Abstract
Purpose
Lipoyltransferase 1 (LIPT1) has been recently identified as a cuproptosis‑related gene. As a key enzyme of lipoic acid metabolism, LIPT1 has been revealed to play important roles in hereditary diseases involved with lipoic acid biosynthesis defects, while its roles in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) remain to be elucidated. Hence, we aimed to explore the roles and mechanisms of LIPT1 in HCC progression.
Methods
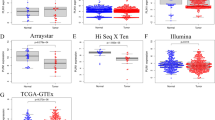
The expression of LIPT1 in HCC tissues and its clinical significance for HCC were evaluated by bioinformatic analysis and in our patient cohort. The influences of LIPT1 on the growth, migration, and lipid metabolism of HCC cells were assessed in vitro. The underlying mechanisms were explored using gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) and molecular experiments.
Results
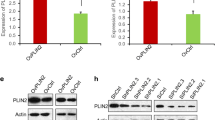
LIPT1 expression was significantly elevated in HCC tissues compared to the normal tissues, and such upregulation was associated with more malignant pathological features and poor prognosis of patients with HCC. LIPT1 silencing significantly inhibited cell proliferation, migration, and lipid content. GSEA revealed that LIPT1 upregulation was significantly associated with various cancer-associated signaling pathways, including the PI3K-AKT signaling pathway and the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Further molecular experiments indicated that LIPT1 silencing repressed the expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARγ) and inactivated the AKT/GSK-3β/β-catenin signaling axis.
Conclusions
Upregulation of LIPT1 is involved in metabolic dysregulation of fatty acid and poor prognosis of HCC patients, which suggests that LIPT1 plays an important role in reprogramming lipid metabolism and could act as a potential prognostic marker and therapeutic target for HCC.








Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used in the current study are available in the following repositories, GEO database (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/), HPA RNA-seq normal tissues (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene/51601), and TCGA database (https://portal.gdc.cancer.gov/).
Abbreviations
- AFP:
-
Alpha-fetoprotein
- CI:
-
Confidence interval
- DSS:
-
Disease special survival
- GEO:
-
Gene Expression Omnibus
- GSEA:
-
Gene set enrichment analysis
- HCC:
-
Hepatocellular carcinoma
- KEGG:
-
Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes
- LIPT1:
-
Lipoyltransferase 1
- NES:
-
Normalized Enrichment Score
- OS:
-
Overall survival
- PFI:
-
Progress-free interval
- ROC:
-
Receiver operating characteristic
- TCGA:
-
The Cancer Genome Atlas
References
Bacci M, Lorito N, Smiriglia A, Morandi A (2021) Fat and furious: lipid metabolism in antitumoral therapy response and resistance. Trends Cancer 7:198–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trecan.2020.10.004
Bindea G, Mlecnik B, Tosolini M, Kirilovsky A, Waldner M, Obenauf AC et al (2013) Spatiotemporal dynamics of intratumoral immune cells reveal the immune landscape in human cancer. Immunity 39:782–795. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2013.10.003
Cheng C, Geng F, Cheng X, Guo D (2018) Lipid metabolism reprogramming and its potential targets in cancer. Cancer Commun (lond) 38:27. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40880-018-0301-4
Clough E, Barrett T (2016) The gene expression omnibus database. Methods Mol Biol 1418:93–110. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-3578-9_5
Fagerberg L, Hallström BM, Oksvold P, Kampf C, Djureinovic D, Odeberg J et al (2014) Analysis of the human tissue-specific expression by genome-wide integration of transcriptomics and antibody-based proteomics. Mol Cell Proteom 13:397–406. https://doi.org/10.1074/mcp.M113.035600
Fujiwara K, Suzuki M, Okumachi Y, Okamura-Ikeda K, Fujiwara T, Takahashi E et al (1999) Molecular cloning, structural characterization and chromosomal localization of human lipoyltransferase gene. Eur J Biochem 260:761–767. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1432-1327.1999.00204.x
Galbraith LCA, Mui E, Nixon C, Hedley A, Strachan D, MacKay G et al (2021) PPAR-gamma induced AKT3 expression increases levels of mitochondrial biogenesis driving prostate cancer. Oncogene 40:2355–2366. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-021-01707-7
Grinchuk OV, Yenamandra SP, Iyer R, Singh M, Lee HK, Lim KH et al (2018) Tumor-adjacent tissue co-expression profile analysis reveals pro-oncogenic ribosomal gene signature for prognosis of resectable hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Oncol 12:89–113. https://doi.org/10.1002/1878-0261
Hänzelmann S, Castelo R, Guinney J (2013) GSVA: gene set variation analysis for microarray and RNA-seq data. BMC Bioinform 14:7. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-14-7
Krishnamurthy N, Kurzrock R (2018) Targeting the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway in cancer: update on effectors and inhibitors. Cancer Treat Rev 62:50–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ctrv.2017.11.002
Li J, Huang Q, Long X, Zhang J, Huang X, Aa J et al (2015) CD147 reprograms fatty acid metabolism in hepatocellular carcinoma cells through Akt/mTOR/SREBP1c and P38/PPARα pathways. J Hepatol 63:1378–1389. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2015.07.039
Lim HY, Sohn I, Deng S, Lee J, Jung SH, Mao M et al (2013) Prediction of disease-free survival in hepatocellular carcinoma by gene expression profiling. Ann Surg Oncol 20:3747–3753. https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-013-3070-y
Liu J, Lichtenberg T, Hoadley KA, Poisson LM, Lazar AJ, Cherniack AD et al (2018) Integrated TCGA pan-cancer clinical data resource to drive high-quality survival outcome analytics. Cell 173:400–416. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2018.02.052
Love MI, Huber W, Anders S (2014) Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol 15:550. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-014-0550-8
Lv H, Liu X, Zeng X, Liu Y, Zhang C, Zhang Q et al (2022) Comprehensive analysis of cuproptosis-related genes in immune infiltration and prognosis in melanoma. Front Pharmacol 13:930041. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2022.930041
Martinez-Reyes I, Chandel NS (2021) Cancer metabolism: looking forward. Nat Rev Cancer 21:669–680. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41568-021-00378-6
Mayr JA, Feichtinger RG, Tort F, Ribes A, Sperl W (2014) Lipoic acid biosynthesis defects. J Inherit Metab Dis 37:553–563. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10545-014-9705-8
Mehraj U, Ganai RA, Macha MA, Hamid A, Zargar MA, Bhat AA et al (2021) The tumor microenvironment as driver of stemness and therapeutic resistance in breast cancer: New challenges and therapeutic opportunities. Cell Oncol (dordr) 44:1209–1229. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13402-021-00634-9
Mei S, Chen X, Wang K, Chen Y (2023) Tumor microenvironment in ovarian cancer peritoneal metastasis. Cancer Cell Int 23:11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12935-023-02854-5
Moldogazieva NT, Zavadskiy SP, Sologova SS, Mokhosoev IM, Terentiev AA (2021) Predictive biomarkers for systemic therapy of hepatocellular carcinoma. Expert Rev Mol Diagn 21:1147–1164. https://doi.org/10.1080/14737159.2021.1987217
Munir R, Lisec J, Swinnen JV, Zaidi N (2019) Lipid metabolism in cancer cells under metabolic stress. Br J Cancer 120:1090–1098. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41416-019-0451-4
Ni M, Solmonson A, Pan C, Yang C, Li D, Notzon A et al (2019) Functional assessment of lipoyltransferase-1 deficiency in cells, mice, and humans. Cell Rep 27:1376-1386.e6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2019.04.005
Patitucci C, Couchy G, Bagattin A, Cañeque T, de Reyniès A, Scoazec JY et al (2017) Hepatocyte nuclear factor 1α suppresses steatosis-associated liver cancer by inhibiting PPARγ transcription. J Clin Invest 127:1873–1888. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI90327
Pavlova NN, Zhu J, Thompson CB (2022) The hallmarks of cancer metabolism: still emerging. Cell Metab 34:355–377. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2022.01.007
Ringelhan M, Pfister D, O’Connor T, Pikarsky E, Heikenwalder M (2018) The immunology of hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Immunol 19(3):222–232. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41590-018-0044-z
Roessler S, Jia HL, Budhu A, Forgues M, Ye QH, Lee JS et al (2010) A unique metastasis gene signature enables prediction of tumor relapse in early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma patients. Cancer Res 70:10202–10212. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-2607
Sharma P, Goswami S, Raychaudhuri D, Siddiqui BA, Singh P, Nagarajan A et al (2023) Immune checkpoint therapy-current perspectives and future directions. Cell 186:1652–1669. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2023.03.006
Snaebjornsson MT, Janaki-Raman S, Schulze A (2020) Greasing the wheels of the cancer machine: the role of lipid metabolism in cancer. Cell Metab 31:62–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2019.11.010
Solmonson A, DeBerardinis RJ (2018) Lipoic acid metabolism and mitochondrial redox regulation. J Biol Chem 293:7522–7530. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.TM117.000259
Song M, Bode AM, Dong Z, Lee MH (2019) AKT as a therapeutic target for cancer. Cancer Res 79:1019–1031. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-18-2738
Soreze Y, Boutron A, Habarou F, Barnerias C, Nonnenmacher L, Delpech H et al (2013) Mutations in human lipoyltransferase gene LIPT1 cause a Leigh disease with secondary deficiency for pyruvate and alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase. Orphanet J Rare Dis 8:192. https://doi.org/10.1186/1750-1172-8-192
Tommasini-Ghelfi S, Murnan K, Kouri FM, Mahajan AS, May JL, Stegh AH (2019) Cancer-associated mutation and beyond: the emerging biology of isocitrate dehydrogenases in human disease. Sci Adv 5(5):eaaw4543. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.aaw4543
Tort F, Ferrer-Cortès X, Thió M, Navarro-Sastre A, Matalonga L, Quintana E et al (2014) Mutations in the lipoyltransferase LIPT1 gene cause a fatal disease associated with a specific lipoylation defect of the 2-ketoacid dehydrogenase complexes. Hum Mol Genet 23:1907–1915. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddt585
Tsvetkov P, Coy S, Petrova B, Dreishpoon M, Verma A, Abdusamad M et al (2022) Copper induces cell death by targeting lipoylated TCA cycle proteins. Science 375:1254–1261. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.abf0529
Xue W, Dong B, Wang Y, Xie Y, Li P, Gong Z et al (2022) A novel prognostic index of stomach adenocarcinoma based on immunogenomic landscape analysis and immunotherapy options. Exp Mol Pathol 128:104832. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexmp.2022.104832
Yan W, Wu X, Zhou W, Fong MY, Cao M, Liu J et al (2018) Cancer-cell-secreted exosomal miR-105 promotes tumour growth through the MYC-dependent metabolic reprogramming of stromal cells. Nat Cell Biol 20:597–609. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41556-018-0083-6
Yan C, Niu Y, Ma L, Tian L, Ma J et al (2022) System analysis based on the cuproptosis-related genes identifies LIPT1 as a novel therapy target for liver hepatocellular carcinoma. J Transl Med 20:452. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12967-022-03630-1
Yang JD, Hainaut P, Gores GJ, Amadou A, Plymoth A, Roberts LR (2019) A global view of hepatocellular carcinoma: trends, risk, prevention and management. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 16:589–604. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41575-019-0186-y
Yi M, Li A, Zhou L, Chu Q, Luo S, Wu K (2021) Immune signature-based risk stratification and prediction of immune checkpoint inhibitor’s efficacy for lung adenocarcinoma. Cancer Immunol Immunother 70:1705–1719. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-020-02817-z
Yu G, Wang LG, Han Y, He QY et al (2012) clusterProfiler: an R package for comparing biological themes among gene clusters. OMICS 16:284–287. https://doi.org/10.1089/omi.2011.0118
Zhang C, Guo C, Li Y, Liu K, Zhao Q, Ouyang L (2021) Identification of claudin-6 as a molecular biomarker in pan-cancer through multiple omics integrative analysis. Front Cell Dev Biol 9:726656. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2021.726656
Zhu W, Peng Y, Wang L, Hong Y, Jiang X, Li Q et al (2018) Identification of α-fetoprotein-specific T-cell receptors for hepatocellular carcinoma immunotherapy. Hepatology 68:574–589. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.29844
Zuo Q, He J, Zhang S, Wang H, Jin G, Jin H et al (2021) PPARγ coactivator-1α suppresses metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma by inhibiting Warburg effect by PPARγ-dependent WNT/β-catenin/pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase isozyme 1 axis. Hepatology 73:644–660. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.31280
Acknowledgements
All authors thank the GEO and TCGA databases for providing the useful data, and all the bioinformatics tools for data analysis, and thank the Xiantao bioinformatics toolbox (https://www.xiantao.love/products) for its help in analyzing the relationship between LIPT1 expression and patients’ clinical parameters.
Funding
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82160590 and 81802884), and The innovative project of Guangxi Key Laboratory of Tumor Immunology and Microenvironmental Regulation, and the Special funding for 2019 Guangxi BaGui Scholars.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conception and design: JG and JL. Acquisition of Data: JL, DT and GG. Performing the experiment: DT and JL. Analysis and interpretation of data: JL, JG, and GG. Writing the manuscript: JL and JG. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests in this work.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was performed in line with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. Approval was granted by the Ethics Committee of Guilin Medical University (GLMC20230226).
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., Tuo, D., Guo, G. et al. Aberrant expression of cuproptosis‑related gene LIPT1 is associated with metabolic dysregulation of fatty acid and prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 149, 15763–15779 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-023-05325-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-023-05325-6