Abstract
Veterinary pharmaceuticals have been extensively used in animal husbandry for control of disease and growth promoters. These compounds are excreted from animals via urine and faeces, end up in the environment through untreated animal waste disposal. Veterinary pharmaceuticals often exist in the complex solid environmental samples such as manure, slurry, and soil which require extensive extraction, clean-up and analysis method. This review highlights the current analytical methods for the analysis of veterinary pharmaceuticals in complex solid environmental matrices, including soil, animal manures and sediment. The aim of this review is to compare and summarize the performance of each method in terms of recovery, method detection limit (MDL) and method quantification limit (MQL).
Access provided by Autonomous University of Puebla. Download conference paper PDF
Similar content being viewed by others
Keywords
Highlights
-
Pharmaceutical analysis in solid samples requires complex extraction method.
-
MeOH:EDTA:McIlvaince buffer is frequently reported as extraction solvent for solids.
-
MeOH:ACN:0.1 M EDTA:McIlvaine extraction buffer is proposed to improve recovery.
-
LC–MS/MS allows multi-residue, sensitive and selective pharmaceuticals analysis.
-
HPLC–UV and HPLC-FLD are still being used due to its lower operating cost.
Introduction
All the while, the trends for analysis of pharmaceuticals in environment are focused in aqueous samples especially on human pharmaceuticals. Unlike human pharmaceuticals, veterinary pharmaceuticals often exist in the complex solid environmental samples such as manure, slurry, and soil. Very few studies have been devoted to pharmaceuticals in solid environmental samples due to pharmaceuticals being a large group of pollutants from different chemical classes with different physico–chemical properties (polar, semi polar, non polar, acidic, basic, neutral, strongly, moderately and weakly sorbed). In this review, we summarized the current available methods for determination of veterinary pharmaceuticals in soil and biological materials; the performance of each method is presented in Table 34.1.
Materials and Methods
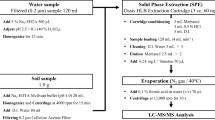
Sample Preparation and Extraction
Ultrasonic extraction is known as a popular technique which is rapid and does not require large volumes of solvent or expensive instrumentation. This method has been successfully applied to pharmaceuticals extraction in solid environmental samples (Blackwell et al. 2004; Kim and Carlson 2007; Carballo et al. 2007; Aust et al. 2008; Karcı and Balcıoğlu 2009). MeOH: EDTA: McIlvaince buffer was frequently reported as extraction solvent for ultrasonication to extract antibiotics from soil and biosolids (Blackwell et al. 2004; Aust et al. 2008; Karcı and Balcıoğlu 2009). However, this extraction buffer limits to extract only high polarity compounds such as antibiotics whereas low polarity compounds such as hormones are often difficult to extract due to the strong partitioning affinity to soil and organic matter (Ho et al. 2012). Therefore, MeOH:ACN:0.1 M EDTA:McIlvaine buffer was proposed by Ho et al. (2012) to improve the recovery of low polarity analytes.
Instrumental Analysis
Liquid chromatography is widely used as a complementary technique to gas chromatography in residue analysis because of its applicability to the determination of polar, water soluble and non-volatile compounds without derivatization. UV detection (Blackwell et al. 2004; Hu et al. 2008; Karcı and Balcıoğlu 2009), and to a lesser extent mass spectrometry (Haller et al. 2002), and fluorescence detection (Blackwell et al. 2004; Karcı and Balcıoğlu 2009), have been used in the detection techniques in coupled to HPLC, for the analysis of pharmaceuticals in solid environmental samples.
Conclusion
The current available methods for determination of veterinary pharmaceuticals in soil and biological material are reviewed and summarized. In general, most of the extraction methods for veterinary pharmaceuticals in soil and biological materials require ultrasonic extraction with the aid of appropriate extraction buffer and subsequently analyzed by HPLC-FLD or LC–MS/MS.
References
Aust MO, Godlinski F, Travis GR, Hao X, McAllister TA, Leinweber P (2008) Distribution of sulfamethazine, chlortetracycline and tylosin in manure and soil of Canadian feedlots after subtherapeutic use in cattle. Environ Pollut 156(3):1243–1251
Blackwell PA, Lützhøft HCH, Ma HP, Sørensen BH, Boxall ABA, Kay P (2004) Ultrasonic extraction of veterinary antibiotics from soils and pig slurry with SPE clean-up and LC-UV and fluorescence detection. Talanta 64(4):1058–1064
Carballo EM, Barreiro CG, Scharf S, Gans O (2007) Environmental monitoring study of selected veterinary antibiotics in animal manure and soils in Austria. Environ Pollut 148(2):570–579
Haller MY, Muller SR, McArdell CS, Alder AC, Suter MJF (2002) Quantification of veterinary antibiotics (sulfonamides and trimethoprim) in animal manure by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 952(1–2):111–120
Ho YB, Zakaria MP, Latif PA, Saari N (2012) Simultaneous determination of veterinary antibiotics and hormone in broiler manure, soil and manure compost by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1262:160–168
Hu XG, Yi L, Zhou QX, Xu L (2008) Determination of thirteen antibiotics residues in manure by solid phase extraction and high performance liquid chromatography. Chin J Anal Chem 36(9):1162–1166
Karcı A, Balcıoğlu IA (2009) Investigation of the tetracycline, sulfonamide, and fluoroquinolone antimicrobial compounds in animal manure and agricultural soils in Turkey. Sci Total Environ 407(16):4652–4664
Kim SC, Carlson K (2007) Quantification of human and veterinary antibiotics in water and sediment using SPE/LC/MS/MS. Anal Bioanal Chem 387:1301–1315
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2014 Springer Science+Business Media Singapore
About this paper
Cite this paper
Ho, Y.B., Zakaria, M.P., Latif, P.A., Saari, N. (2014). Determination of Veterinary Pharmaceuticals Residue in Soil and Biological Materials: A Review of Current Analytical Methods. In: Aris, A., Tengku Ismail, T., Harun, R., Abdullah, A., Ishak, M. (eds) From Sources to Solution. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-4560-70-2_34
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-4560-70-2_34
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-4560-69-6
Online ISBN: 978-981-4560-70-2
eBook Packages: Earth and Environmental ScienceEarth and Environmental Science (R0)