Abstract
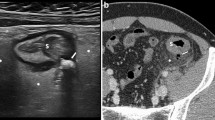
PURPOSE: The most valuable radiologic examination to be done initially when acute left colonic diverticulitis is suspected is still a matter of controversy. This study compares the performance between water-soluble contrast enema and computed tomography. METHODS: From 1986 to 1997, all patients admitted in our emergency center with clinically suspected left-colonic diverticulitis had a contrast enema and a computed tomography within 72 hours of their admission, unless clinical findings required immediate laparotomy. They were prospectively included in the study if one or both radiologic examinations showed signs of acute diverticulitis or diverticulitis was surgically removed and histologically proven or both. Diverticulitis was considered moderate when computed tomography showed localized thickening of the colonic wall (5 mm or more) and inflammation of pericolic fat and contrast enema showed segmental lumen narrowing and tethered mucosa; it was considered severe when abscess or extraluminal air or contrast or all three were observed on computed tomography and when one or both of the last two signs were seen on contrast enema. Of 542 patients, 420 who had both computed tomography and contrast enema entered the study. RESULTS: The performance of computed tomography was significantly superior to contrast enema in terms of sensitivity (98vs. 92 percent;P=0.01), which was calculated from patients who had their colon removed and whose diverticulitis was histologically proven, and in the evaluation of the severity of the inflammation (26vs. 9 percent;P=0.02). Moreover, of 69 patients who had an associated abscess seen on computed tomography, only 20 (29 percent) had indirect signs of this complication on contrast enema. CONCLUSIONS: In the diagnostic evaluation of acute left-colonic diverticulitis, computed tomography should be preferred to contrast enema as the initial radiologic examination because of its statistically significant superiority in sensitivity and for its significantly better performance in the detection of severe infection, especially when an abscess is associated with the disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Rodkey GV, Welch CE. Diverticulitis of the colon: evolution in concept and therapy. Surg Clin North Am 1965;45:1231–43.
Parks TG. Natural history of diverticular disease of the colon. Clin Gastroenterol 1975;4:53–69.
Horner JL. Natural history of diverticulosis of the colon. Am J Dig Dis 1958;3:343–50.
Ambrosetti P, Robert JH, Witzig JA,et al. Acute left colonic diverticulitis: a prospective analysis of 226 consecutive cases. Surgery 1994;115:546–50.
Schwerk WB, Schwarz S, Rothmund M. Sonography in acute colonic diverticulitis: a prospective study. Dis Colon Rectum 1992;35:1077–84.
Verbank J, Lambrecht S, Rutgeerts L,et al. Can sonography diagnose acute colonic diverticulitis in patients with acute intestinal inflammation? A prospective study. J Clin Ultrasound 1989;17:661–6.
Balthazar EJ, Megibow A, Schinella RA, Gordon R. Limitations in the CT diagnosis of acute diverticulitis: comparison of CT, contrast enema, and pathologic findings in 16 patients. AJR 1990;154:281–5.
Birnbaum BA, Balthazar EJ. CT of appendicitis and diverticulitis. Radiol Clin North Am 1994;32:885–98.
Cho KC, Morehouse HT, Alterman DD, Thornhill BA. Sigmoid diverticulitis: diagnostic role of CT—comparison with barium enema studies. Radiology 1990;176:111–5.
Stefansson T, Nyman R, Nilsson S, Ekbom A, Påhlman L. Diverticulitis of the sigmoid colon. A comparison of CT, colonic enema and laparoscopy. Acta Radiologica 1997;38:313–9.
Smith TR, Cho KC, Morehouse HT, Kratka PS. Comparison of computed tomography and contrast enema evaluation of diverticulitis. Dis Colon Rectum 1990;33:1–6.
Hulnick DH, Megibow AJ, Balthazar EJ, Naidich DP, Bosniak MA. Computed tomography in the evaluation of diverticulitis. Radiology 1984;152:491–5.
Johnson CD, Baker ME, Rice RP, Silverman P, Thompson WM. Diagnosis of diverticulitis: comparison of barium enema and CT. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1987;148:541–6.
Labs JD, Sarr MG, Fishman EK, Siegelman SS, Cameron JL. Complications of acute diverticulitis of the colon: improved early diagnosis with computed tomography. Am J Surg 1988;155:331–5.
Ferzoco LB, Raptopoulos V, Silen W. Acute diverticulitis. N Engl J Med 1998; 21: 1521–6.
Rao PM, Rhea JT, Novelline RA,et al. Helical CT with only colonic contrast material for diagnosing diverticulitis: prospective evaluation of 150 patients. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1998;170:1445–9.
Mueller PR, Saini S, Wittenburg J,et al. Sigmoid diverticular abscess: percutaneous drainage as an adjunct to surgical resection in 24 cases. Radiology 1987;164:321–5.
Morris J, Stellato TA, Lieberman J, Haaga JR. The utility of computed tomography in colonic diverticulitis. Ann Surg 1986;204:128–32.
Neff CC, vanSonnenberg E, Casola G,et al. Diverticular abscesses: percutaneous drainage. Radiology 1987;163:15–8.
Ambrosetti P, Grossholz M, Becker C, Terrier F, Morel Ph. Computed tomography in acute left colonic diverticulitis. Br J Surg 1997;84:532–4.
Ambrosetti P, Robert J, Witzig JA,et al. Prognostic factors from computed tomography in acute left colonic diverticulitis. Br J Surg 1992;79:117–9.
McKee RF, Deignan RW, Krukowski ZH. Radiological investigation in acute diverticulitis. Br J Surg 1993;80:560–5.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
Ambrosetti, P., Jenny, A., Becker, C. et al. Acute left colonic diverticulitis—compared performance of computed tomography and water-soluble contrast enema. Dis Colon Rectum 43, 1363–1367 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02236631
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02236631