Abstract
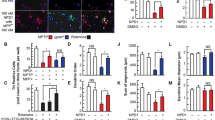
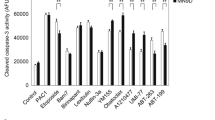
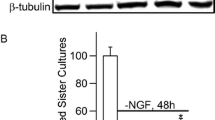
Investigation of mechanisms responsible for dopaminergic neuron death is critical for understanding the pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease, yet this is often quite challenging technically. Here, we describe detailed methods for culturing primary mesencephalic dopaminergic neurons and examining the activation of c-Jun N-terminal protein Kinase (JNK) in these cultures. We utilized immunocytochemistry and computerized analysis to quantify the number of surviving dopaminergic neurons and JNK activation in dopaminergic neurons. TUNEL staining was used to quantify apoptotic cell death. siRNA was used to specifically inhibit JNK3, the neural specific isoform of JNK. Our data implicate the activation of JNK3 in rotenone-induced dopaminergic neuron apoptosis.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Honig, L. S., and Rosenberg, R. N. (2000) Apoptosis and neurologic disease. Am J Med 108, 317–30.
Shimoda, K., Sauve, Y., Marini, A., Schwartz, J. P., and Commissiong, J. W. (1992) A high percentage yield of tyrosine hydroxylase-positive cells from rat E14 mesencephalic cell culture. Brain Res 586, 319–31.
Choi, W. S., Abel, G., Klintworth, H., Flavell, R. A., and Xia, Z. (2010) JNK3 Mediates Paraquat- and Rotenone-Induced Dopaminergic Neuron Death. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 69, 511–20.
Choi, W. S., Kruse, S. E., Palmiter, R. D., and Xia, Z. (2008) Mitochondrial complex I inhibition is not required for dopaminergic neuron death induced by rotenone, MPP+, or paraquat. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105, 15136–41.
Green, D. R. (2005) Apoptotic pathways: ten minutes to dead. Cell 121, 671–4.
Hsuan, S. L., Klintworth, H. M., and Xia, Z. (2006) Basic fibroblast growth factor protects against rotenone-induced dopaminergic cell death through activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1/2 and phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase pathways. J Neurosci 26, 4481–91.
Klintworth, H., Newhouse, K., Li, T., Choi, W. S., Faigle, R., and Xia, Z. (2007) Activation of c-Jun N-terminal protein kinase is a common mechanism underlying paraquat- and rotenone-induced dopaminergic cell apoptosis. Toxicol Sci 97, 149–62.
Choi, W. S., Yoon, S. Y., Chang, II, Choi, E. J., Rhim, H., Jin, B. K., Oh, T. H., Krajewski, S., Reed, J. C., and Oh, Y. J. (2000) Correlation between structure of Bcl-2 and its inhibitory function of JNK and caspase activity in dopaminergic neuronal apoptosis. J Neurochem 74, 1621–6.
Putcha, G. V., Le, S., Frank, S., Besirli, C. G., Clark, K., Chu, B., Alix, S., Youle, R. J., LaMarche, A., Maroney, A. C., and Johnson, E. M., Jr. (2003) JNK-mediated BIM phosphorylation potentiates BAX-dependent apoptosis. Neuron 38, 899–914.
Caughlan, A., Newhouse, K., Namgung, U., and Xia, Z. (2004) Chlorpyrifos induces apoptosis in rat cortical neurons that is regulated by a balance between p38 and ERK/JNK MAP kinases. Toxicol Sci 78, 125–34.
Newhouse, K., Hsuan, S. L., Chang, S. H., Cai, B., Wang, Y., and Xia, Z. (2004) Rotenone-induced apoptosis is mediated by p38 and JNK MAP kinases in human dopaminergic SH-SY5Y cells. Toxicol Sci 79, 137–46.
Namgung, U., and Xia, Z. (2000) Arsenite-induced apoptosis in cortical neurons is mediated by c-Jun N-terminal protein kinase 3 and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase. J Neurosci 20, 6442–51.
Peng, J., Mao, X. O., Stevenson, F. F., Hsu, M., and Andersen, J. K. (2004) The herbicide paraquat induces dopaminergic nigral apoptosis through sustained activation of the JNK pathway. J Biol Chem 279, 32626–32.
Eminel, S., Klettner, A., Roemer, L., Herdegen, T., and Waetzig, V. (2004) JNK2 translocates to the mitochondria and mediates cytochrome c release in PC12 cells in response to 6-hydroxydopamine. J Biol Chem 279, 55385–92.
Gupta, S., Barrett, T., Whitmarsh, A. J., Cavanagh, J., Sluss, H. K., Derijard, B., and Davis, R. J. (1996) Selective interaction of JNK protein kinase isoforms with transcription factors. EMBO J. 15, 2760–70.
Fire, A., Xu, S., Montgomery, M. K., Kostas, S. A., Driver, S. E., and Mello, C. C. (1998) Potent and specific genetic interference by double-stranded RNA in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature 391, 806–11.
Zamore, P. D., Tuschl, T., Sharp, P. A., and Bartel, D. P. (2000) RNAi: double-stranded RNA directs the ATP-dependent cleavage of mRNA at 21 to 23 nucleotide intervals. Cell 101, 25–33.
Wang, Y., Luo, W., and Reiser, G. (2007) Proteinase-activated receptor-1 and −2 induce the release of chemokine GRO/CINC-1 from rat astrocytes via differential activation of JNK isoforms, evoking multiple protective pathways in brain. Biochem J 401, 65–78.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Post-doctoral Fellowship Program of KOSEF (WSC), Environmental Pathology/Toxicology Training Grant T32 ES007032 (HMK) and NIH Grants ES012215 and ES013696 (ZX).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2011 Springer Science+Business Media, LLC
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Choi, WS., Klintworth, H.M., Xia, Z. (2011). JNK3-Mediated Apoptotic Cell Death in Primary Dopaminergic Neurons. In: Costa, L., Giordano, G., Guizzetti, M. (eds) In Vitro Neurotoxicology. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 758. Humana Press, Totowa, NJ. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-61779-170-3_19
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-61779-170-3_19
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana Press, Totowa, NJ
Print ISBN: 978-1-61779-169-7
Online ISBN: 978-1-61779-170-3
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols