Abstract
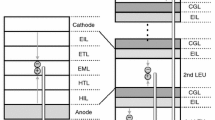
White organic light-emitting devices (OLEDs) have attracted considerable interest for use in solid-state flat-panel lighting. The operational lifetime of OLEDs decreases with increasing current density or luminance because the larger the number of holes and electrons passes through organic layer, the more electrochemical side reactions of organic compounds occur. A particular approach to solve this issue is tandem structure of OLEDs, in which plural light-emitting units (LEUs) are stacked in series through a charge generation layer (CGL). The tandem OLEDs have been fabricated to attain long operational lifetimes under high luminance. In addition, electron injection layers (EILs) are also important to reduce electron injection barrier from the CGL into the first LEU. Tandem OLEDs with two LEUs can exhibit a twofold increase in luminance compared with a single LEU device under an identical current density. Therefore, current efficiency and operational lifetime of tandem OLEDs can also be improved in comparison with those of conventional single LEU OLEDs. This tandem structure is now used in the actual application of OLED for white lighting manufactured in the industry.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adachi C, Baldo MA, Thompson ME, Forrest SR (2001) Nearly 100% internal phosphorescence efficiency in an organic light-emitting device. J Appl Phys 90:5048–5051
Aizawa N, Pu Y-J, Chiba T, Kawata S, Sasabe H, Kido J (2014a) Instant low-temperature cross-linking of poly(N-vinylcarbazole) for solution-processed multilayer blue phosphorescent organic light-emitting devices. Adv Mater 26:7543–7546
Aizawa N, Pu Y-J, Watanabe M, Chiba T, Ideta K, Toyota N, Igarashi M, Suzuri Y, Sasabe H, Kido J (2014b) Solution-processed multilayer small-molecule light-emitting devices with high-efficiency white-light emission. Nat Commun 5:5756
Akatsuka T, Roldan-Carmona C, Orti E, Bolink HJ (2014) Dynamically doped white light emitting tandem devices. Adv Mater 26:770–774
Bolink HJ, Brine H, Coronado E, Sessolo M (2010) Phosphorescent hybrid organic-inorganic light-emitting diodes. Adv Mater 22:2198–2201
Burn PL, Lo SC, Samuel IDW (2007) The development of light-emitting dendrimers for displays. Adv Mater 19:1675–1688
Chan MY, Lai SL, Lau KM, Fung MK, Lee CS, Lee ST (2007) Influences of connecting unit architecture on the performance of tandem organic light-emitting devices. Adv Funct Mater 17:2509–2514
Chang CC, Chen JF, Hwang SW, Chen CH (2005) Highly efficient white organic electroluminescent devices based on tandem architecture. Appl Phys Lett 87:253501
Chen CW, Lu YJ, Wu CC, Wu EHE, Chu CW, Yang Y (2005) Effective connecting architecture for tandem organic light-emitting devices. Appl Phys Lett 87:241121
Chen S, Manders JR, Tsang SW, So F (2012) Metal oxides for interface engineering in polymer solar cells. J Mater Chem 22:24202–24212
Chiba T, Pu Y-J, Miyazaki R, Nakayama K, Sasabe H, Kido J (2011) Ultra-high efficiency by multiple emission from stacked organic light-emitting devices. Org Electron 12:710–715
Chiba T, Pu Y-J, Hirasawa M, Masuhara A, Sasabe H, Kido J (2012a) Solution-processed inorganic-organic hybrid electron injection layer for polymer light-emitting devices. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 4:6104–6108
Chiba T, Pu Y-J, Sasabe H, Kido J, Yang Y (2012b) Solution-processed organic light-emitting devices with two polymer light-emitting units connected in series by a charge-generation layer. J Mater Chem 22:22769
Chiba T, Pu Y-J, Kido J (2015) Solution-processed white phosphorescent tandem organic light-emitting devices. Adv Mater 27:4681–4687
Ding L, Tang X, Xu MF, Shi XB, Wang ZK, Liao LS (2014) Lithium hydride doped intermediate connector for high-efficiency and long-term stable tandem organic light-emitting diodes. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6:18228–18232
Earmme T, Jenekhe SA (2012) Solution-processed, alkali metal-salt-doped, electron-transport layers for high-performance phosphorescent organic light-emitting diodes. Adv Funct Mater 22:5126–5136
Earmme T, Ahmed E, Jenekhe SA (2010) Solution-processed highly efficient blue phosphorescent polymer light-emitting diodes enabled by a new electron transport material. Adv Mater 22:4744–4748
Friend RH, Gymer RW, Holmes AB, Burroughes JH, Marks RN, Taliani C, Bradley DDC, Dos Santos DA, Bredas JL, Logdlund M, Salaneck WR (1999) Electroluminescence in conjugated polymers. Nature 397:121–128
Gao CH, Zhu XZ, Zhang L, Zhou DY, Wang ZK, Liao LS (2013) Comparative studies on the inorganic and organic p-type dopants in organic light-emitting diodes with enhanced hole injection. Appl Phys Lett 102:153301
Gong X, Wang S, Moses D, Bazan GC, Heeger AJ (2005) Multilayer polymer light-emitting diodes: white-light emission with high efficiency. Adv Mater 17:2053–2058
Guo FW, Ma DG (2005) White organic light-emitting diodes based on tandem structures. Appl Phys Lett 87:173510
Hamwi S, Meyer J, Kroger M, Winkler T, Witte M, Riedl T, Kahn A, Kowalsky W (2010) The role of transition metal oxides in charge-generation layers for stacked organic light-emitting diodes. Adv Funct Mater 20:1762–1766
Han T-H, Lee Y, Choi M-R, Woo S-H, Bae S-H, Hong BH, Ahn J-H, Lee T-W (2012) Extremely efficient flexible organic light-emitting diodes with modified graphene anode. Nat Photonics 6:105–110
Helander MG, Wang ZB, Qiu J, Greiner MT, Puzzo DP, Liu ZW, Lu ZH (2011) Chlorinated indium tin oxide electrodes with high work function for organic device compatibility. Science 332:944–947
Ho PKH, Kim JS, Burroughes JH, Becker H, Li SFY, Brown TM, Cacialli F, Friend RH (2000) Molecular-scale interface engineering for polymer light-emitting diodes. Nature 404:481–484
Ho MH, Chen TM, Yeh PC, Hwang SW, Chen CH (2007) Highly efficient p-i-n white organic light emitting devices with tandem structure. Appl Phys Lett 91:233507
Hofle S, Bruns M, Strassle S, Feldmann C, Lemmer U, Colsmann A (2013) Tungsten oxide buffer layers fabricated in an inert sol-gel process at room-temperature for blue organic light-emitting diodes. Adv Mater 25:4113–4116
Hofle S, Schienle A, Bruns M, Lemmer U, Colsmann A (2014a) Enhanced electron injection into inverted polymer light-emitting diodes by combined solution-processed zinc oxide/polyethylenimine interlayers. Adv Mater 26:2750–2754
Hofle S, Schienle A, Bernhard C, Bruns M, Lemmer U, Colsmann A (2014b) Solution processed, white emitting tandem organic light-emitting diodes with inverted device architecture. Adv Mater 26:5155–5159
Hofle S, Bernhard C, Bruns M, Kubel C, Scherer T, Lemmer U, Colsmann A (2015) Charge generation layers for solution processed tandem organic light emitting diodes with regular device architecture. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7:8132–8137
Hong K, Lee JL (2012) Charge generation mechanism of metal oxide interconnection in tandem organic light emitting diodes. J Phys Chem C 116:6427–6433
Huang JS, Li G, Wu E, Xu QF, Yang Y (2006) Achieving high-efficiency polymer white-light-emitting devices. Adv Mater 18:114–117
Huang J, Xu Z, Yang Y (2007) Low-work-function surface formed by solution-processed and thermally deposited nanoscale layers of cesium carbonate. Adv Funct Mater 17:1966–1973
Huang F, Zhang Y, Liu MS, Jen AKY (2009) Electron-rich alcohol-soluble neutral conjugated polymers as highly efficient electron-injecting materials for polymer light-emitting diodes. Adv Funct Mater 19:2457–2466
Kabra D, Lu LP, Song MH, Snaith HJ, Friend RH (2010) Efficient single-layer polymer light-emitting diodes. Adv Mater 22:3194–3198
Kanno H, Giebink NC, Sun YR, Forrest SR (2006a) Stacked white organic light-emitting devices based on a combination of fluorescent and phosphorescent emitters. Appl Phys Lett 89:023503
Kanno H, Holmes RJ, Sun Y, Kena-Cohen S, Forrest SR (2006b) White stacked electrophosphorescent organic light-emitting devices employing MoO3 as a charge-generation layer. Adv Mater 18:339–342
Kido J, Kimura M, Nagai K (1995) Multilayer white light-emitting organic electroluminescent device. Science 267:1332–1334
Kim YK, Kim JW, Park Y (2009) Energy level alignment at a charge generation interface between 4,4(′)-bis(N-phenyl-1-naphthylamino)biphenyl and 1,4,5,8,9,11-hexaazatriphenylene-hexacarbonitrile. Appl Phys Lett 94:063305
Kim YH, Han TH, Cho H, Min SY, Lee CL, Lee TW (2014) Polyethylene imine as an ideal interlayer for highly efficient inverted polymer light-emitting diodes. Adv Funct Mater 24:3808–3814
Kondakova ME, Deaton JC, Pawlik TD, Giesen DJ, Kondakov DY, Young RH, Royster TL, Comfort DL, Shore JD (2010) Highly efficient fluorescent-phosphorescent triplet-harvesting hybrid organic light-emitting diodes. J Appl Phys 107:014515
Kroger M, Hamwi S, Meyer J, Riedl T, Kowalsky W, Kahn A (2009) Role of the deep-lying electronic states of MoO3 in the enhancement of hole-injection in organic thin films. Appl Phys Lett 95:123301
Lee TW, Noh T, Choi BK, Kim MS, Shin DW, Kido J (2008) High-efficiency stacked white organic light-emitting diodes. Appl Phys Lett 92:043301
Lee S, Kim KH, Limbach D, Park YS, Kim JJ (2013) Low roll-off and high efficiency orange organic light emitting diodes with controlled co-doping of green and red phosphorescent dopants in an exciplex forming co-host. Adv Funct Mater 23:4105–4110
Lee S, Shin H, Kim JJ (2014) High-efficiency orange and tandem white organic light-emitting diodes using phosphorescent dyes with horizontally oriented emitting dipoles. Adv Mater 26:5864–5868
Leem DS, Lee JH, Kim JJ, Kang JW (2008) Highly efficient tandem p-i-n organic light-emitting diodes adopting a low temperature evaporated rhenium oxide interconnecting layer. Appl Phys Lett 93:103304
Liao LS, Klubek KP (2008) Power efficiency improvement in a tandem organic light-emitting diode. Appl Phys Lett 92:223311
Liao LS, Klubek KP, Tang CW (2004) High-efficiency tandem organic light-emitting diodes. Appl Phys Lett 84:167
Liao LS, Slusarek WK, Hatwar TK, Ricks ML, Comfort DL (2008) Tandem organic light-emitting mode using hexaazatriphenylene hexacarbonitrile in the intermediate connector. Adv Mater 20:324–329
Liu J, Huang SJ, Shi XD, Wu XK, Wang J, He GF (2013) Charge separation process in an ultrathin electron-injecting bilayer-assisted charge generation unit for tandem organic light-emitting diodes. J Phys Chem C 117:13887–13893
Matsumoto T, Nakada T, Endo J, Mori K, Kawamura N, Yokoi A, Kido J (2003) SID 03 Digest 979
Matsumoto R, Nakada T, Endo J, Mori K, Kawamura N, Yokoi A, Kido K (2003) 27.5L: Late-news paper: multiphoton organic EL device having charge generation layer. SID 03 DIGEST
Meerheim R, Walzer K, Pfeiffer M, Leo K (2006) Ultrastable and efficient red organic light emitting diodes with doped transport layers. Appl Phys Lett 89:061111
Meyer J, Kroger M, Hamwi S, Gnam F, Riedl T, Kowalsky W, Kahn A (2010) Charge generation layers comprising transition metal-oxide/organic interfaces: electronic structure and charge generation mechanism. Appl Phys Lett 96:193302
Niu YH, Liu MS, Ka JW, Bardeker J, Zin MT, Schofield R, Chi Y, Jen AKY (2007) Crosslinkable hole-transport layer on conducting polymer for high-efficiency white polymer light-emitting diodes. Adv Mater 19:300–304
Park JS, Lee JM, Hwang SK, Lee SH, Lee HJ, Lee BR, Park HI, Kim JS, Yoo S, Song MH, Kim SO (2012) A ZnO/N-doped carbon nanotube nanocomposite charge transport layer for high performance optoelectronics. J Mater Chem 22:12695–12700
Park YS, Lee S, Kim KH, Kim SY, Lee JH, Kim JJ (2013) Exciplex-forming co-host for organic light-emitting diodes with ultimate efficiency. Adv Funct Mater 23:4914–4920
Perumal A, Faber H, Yaacobi-Gross N, Pattanasattayavong P, Burgess C, Jha S, McLachlan MA, Stavrinou PN, Anthopoulos TD, Bradley DDC (2015) High-efficiency, solution-processed, multilayer phosphorescent organic light-emitting diodes with a copper thiocyanate hole-injection/hole-transport layer. Adv Mater 27:93–100
Png RQ, Chia PJ, Tang JC, Liu B, Sivaramakrishnan S, Zhou M, Khong SH, Chan HS, Burroughes JH, Chua LL, Friend RH, Ho PK (2010) High-performance polymer semiconducting heterostructure devices by nitrene-mediated photocrosslinking of alkyl side chains. Nat Mater 9:152–158
Qi XF, Slootsky M, Forrest S (2008) Stacked white organic light emitting devices consisting of separate red, green, and blue elements. Appl Phys Lett 93:193306
Qian L, Zheng Y, Choudhury KR, Bera D, So F, Xue JG, Holloway PH (2010) Electroluminescence from light-emitting polymer/ZnO nanoparticle heterojunctions at sub-bandgap voltages. Nano Today 5:384–389
Reineke S, Lindner F, Schwartz G, Seidler N, Walzer K, Lussem B, Leo K (2009) White organic light-emitting diodes with fluorescent tube efficiency. Nature 459:234–238
Sasabe H, Takamatsu J, Motoyama T, Watanabe S, Wagenblast G, Langer N, Molt O, Fuchs E, Lennartz C, Kido J (2010) High-efficiency blue and white organic light-emitting devices incorporating a blue iridium carbene complex. Adv Mater 22:5003–5007
Sasabe H, Minamoto K, Pu YJ, Hirasawa M, Kido J (2012) Ultra high-efficiency multi-photon emission blue phosphorescent OLEDs with external quantum efficiency exceeding 40%. Org Electron 13:2615–2619
Schwartz G, Pfeiffer M, Reineke S, Walzer K, Leo K (2007) Harvesting triplet excitons from fluorescent blue emitters in white organic light-emitting diodes. Adv Mater 19:3672–3676
Seino Y, Sasabe H, Pu YJ, Kido J (2014) High-performance blue phosphorescent OLEDs using energy transfer from Exciplex. Adv Mater 26:1612–1616
Shen ZL, Burrows PE, Bulovic V, Forrest SR, Thompson ME (1997) Three-color, tunable, organic light-emitting devices. Science 276:2009–2011
Stolz S, Scherer M, Mankel E, Lovrincic R, Schinke J, Kowalsky W, Jaegermann W, Lemmer U, Mechau N, Hernandez-Sosa G (2014) Investigation of solution-processed ultrathin electron injection layers for organic light-emitting diodes. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6:6616–6622
Su SJ, Gonmori E, Sasabe H, Kido J (2008) Highly efficient organic blue-and white-light-emitting devices having a carrier- and exciton-confining structure for reduced efficiency roll-off. Adv Mater 20:4189–4194
Sun Y, Giebink NC, Kanno H, Ma B, Thompson ME, Forrest SR (2006) Management of singlet and triplet excitons for efficient white organic light-emitting devices. Nature 440:908–912
Sun HD, Guo QX, Yang DZ, Chen YH, Chen JS, Ma DG (2015) High efficiency tandem organic light emitting diode using an organic heterojunction as the charge generation layer: an investigation into the charge generation model and device performance. ACS Photonics 2:271–279
Talik NA, Yeoh KH, Ng CYB, Yap BK, Woon KL (2014) Efficient green phosphorescent tandem organic light emitting diodes with solution processable mixed hosts charge generating layer. J Lumin 154:345–349
Terai M, Tsutsui T (2007) Electric-field-assisted bipolar charge generation from internal charge separation zone composed of doped organic bilayer. Appl Phys Lett 90:083502
Tsutsui T, Terai M (2004) Electric field-assisted bipolar charge spouting in organic thin-film diodes. Appl Phys Lett 84:440–442
Vaynzof Y, Kabra D, Chua LL, Friend RH (2011) Improved electron injection in poly(9,9′-dioctylfluorene)-co-benzothiodiazole via cesium carbonate by means of coannealing. Appl Phys Lett 98:113306
Yan F, Chen R, Sun HD, Sun XW (2013) Silver nanoparticle facilitated charge generation in tandem organic light-emitting devices. Appl Phys Lett 102:203303
Yang X, Müller DC, Neher D, Meerholz K (2006) Highly efficient polymeric electrophosphorescent diodes. Adv Mater 18:948–954
Yang JP, Xiao Y, Deng YH, Duhm S, Ueno N, Lee ST, Li YQ, Tang JX (2012) Electric-field-assisted charge generation and separation process in transition metal oxide-based interconnectors for tandem organic light-emitting diodes. Adv Funct Mater 22:600–608
Yook KS, Jeon SO, Min SY, Lee JY, Yang HJ, Noh T, Kang SK, Lee TW (2010) Highly efficient p-i-n and tandem organic light-emitting devices using an air-stable and low-temperature-evaporable metal azide as an n-dopant. Adv Funct Mater 20:1797–1802
Youn H, Yang M (2010) Solution processed polymer light-emitting diodes utilizing a ZnO/organic ionic interlayer with Al cathode. Appl Phys Lett 97:243302
Zhang Y, Lee J, Forrest SR (2014) Tenfold increase in the lifetime of blue phosphorescent organic light-emitting diodes. Nat Commun 5:5008
Zhao YB, Tan ST, Demir HV, Sun XW (2015) Highly stable and high power efficiency tandem organic light-emitting diodes with transition metal oxide-based charge generation layers. Org Electron 23:70–75
Zhou Y, Fuentes-Hernandez C, Shim J, Meyer J, Giordano AJ, Li H, Winget P, Papadopoulos T, Cheun H, Kim J, Fenoll M, Dindar A, Haske W, Najafabadi E, Khan TM, Sojoudi H, Barlow S, Graham S, Bredas JL, Marder SR, Kahn A, Kippelen B (2012) A universal method to produce low-work function electrodes for organic electronics. Science 336:327–332
Zhou DY, Cui LS, Zhang YJ, Liao LS, Aziz H (2014a) Low driving voltage simplified tandem organic light-emitting devices by using exciplex-forming hosts. Appl Phys Lett 105:153302
Zhou DY, Zu FS, Zhang YJ, Shi XB, Aziz H, Liao LS (2014b) Highly stable and efficient tandem organic light-emitting devices with intermediate connectors using lithium amide as n-type dopant. Appl Phys Lett 105:083301
Zhou DY, Shi XB, Liu Y, Gao CH, Wang K, Liao LS (2014c) Role of hole injection layer in intermediate connector of tandem organic light-emitting devices. Org Electron 15:3694–3701
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Section Editor information
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 Springer Japan KK, part of Springer Nature
About this entry
Cite this entry
Chiba, T., Pu, YJ., Kido, J. (2018). White OLED (WOLED) and Charge Generation Layer (CGL). In: Adachi, C., Hattori, R., Kaji, H., Tsujimura, T. (eds) Handbook of Organic Light-Emitting Diodes. Springer, Tokyo. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-4-431-55761-6_20-1
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-4-431-55761-6_20-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Tokyo
Print ISBN: 978-4-431-55761-6
Online ISBN: 978-4-431-55761-6
eBook Packages: Springer Reference Physics and AstronomyReference Module Physical and Materials ScienceReference Module Chemistry, Materials and Physics