Abstract
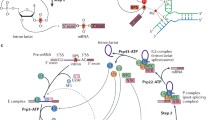
Pre-mRNA splicing is a key step for generating mature protein-coding mRNA. An RNA–protein complex known as the spliceosome carries out the chemistry of pre-mRNA splicing. However, several pre-spliceosomal intermediates are assembled on the pre-mRNA before the formation of the catalytically activated spliceosome. The progression to the activated spliceosome involves a cascade of the rearrangement events of the RNA–RNA, RNA–protein, and protein–protein interactions within the pre-spliceosomal intermediates. These rearrangements generate multiple combinatorial interactions of the spliceosome with the substrate, which enhances the accuracy of the splice site selection. Each rearrangement also represents a step at which splicing can potentially be subjected to regulation. The aim of this chapter is to provide an overview of the components of the spliceosome and their rearrangements along the spliceosome assembly pathway.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berget SM, Moore C, Sharp PA (1977) Spliced segments at the 5′ terminus of adenovirus 2 late mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 74:3171–3175
Brody E, Abelson J (1985) The “spliceosome”: yeast pre-messenger RNA associates with a 40S complex in a splicing-dependent reaction. Science 228:963–967
Jurica MS, Moore MJ (2002) Capturing splicing complexes to study structure and mechanism. Methods 28:336–345
Luhrmann R, Stark H (2009) Structural mapping of spliceosomes by electron microscopy. Curr Opin Struct Biol 19:96–102
Wahl MC, Will CL, Luhrmann R (2009) The spliceosome: design principles of a dynamic RNP machine. Cell 136:701–718
Consortium IHGS (2004) Finishing the euchromatic sequence of the human genome. Nature 431:931–945
House AE, Lynch KW (2006) An exonic splicing silencer represses spliceosome assembly after ATP-dependent exon recognition. Nat Struct Mol Biol 13:937–944
Sharma S, Kohlstaedt LA, Damianov A, Rio DC, Black DL (2008) Polypyrimidine tract binding protein controls the transition from exon definition to an intron defined spliceosome. Nat Struct Mol Biol 15:183–191
Schneider M, Will CL, Anokhina M, Tazi J, Urlaub H et al (2010) Exon definition complexes contain the tri-snRNP and can be directly converted into B-like precatalytic splicing complexes. Mol Cell 38:223–235
Nilsen TW (1994) RNA-RNA interactions in the spliceosome: unraveling the ties that bind. Cell 78:1–4
Staley JP, Guthrie C (1998) Mechanical devices of the spliceosome: motors, clocks, springs, and things. Cell 92:315–326
Zhou Z, Licklider LJ, Gygi SP, Reed R (2002) Comprehensive proteomic analysis of the human spliceosome. Nature 419:182–185
Rappsilber J, Ryder U, Lamond AI, Mann M (2002) Large-scale proteomic analysis of the human spliceosome. Genome Res 12:1231–1245
Behzadnia N, Golas MM, Hartmuth K, Sander B, Kastner B et al (2007) Composition and three-dimensional EM structure of double affinity-purified, human prespliceosomal A complexes. EMBO J 26:1737–1748
Deckert J, Hartmuth K, Boehringer D, Behzadnia N, Will CL et al (2006) Protein composition and electron microscopy structure of affinity-purified human spliceosomal B complexes isolated under physiological conditions. Mol Cell Biol 26:5528–5543
Jurica MS, Licklider LJ, Gygi SR, Grigorieff N, Moore MJ (2002) Purification and characterization of native spliceosomes suitable for three-dimensional structural analysis. RNA 8:426–439
Grote M, Wolf E, Will CL, Lemm I, Agafonov DE et al (2010) Molecular architecture of the human Prp19/CDC5L complex. Mol Cell Biol 30:2105–2119
Schwer B (2008) A conformational rearrangement in the spliceosome sets the stage for Prp22-dependent mRNA release. Mol Cell 30:743–754
Schwer B, Guthrie C (1992) A conformational rearrangement in the spliceosome is dependent on PRP16 and ATP hydrolysis. EMBO J 11:5033–5039
Pan Q, Shai O, Lee LJ, Frey BJ, Blencowe BJ (2008) Deep surveying of alternative splicing complexity in the human transcriptome by high-throughput sequencing. Nat Genet 40:1413–1415
Cooper TA, Wan L, Dreyfuss G (2009) RNA and disease. Cell 136:777–793
Wang ET, Sandberg R, Luo S, Khrebtukova I, Zhang L et al (2008) Alternative isoform regulation in human tissue transcriptomes. Nature 456:470–476
Schneider M, Hsiao HH, Will CL, Giet R, Urlaub H et al (2010) Human PRP4 kinase is required for stable tri-snRNP association during spliceosomal B complex formation. Nat Struct Mol Biol 17:216–221
Pomeranz Krummel DA, Oubridge C, Leung AK, Li J, Nagai K (2009) Crystal structure of human spliceosomal U1 snRNP at 5.5 A resolution. Nature 458:475–480
Dybkov O, Will CL, Deckert J, Behzadnia N, Hartmuth K et al (2006) U2 snRNA-protein contacts in purified human 17S U2 snRNPs and in spliceosomal A and B complexes. Mol Cell Biol 26:2803–2816
Song EJ, Werner SL, Neubauer J, Stegmeier F, Aspden J et al (2010) The Prp19 complex and the Usp4Sart3 deubiquitinating enzyme control reversible ubiquitination at the spliceosome. Genes Dev 24:1434–1447
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2014 Springer Science+Business Media, LLC
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Chiou, Nt., Lynch, K.W. (2014). Mechanisms of Spliceosomal Assembly. In: Hertel, K. (eds) Spliceosomal Pre-mRNA Splicing. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 1126. Humana Press, Totowa, NJ. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-62703-980-2_3
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-62703-980-2_3
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana Press, Totowa, NJ
Print ISBN: 978-1-62703-979-6
Online ISBN: 978-1-62703-980-2
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols