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10350-004-6549-6
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10350-004-6549-6