Abstract
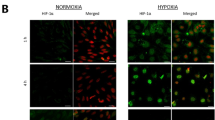
The goal of this chapter is to highlight methods used to demonstrate in vivo changes in astrocyte expression at the blood–brain barrier (BBB). Loss of BBB integrity is seen in many acute and chronic disease conditions. However, despite the importance of the BBB to homeostasis and correct functioning of the CNS, the nature of factors responsible for the induction and maintenance of BBB properties in development and the adult remains unclear. We have studied the role of astrocytes in modulating BBB integrity in two in vivo models using a gliotoxin (3-chloropropanediol), and under hypoxic stress. 3-chloropropanediol-induced astrocytic loss within the inferior colliculus leads to loss of endothelial tight junction protein expression and loss of BBB integrity. As glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP)-immunopositive astrocytes repopulated the lesion, tight junction protein expression returned to paracellular domains and BBB integrity was restored. Under hypoxic conditions, increased GFAP expression was seen with changes in tight junction protein expression and loss of BBB integrity. These studies suggest a critical role for glial/endothelial interactions in regulating BBB integrity in health and disease.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wolburg, H., and Lippoldt, A. (2002) Tight junctions of the blood-brain barrier: development, composition and regulation. Vasc. Pharmacol. 38, 323–337
Abbott, N.J. (2002) Astrocyte-endothelial interactions and blood-brain barrier permeability. J. Anat. 200, 629-638.
Furuse, M., Hirase, T., Itoh, M., Nagafuchi, A., Yonemura, S., Tsukita, S., and Tsukita, S. (1993) Occludin—a novel integral membrane-protein localizing at tight junctions. J. Cell Biol. 123, 1777–1788.
Kniesel, U., and Wolburg, H. (2000) Tight junctions of the blood-brain barrier. Cell Mol. Neurobiol. 20, 57–76.
Plumb, J., McQuaid, S., Mirakhur, M., and Kirk, J. (2002) Abnormal endothelial tight junctions in active lesions and normal-appearing white matter in multiple sclerosis. Brain Pathol. 12, 154–169.
Abbott, N.J., Ronnback, L., Hansson, E. (2006) Astrocyte-endothelial interactions at the blood-brain barrier. Nature Rev. 7, 41–53.
Rubin, L.L., Barbu, K., Bard, F., Cannon, C., Hall, D.E., Horner, H., Janatpour, M., Liaw, C., Manning, K., Morales, J., Porter, S., Tanner, L., Tomaselli, K., and Yednock, T. (1991) Differentiation of brain endothelial-cells in cell culture. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 633, 420–425.
Sobue, K., Yamamoto, N., Yoneda, K., Hodgson, M.E., Yamashiro, K., Tsuruoka, N., Tsuda, T., Katsuya, H., Miura, Y., Asai, K., and Kato, T. (1999) Induction of blood-brain barrier properties in immortalized bovine brain endothelial cells by astrocytic factors. Neurosci. Res. 35, 155– 164.
Prat, A., Biernacki, K., Wosik, K., Antel, J.P. (2001) Glial cell influence on the human blood-brain barrier. Glia 36, 145–155.
Willis, C.L., Leach, L., Clarke, G.J., Nolan, C.C., and Ray, D.E. (2004) Reversible disruption of tight junction complexes in the rat blood-brain barrier, following transitory focal astrocyte loss. Glia 48, 1–13.
Willis, C.L., Nolan, C.C., Reith, S.N., Lister, T., Guerin, C.J., Mavroudis, G., Prior M.J.W., and Ray, D.E. (2004) Focal astrocyte loss is followed by microvascular damage, with subsequent repair of the blood-brain barrier in the apparent absence of direct astrocytic contact. Glia 45, 325–337.
Willis, C.L., Meske, D.S., and Davis, T.P. (2010) Protein kinase C activation modulates reversible increase in cortical blood-brain barrier permeability and tight junction protein expression during hypoxia and posthypoxic reoxygenation. JCBFM 30:1847–1859.
Witt, K.A., Mark, K.S., Hom, S., Davis, T.P. (2003) Effects of hypoxia-reoxygenation on rat blood-brain barrier permeability and junctional protein expression. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 285:H2820–2831.
Rigor, R.R., Hawkins, B.T., Miller, D.S. (2010) Activation of PKC isoform βI at the blood–brain barrier rapidly decreases P-glycoprotein activity and enhances drug delivery to the brain. JCBFM 30:1373–1383.
Acknowledgments
The work was supported by a Medical Research Council U.K. Program grant and American Heart Association grant (AHA) SDG2170105 (CLW).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2012 Springer Science+Business Media, LLC
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Willis, C.L. (2012). Imaging In Vivo Astrocyte/Endothelial Cell Interactions at the Blood–Brain Barrier. In: Milner, R. (eds) Astrocytes. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 814. Humana Press. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-61779-452-0_34
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-61779-452-0_34
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana Press
Print ISBN: 978-1-61779-451-3
Online ISBN: 978-1-61779-452-0
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols