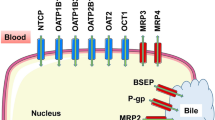
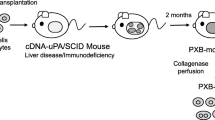
Abstract
Recent developments in animal models have allowed the creation of mice with genetic alterations that cause hepatocyte damage that results, over time, in the loss of native hepatocytes. If donor, human hepatocytes are transplanted into these animals, they repopulate the host liver, frequently replacing over 70% of the native liver with human cells. Immunodeficient mice that overexpress urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA) and, alternatively, with a knockout of the fumarylacetoacetate hydrolase (Fah) genes are the two most common mouse models for these studies. These mice are called chimeric or “humanized” because the liver is now partially repopulated with human cells. In this report we will review the published work with respect to Phase I and Phase II metabolic pathways and the expression of hepatic transport proteins. While the studies are still at the descriptive stage, it is already clear that some humanized mice display high levels of repopulation with human hepatocytes, express basal and inducible human CYP450 genes, and human conjugation and hepatic transport pathways. When the strengths and weaknesses of these humanized mouse models are fully understood, they will likely be quite valuable for investigations of human liver-mediated metabolism and excretion of drugs and xenobiotics, drug–drug interactions, and for short- and long-term investigation of the toxicity of drugs or chemicals with significant human exposure.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Xie, W., Barwick, J.L., Downes, M. et al. (2000) Humanized xenobiotic response in mice expressing nuclear receptor SXR. Nature 406, 435–439.
Uno, S., Endo, K., Ishida, Y. et al. (2009) CYP1A1 and CYP1A2 expression: comparing ‘humanized’ mouse lines and wild-type mice; comparing human and mouse hepatoma-derived cell lines. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 237, 119–126.
Bedell, M.A., Jenkins, N.A., and Copeland, N.G. (1996) Good genes in bad neighbourhoods. Nat. Genet. 12, 229–232.
Milot, E., Fraser, P., and Grosveld, F. (1996) Position effects and genetic disease. Trends Genet. 12, 123–126.
Muller, K., Heller, H., and Doerfler, W. (2001) Foreign DNA integration. Genome-wide perturbations of methylation and transcription in the recipient genomes. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 14271–14278.
Bonyadi, M., Rusholme, S.A., Cousins, F.M. et al. (1997) Mapping of a major genetic modifier of embryonic lethality in TGF beta 1 knockout mice. Nat. Genet. 15, 207–211.
Cranston, A. and Fishel, R. (1999) Female embryonic lethality in Msh2-Trp53 nullizygous mice is strain dependent. Mamm. Genome 10, 1020–1022.
Bennett, L.M., McAllister, K.A., Blackshear, P.E. et al. (2000) BRCA2-null embryonic survival is prolonged on the BALB/c genetic background. Mol. Carcinog. 28, 174–183.
Jiang, Z., Dalton, T.P., Jin, L. et al. (2005) Toward the evaluation of function in genetic variability: characterizing human SNP frequencies and establishing BAC-transgenic mice carrying the human CYP1A1_CYP1A2 locus. Hum. Mutat. 25, 196–206.
Cheung, C., Ma, X., Krausz, K.W. et al. (2005) Differential metabolism of 2-amino-1-methyl-6-phenylimidazo[4,5-b]pyridine (PhIP) in mice humanized for CYP1A1 and CYP1A2. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 18, 1471–1478.
Strom, S.C., Pisarov, L.A., Dorko, K., Thompson, M.T., Schuetz, J.D., and Schuetz, E.G. (1996) Use of human hepatocytes to study P450 gene induction. Methods Enzymol. 272, 388–401.
Pichard-Garcia, L., Gerbal-Chaloin, S., Ferrini, J.B., Fabre, J.M., and Maurel, P. (2002) Use of long-term cultures of human hepatocytes to study cytochrome P450 gene expression. Methods Enzymol. 357, 311–321.
Pascussi, J.M., Gerbal-Chaloin, S., Drocourt, L. et al. (2004) Cross-talk between xenobiotic detoxication and other signalling pathways: clinical and toxicological consequences. Xenobiotica 34, 633–664.
Hewitt, N.J., Lechon, M.J., Houston, J.B. et al. (2007) Primary hepatocytes: current understanding of the regulation of metabolic enzymes and transporter proteins, and pharmaceutical practice for the use of hepatocytes in metabolism, enzyme induction, transporter, clearance, and hepatotoxicity studies. Drug Metab. Rev. 39, 159–234.
LeCluyse, E.L. (2001) Human hepatocyte culture systems for the in vitro evaluation of cytochrome P450 expression and regulation. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 13, 343–368.
Lecureur, V., Courtois, A., Payen, L., Verhnet, L., Guillouzo, A., and Fardel, O. (2000) Expression and regulation of hepatic drug and bile acid transporters. Toxicology 153, 203–219.
Schuetz, E.G., Schuetz, J.D., Thompson, M.T., Fisher, R.A., Madariage, J.R., and Strom, S.C. (1995) Phenotypic variability in induction of P-glycoprotein mRNA by aromatic hydrocarbons in primary human hepatocytes. Mol. Carcinog. 12, 61–65.
Lamba, J.K., Lamba, V., Yasuda, K. et al. (2004) Expression of constitutive androstane receptor splice variants in human tissues and their functional consequences. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 311, 811–821.
Lamba, J., Strom, S., Venkataramanan, R. et al. (2006) MDR1 genotype is associated with hepatic cytochrome P450 3A4 basal and induction phenotype. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 79, 325–338.
Ferrini, J.B., Pichard, L., Domergue, J., and Maurel, P. (1997) Long-term primary cultures of adult human hepatocytes. Chem. Biol. Inter. 107, 31–45.
Runge, D., Kohler, C., Kostrubsky, V.E. et al. (2000) Induction of cytochrome P450 (CYP)1A1, CYP1A2, and CYP3A4 but not of CYP2C9, CYP2C19, multidrug resistance (MDR-1) and multidrug resistance associated protein (MRP-1) by prototypical inducers in human hepatocytes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 273, 333–341.
Dandri, M., Burda, M.R., Torok, E. et al. (2001) Repopulation of mouse liver with human hepatocytes and in vivo infection with hepatitis B virus. Hepatology 33, 981–988.
Mercer, D.F., Schiller, D.E., Elliott, J.F. et al. (2001) Hepatitis C virus replication in mice with chimeric human livers. Nat. Med. 7, 927–933.
Tateno, C., Yoshizane, Y., Saito, N. et al. (2004) Near completely humanized liver in mice shows human-type metabolic responses to drugs. Am. J. Pathol. 165, 901–912.
Katoh, M., Matsui, T., Nakajima, M. et al. (2004) Expression of human cytochromes P450 in chimeric mice with humanized liver. Drug Metab. Dispos. 32, 1402–1410.
Katoh, M., Matsui, T., Okumura, H. et al. (2005) Expression of human phase II enzymes in chimeric mice with humanized liver. Drug Metab. Dispos. 33, 1333–1340.
Nishimura, M., Yokoi, T., Tateno, C. et al. (2005) Induction of human CYP1A2 and CYP3A4 in primary culture of hepatocytes from chimeric mice with humanized liver. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 20, 121–126.
Nishimura, M., Yoshitsugu, H., Yokoi, T. et al. (2005) Evaluation of mRNA expression of human drug-metabolizing enzymes and transporters in chimeric mouse with humanized liver. Xenobiotica 35, 877–890.
Azuma, H., Paulk, N., Ranade, A. et al. (2007) Robust expansion of human hepatocytes in Fah–/–/Rag2–/–/Il2rg–/– mice. Nat. Biotechnol. 25, 903–910.
Overturf, K., al-Dhalimy, M., Ou, C.N., Finegold, M., and Grompe, M. (1997) Serial transplantation reveals the stem-cell-like regenerative potential of adult mouse hepatocytes. Am. J. Pathol. 151, 1273–1280.
Overturf, K., Al-Dhalimy, M., Finegold, M., and Grompe, M. (1999) The repopulation potential of hepatocyte populations differing in size and prior mitotic expansion. Am. J. Pathol. 155, 2135–2143.
Katoh, M., Watanabe, M., Tabata, T. et al. (2005) In vivo induction of human cytochrome P450 3A4 by rifabutin in chimeric mice with humanized liver. Xenobiotica 35, 863–875.
Bissig, K.D., Le, T.T., Woods, N.B., and Verma, I.M. (2007) Repopulation of adult and neonatal mice with human hepatocytes: a chimeric animal model. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 104, 20507–20511.
Skvorak, K.J., Paul, H.S., Dorko, K. et al. (2009) Hepatocyte transplantation improves phenotype and extends survival in a murine model of intermediate maple syrup urine disease. Mol. Ther. (Epub ahead of print).
Emoto, K., Tateno, C., Hino, H. et al. (2005) Efficient in vivo xenogeneic retroviral vector-mediated gene transduction into human hepatocytes. Hum. Gene. Ther. 16, 1168–1174.
Katoh, M., Sawada, T., Soeno, Y. et al. (2007) In vivo drug metabolism model for human cytochrome P450 enzyme using chimeric mice with humanized liver. J. Pharm. Sci. 96, 428–437.
Aoki, K., Kashiwagura, Y., Horie, T. et al. (2006) Characterization of humanized liver from chimeric mice using coumarin as a human CYP2A6 and mouse CYP2A5 probe. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 21, 277–285.
Katoh, M., Matsui, T., Nakajima, M. et al. (2005) In vivo induction of human cytochrome P450 enzymes expressed in chimeric mice with humanized liver. Drug Metab. Dispos. 33, 754–763.
Emoto, C., Yamato, Y., Sato, Y. et al. (2008) Non-invasive method to detect induction of CYP3A4 in chimeric mice with a humanized liver. Xenobiotica 38, 239–248.
Okumura, H., Katoh, M., Sawada, T. et al. (2007) Humanization of excretory pathway in chimeric mice with humanized liver. Toxicol. Sci. 97, 533–538.
Meuleman, P., Libbrecht, L., De Vos, R. et al. (2005) Morphological and biochemical characterization of a human liver in a uPA-SCID mouse chimera. Hepatology 41, 847–856.
Davila, J.C., Cezar, G.G., Thiede, M., Strom, S., Miki, T., and Trosko, J. (2004) Use and application of stem cells in toxicology. Toxicol. Sci. 79, 214–223.
Sato, Y., Yamada, H., Iwasaki, K. et al. (2008) Human hepatocytes can repopulate mouse liver: histopathology of the liver in human hepatocyte-transplanted chimeric mice and toxicologic responses to acetaminophen. Toxicol. Pathol. 36, 581–591.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2010 Humana Press
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Strom, S.C., Davila, J., Grompe, M. (2010). Chimeric Mice with Humanized Liver: Tools for the Study of Drug Metabolism, Excretion, and Toxicity. In: Maurel, P. (eds) Hepatocytes. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 640. Humana Press. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-60761-688-7_27
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-60761-688-7_27
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana Press
Print ISBN: 978-1-60761-687-0
Online ISBN: 978-1-60761-688-7
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols