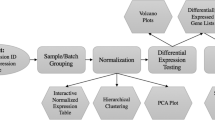
Abstract
Microarrays are a valuable technology to study fungal physiology on a transcriptomic level. Various microarray platforms are available comprising both single and two channel arrays. Despite different technologies, preprocessing of microarray data generally includes quality control, background correction, normalization, and summarization of probe level data. Subsequently, depending on the experimental design, diverse statistical analysis can be performed, including the identification of differentially expressed genes and the construction of gene coexpression networks.
We describe how Bioconductor, a collection of open source and open development packages for the statistical programming language R, can be used for dissecting microarray data. We provide fundamental details that facilitate the process of getting started with R and Bioconductor. Using two publicly available microarray datasets from Aspergillus niger, we give detailed protocols on how to identify differentially expressed genes and how to construct gene coexpression networks.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gentleman, R. C., Carey, V. J., Bates, D. M., Bolstad, B., Dettling, M., Dudoit, S., Ellis, B., Gautier, L., Ge, Y., Gentry, J., Hornik, K., Hothorn, T., Huber, W., Iacus, S., Irizarry, R., Leisch, F., Li, C., Maechler, M., Rossini, A. J., Sawitzki, G., Smith, C., Smyth, G., Tierney, L., Yang, J. Y., and Zhang, J. (2004) Bioconductor: open software development for computational biology and bioinformatics Genome Biol 5, R80.
Jorgensen, T. R., Nitsche, B. M., Lamers, G. E., Arentshorst, M., van den Hondel, C. A., and Ram, A. F. Transcriptomic insights into the physiology of Aspergillus niger approaching a specific growth rate of zero Appl Environ Microbiol 76, 5344–55.
Martens-Uzunova, E. S., Zandleven, J. S., Benen, J. A., Awad, H., Kools, H. J., Beldman, G., Voragen, A. G., Van den Berg, J. A., and Schaap, P. J. (2006) A new group of exo-acting family 28 glycoside hydrolases of Aspergillus niger that are involved in pectin degradation Biochem J 400, 43–52.
Team, R. D. C. (2010) R: A language and environment for statistical computing., R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria.
Gautier, L., Cope, L., Bolstad, B. M., and Irizarry, R. A. (2004) affy--analysis of Affymetrix GeneChip data at the probe level Bioinformatics 20, 307–15.
MacDonald, J. W. (2008) affycoretools: Functions useful for those doing repetitive analyses with Affymetrix GeneChips.
Bolstad, B. M., Collin, F., Brettschneider, J., Simpson, K., Cope, L., Irizarry, R. A., and Speed, T. P. (2005) Quality Assessment of Affymetrix GeneChip Data. in “Bioinformatics and Computational Biology Solutions Using R and Bioconductor.”, Springer, New York.
Smyth, G. K. (2004) Linear models and empirical bayes methods for assessing differential expression in microarray experiments Stat Appl Genet Mol Biol 3, Article3.
Gentleman, R., Carey, V., Huber, W., and Hahne, F. genefilter: methods for filtering genes from microarray experiments.
Irizarry, R. A., Gautier, L., Huber, W., and Bolstad, B. (2006) makecdfenv: CDF Environment Maker.
Irizarry, R. A., Bolstad, B. M., Collin, F., Cope, L. M., Hobbs, B., and Speed, T. P. (2003) Summaries of Affymetrix GeneChip probe level data Nucleic Acids Res 31, e15.
Naef, F., Lim, D. A., Patil, N., and Magnasco, M. (2002) DNA hybridization to mismatched templates: a chip study Phys Rev E Stat Nonlin Soft Matter Phys 65, 040902.
Benjamini, Y., and Hochberg, Y. (1995) Controlling the False Discovery Rate: A Practical and Powerful Approach to Multiple Testing Journal of the Royal Statistical Society. Series B (Methodological) 57, 289–300.
Bourgon, R., Gentleman, R., and Huber, W. Independent filtering increases detection power for high-throughput experiments Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107, 9546–51.
Baron, R. M., and Kenny, D. A. (1986) The moderator-mediator variable distinction in social psychological research: conceptual, strategic, and statistical considerations J Pers Soc Psychol 51, 1173–82.
Usadel, B., Obayashi, T., Mutwil, M., Giorgi, F. M., Bassel, G. W., Tanimoto, M., Chow, A., Steinhauser, D., Persson, S., and Provart, N. J. (2009) Co-expression tools for plant biology: opportunities for hypothesis generation and caveats Plant Cell Environ 32, 1633–51.
Harr, B., and Schlotterer, C. (2006) Comparison of algorithms for the analysis of Affymetrix microarray data as evaluated by co-expression of genes in known operons Nucleic Acids Res 34, e8.
Lim, W. K., Wang, K., Lefebvre, C., and Califano, A. (2007) Comparative analysis of microarray normalization procedures: effects on reverse engineering gene networks Bioinformatics 23, i282–8.
Li, C., and Wong, W. H. (2001) Model-based analysis of oligonucleotide arrays: expression index computation and outlier detection Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98, 31–6.
Hahne, F., Huber, W., Gentleman, R., and Falcon, S. (2008) Bioconductor case studies, Springer Verlag.
Shannon, P., Markiel, A., Ozier, O., Baliga, N. S., Wang, J. T., Ramage, D., Amin, N., Schwikowski, B., and Ideker, T. (2003) Cytoscape: a software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks Genome Res 13, 2498–504.
Bader, G. D., and Hogue, C. W. (2003) An automated method for finding molecular complexes in large protein interaction networks BMC Bioinformatics 4, 2.
Maere, S., Heymans, K., and Kuiper, M. (2005) BiNGO: a Cytoscape plugin to assess overrepresentation of gene ontology categories in biological networks Bioinformatics 21, 3448–9.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a grant of SenterNovem IOP Genomics project IGE07008. Part of this work was carried out within the research program of the Kluyver Centre for Genomics of Industrial Fermentation, which is part of the Netherlands Genomics Initiative/Netherlands Organization for Scientific Research. We thank T.G. Homan for discussions and proof reading of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2012 Springer Science+Business Media, LLC
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Nitsche, B.M., Ram, A.F.J., Meyer, V. (2012). The Use of Open Source Bioinformatics Tools to Dissect Transcriptomic Data. In: Bolton, M., Thomma, B. (eds) Plant Fungal Pathogens. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 835. Humana Press. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-61779-501-5_19
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-61779-501-5_19
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana Press
Print ISBN: 978-1-61779-500-8
Online ISBN: 978-1-61779-501-5
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols