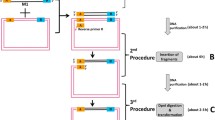
Abstract
Identification of unknown sequences that flank known sequences of interest requires PCR amplification of DNA fragments that contain the junction between the known and unknown flanking sequences. Since amplified products often contain a mixture of specific and nonspecific products, the quick and clean (QC) cloning procedure was developed to clone specific products only. QC cloning is a ligation-independent cloning procedure that relies on the exonuclease activity of T4 DNA polymerase to generate single-stranded extensions at the ends of the vector and insert. A specific feature of QC cloning is the use of vectors that contain a sequence called catching sequence that allows cloning specific products only. QC cloning is performed by a one-pot incubation of insert and vector in the presence of T4 DNA polymerase at room temperature for 10 min followed by direct transformation of the incubation mix in chemo-competent Escherichia coli cells.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Frohman MA, Dush MK, Martin GR (1988) Rapid production of full-length cDNAs from rare transcripts: amplification using a single gene-specific oligonucleotide primer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:8998–9002
Mueller PR, Wold B (1989) In vivo footprinting of a muscle specific enhancer by ligation mediated PCR. Science 246:780–786
Riley J, Butler R, Ogilvie D et al (1990) A novel, rapid method for the isolation of terminal sequences from yeast artificial chromosome (YAC) clones. Nucleic Acids Res 18:2887–2890
Rosenthal A, Jones DS (1990) Genomic walking and sequencing by oligo-cassette mediated polymerase chain reaction. Nucleic Acids Res 18:3095–3096
Liu YG, Whittier RF (1995) Thermal asymmetric interlaced PCR: automatable amplification and sequencing of insert end fragments from P1 and YAC clones for chromosome walking. Genomics 25:674–681
Tonooka Y, Fujishima M (2009) Comparison and critical evaluation of PCR-mediated methods to walk along the sequence of genomic DNA. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 85:37–43
Thieme F, Engler C, Kandzia R et al (2011) Quick and clean cloning: a ligation-independent cloning strategy for selective cloning of specific PCR products from non-specific mixes. PLoS One 6:e20556
Aslanidis C, de Jong PJ (1990) Ligation-independent cloning of PCR products (LIC-PCR). Nucleic Acids Res 18:6069–6074
Yang YS, Watson WJ, Tucker PW et al (1993) Construction of recombinant DNA by exonuclease recession. Nucleic Acids Res 21:1889–1893
Li MZ, Elledge SJ (2007) Harnessing homologous recombination in vitro to generate recombinant DNA via SLIC. Nat Methods 4:251–256
Bendandi M, Marillonnet S, Kandzia R et al (2010) Rapid, high-yield production in plants of individualized idiotype vaccines for non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Ann Oncol 21:2420–2427
Aslanidis C, de Jong PJ, Schmitz G (1994) Minimal length requirement of the single-stranded tails for ligation-independent cloning (LIC) of PCR products. PCR Methods Appl 4:172–177
Engler C, Kandzia R, Marillonnet S (2008) A one pot, one step, precision cloning method with high throughput capability. PLoS One 3:e3647
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2014 Springer Science+Business Media, New York
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Thieme, F., Marillonnet, S. (2014). Quick and Clean Cloning. In: Valla, S., Lale, R. (eds) DNA Cloning and Assembly Methods. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 1116. Humana Press, Totowa, NJ. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-62703-764-8_3
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-62703-764-8_3
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana Press, Totowa, NJ
Print ISBN: 978-1-62703-763-1
Online ISBN: 978-1-62703-764-8
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols