Abstract
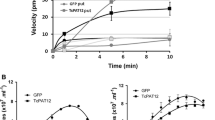
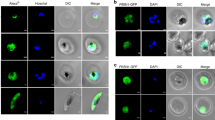
Polyamines are aliphatic polycations that function in key cellular processes such as growth, differentiation, and macromolecular biosynthesis. Intracellular polyamines pools are maintained from de novo synthesis and from transport of polyamines from the extracellular milieu. This acquisition of exogenous polyamines is mediated by cell surface transporter proteins. Protozoan parasites are the etiologic agents of a plethora of devastating and often fatal diseases in humans and their domestic animals. These pathogens accommodate de novo and/or salvage mechanisms for polyamine acquisition. Because of its therapeutic relevance, the polyamine biosynthetic pathway has been thoroughly investigated in many genera of protozoan parasites, but the polyamine permeation pathways have generally been ignored. Our group has now identified at the molecular level polyamine transporters from two species of protozoan parasites, Leishmania major and Trypanosoma cruzi, characterized these polytopic proteins with respect to ligand specificities and affinities, and determined the subcellular environments in which these transporters reside.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pegg AE, McGovern KA, Wiest L (1987) Decarboxylation of alpha-difluoromethylornithine by ornithine decarboxylase. Biochem J 241:305–307
Bacchi CJ, McCann PP (1987) Parasitic protozoa and polyamines. In: McCann PP, Pegg AE, Sjoerdsma A (eds) Inhibition of polyamine metabolism: biological significance and basis for new therapies. Academic, Orlando, FL, pp 317–344
Burri C, Brun R (2003) Eflornithine for the treatment of human African trypanosomiasis. Parasitol Res 90(Supp 1):S49–S52
Pepin J, Milord F (1994) The treatment of human African trypanosomiasis. Adv Parasitol 33:1–47
Van Nieuwenhove S, Schechter PJ, Declercq J, Bone G, Burke J, Sjoerdsma A (1985) Treatment of gambiense sleeping sickness in the Sudan with oral DFMO (DL-alpha-difluoromethylornithine), an inhibitor of ornithine decarboxylase; first field trial. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 79:692–698
Bacchi CJ, Nathan HC, Yarlett N, Goldberg B, McCann PP, Bitonti AJ, Sjoerdsma A (1992) Cure of murine Trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense infections with an S-adenosylmethionine decarboxylase inhibitor. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 36:2736–2740
Bitonti AJ, Byers TL, Bush TL, Casara PJ, Bacchi CJ, Clarkson AB Jr, McCann PP, Sjoerdsma A (1990) Cure of Trypanosoma brucei brucei and Trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense infections in mice with an irreversible inhibitor of S-adenosylmethionine decarboxylase. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 34:1485–1490
Bitonti AJ, Dumont JA, McCann PP (1986) Characterization of Trypanosoma brucei brucei S-adenosyl-L-methionine decarboxylase and its inhibition by Berenil, pentamidine and methylglyoxal bis(guanylhydrazone). Biochem J 237:685–689
Danzin C, Marchal P, Casara P (1990) Irreversi-ble inhibition of rat S-adenosylmethionine decarboxylase by 5’-([(Z)-4-amino-2-butenyl]methylamino)-5’-deoxyadenosine. Biochem Pharmacol 40:1499–1503
Balana-Fouce R, Escribano MI, Alunda JM (1991) Leishmania infantum: polyamine biosynthesis and levels during the growth of promastigotes. Int J Biochem 23:1213–1217
Ariyanayagam MR, Fairlamb AH (1997) Diamine auxotrophy may be a universal feature of Trypanosoma cruzi epimastigotes. Mol Biochem Parasitol 84:111–121
Carrillo C, Cejas S, Gonzalez NS, Algranati ID (1999) Trypanosoma cruzi epimastigotes lack ornithine decarboxylase but can express a foreign gene encoding this enzyme. FEBS Lett 454:192–196
Magagnin S, Bertran J, Werner A, Markovich D, Biber J, Palacin M, Murer H (1992) Poly(A)+ RNA from rabbit intestinal mucosa induces b0,+ and y+ amino acid transport activities in Xenopus laevis oocytes. J Biol Chem 267:15384–15390
Sanchez MA, Tryon R, Green J, Boor I, Landfear SM (2002) Six related nucleoside/nucleobase transporters from Trypanosoma brucei exhibit distinct biochemical functions. J Biol Chem 277:21499–21504
Hasne MP, Ullman B (2005) Identification and characterization of a polyamine permease from the protozoan parasite Leishmania major. J Biol Chem 280:15188–15194
Nishimura H, Pallardo FV, Seidner GA, Vannucci S, Simpson IA, Birnbaum MJ (1993) Kinetics of GLUT1 and GLUT4 glucose transporters expressed in Xenopus oocytes.J Biol Chem 268:8514–8520
Ha DS, Schwarz JK, Turco SJ, Beverley SM (1996) Use of the green fluorescent protein as a marker in transfected Leishmania. Mol Biochem Parasitol 77:57–64
Wirtz E, Hartmann C, Clayton C (1994) Gene expression mediated by bacteriophage T3 and T7 RNA polymerases in transgenic trypanosomes. Nucleic Acids Res 22:3887–3894
Kelly JM, Ward HM, Miles MA, Kendall G (1992) A shuttle vector which facilitates the expression of transfected genes in Trypanosoma cruzi and Leishmania. Nucleic Acids Res 20:3963–3969
Montalvetti A, Rohloff P, Docampo R (2004) A functional aquaporin co-localizes with the vacuolar proton pyrophosphatase to acidocalcisomes and the contractile vacuole complex of Trypanosoma cruzi. J Biol Chem 279:38673–38682
Arriza JL, Kavanaugh MP, Fairman WA, Wu YN, Murdoch GH, North RA, Amara SG (1993) Cloning and expression of a human neutral amino acid transporter with structural similarity to the glutamate transporter gene family. J Biol Chem 268:15329–15332
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by Grant-in-Aid #0950095G provided by the American Heart Association and by Grant AI41622 from the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Disease.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2011 Springer Science+Business Media, LLC
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Hasne, MP., Ullman, B. (2011). Genetic and Biochemical Analysis of Protozoal Polyamine Transporters. In: Pegg, A., Casero, Jr., R. (eds) Polyamines. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 720. Humana Press. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-61779-034-8_19
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-61779-034-8_19
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana Press
Print ISBN: 978-1-61779-033-1
Online ISBN: 978-1-61779-034-8
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols