Abstract
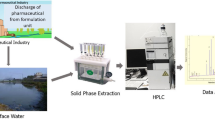
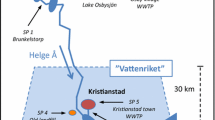
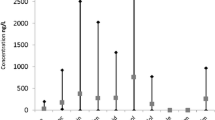
Drugs and drug metabolites are a new class of organic micropollutants which have been found in low concentrations (ng 1−1 to µg 1−1) in wastewater, ground and surface water (Hailing-Sørensen et al. 1997; Heberer 2002; Kümmerer 2001; Sacher et al. 2002; Spengler et al. 2001). Recent monitoring studies indicate that in many cases the main route for human drugs entering the aquatic environment is via treated or untreated sewage effluent (Sacher et al. 2002; Heberer 2002). Because it is common (and — with the exception of e.g. cytostatics — legal) practice in many countries to discard expired and unwanted drugs, household waste and landfills can also be expected to be a source of pharmaceutical products. Since many of the disposal sites are still open dumps without protective barriers and leachate collection systems, there is a danger of infiltration of contaminated leachates into the soil influencing the quality of groundwater near landfills. The present article gives an overview on the presence of drugs in municipal landfills and landfill leachates as found in the few publications available so far.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abfallablagerungsverordnung (AbfAbiV) (2001) Verordnung über die umweltverträgliche Ablagerung von Siedlungsabfällen und über biologische Abfallbehandlungsanlagen. Bundesgesetzblatt Teil I, Nr.1o, 27. Februar 2001, p 305
Ahel M, Jelièic I (zoos) Phenazone analgesics in soil and groundwater below a municipal solid waste landfill. In: Daughton CG, Jones-Lepp TL (eds) Pharmaceuticals and personal care products in the environment: scientific and regulatory issues. American Chemical Society, Washington, DC (Symposium Series 791: 100–115 )
Breidenich N (2003) Arzneimittel in Deponiesickerwässern. In: FEI e.V. Stuttgart (ed) Organische Spurenstoffe im Wasser – kleine Konzentrationen – große Wirkung? Kommissionsverlag Oldenbourg Industrieverlag, München (Stuttgarter Berichte zur Siedlungswasserwirtschaft,vol 173, 3. Hydrochemisches und Hydrobiologisches Kolloquium, Stuttgart, pp 25–35, ISBN 3–486–26552–0)
Eckel WP, Ross B, Isensee R (1993) Pentobarbital found in ground water. Ground Water 31: 801–804
Halling-Sorensen B, Nors Nielsen S, Lanzky PF, Ingerslev F, Holten-Lützhoft HC, Jorgensen SE (1997) Occurrence, fate and effects of pharmaceutical substances in the environment–a review. Chemosphere 36: 357–393
Heberer T (2002) Occurrence, fate, and removal of pharmaceutical residues in the aquatic environment: a review of recent research data. Toxicol Lett 131: 5–17
Holm JV, Rugge K, Bjerg PL,Christensen TH (1995) Occurrence and distribution of pharmaceutical organic compounds in the groundwater downgradient of a landfill (Grinsted, Denmark). Environ Sci Techn 29: 1415–1420
Kämmerer K (2001) Pharmaceuticals in the environment. Sources, fate, effects and risks. Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Sacher F, Gabriel S, Metzinger M, Stretz A, Wenz M, Lange FT, Brauch H-J, Blankenhorn I (2002) Arzneimittelwirkstoffe im Grundwasser–Ergebnisse eines Monitoring-Programmes in Baden-Württemberg. Vom Wasser 99: 183–196
Schneider C, Möhle E, Stenz G, Krauß P, Metzger JW (2001) Arzneimittel in Siedlungsabfällen und in Deponiesickerwässern. Müll und Abfall 33 (6): 362–369
Spengler P, Körner W, Metzger JW (2001) Substances with estrogenic activity in effluents of sewage treat- ment plants in southwest Germany. Part I: Chemical analysis. Environ Toxicol Chem 20: 2133–2141
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2004 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Metzger, J.W. (2004). Drugs in Municipal Landfills and Landfill Leachates. In: Kümmerer, K. (eds) Pharmaceuticals in the Environment. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-09259-0_10
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-09259-0_10
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-662-09261-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-662-09259-0
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive