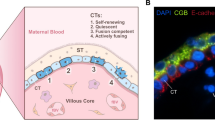
Summary
It has been known for more than 150 years that syncytial fusion is a normal feature in biological systems. In humans there are two larger syncytial tissues: skeletal muscles fibers and placental syncytiotrophoblast. Other fusion events take place as well from fertilization of the oocyte to infection of human cells by enveloped viruses (however, the latter does not necessarily lead to syncytium formation).
Although knowledge of the fusion process is incomplete, it is clear that membranes do not fuse easily; specific proteins and other factors are required and are selectively activated. In this chapter, we describe the classic proteins, such as the syncytins, assumed to be involved in the fusion process. We also describe other factors that may play roles in the fusion process or in the preparation of the cells to fuse, such as charged phospholipids, divalent cations, and intracellular proteases. Finally, we speculate on why trophoblast cells fuse in vitro and deal with in vitro models of trophoblast fusion and how their fusion rates can be quantified.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen, E. H. and Olson, E. N. (2004) Towards a molecular pathway for myoblast fusion in Drosophila. Trends Cell Biol. 14, 452–460.
Chen, E. H. and Olson, E. N. (2005) Unveiling the mechanisms of cell–cell fusion. Science 308, 369–373.
Potgens, A. J., Schmitz, U., Bose, P., Versmold, A., Kaufmann, P., and Frank, H. G. (2002) Mechanisms of syncytial fusion: a review. Placenta 23 (Suppl. A), S107–S113.
Potgens, A. J., Drewlo, S., Kokozidou, M., and Kaufmann, P. (2004) Syncytin: the major regulator of trophoblast fusion? Recent developments and hypotheses on its action. Hum. Reprod. Update 10, 487–496.
Huppertz, B., Bartz, C., and Kokozidou, M. (2006) Trophoblast fusion: fusogenic proteins, syncytins and ADAMs, and other prerequisites for syncytial fusion. Micron 37, 509–517.
Benirschke, K., Kaufmann, P., and Baergen, R. (2006). Pathology of the Human Placenta, 5th ed. Springer, New York.
Kuzmin, P. I., Zimmerberg, J., Chizmadzhev, Y. A., and Cohen, F. S. (2001) A quantitative model for membrane fusion based on low-energy intermediates. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 98, 7235–7240.
Midgley, A., Pierce, G., Denau, G., and Gosling, J. (1963) Morphogenesis of syncytio-trophoblast in vivo: an autoradiographic demonstration. Science 141, 350–351.
Panigel, M. (1993) The origin and structure of extraembryonic tissues, in The Human Placenta (C. Redman, I. Sargent, and P. Starkey, eds.). Blackwell Scientific Publications, London, pp. 3–32.
Castellucci, M., Kaufmann, P., and Bischof, P. (1990) Extracellular matrix influences hormone and protein production by human chorionic villi. Cell Tissue Res. 262, 135–142.
Huppertz, B., Kaufmann, P., and Kingdom, J. C. P. (2002) Trophoblast turnover in health and disease. Fetal Maternal Med. Rev. 13, 17–32.
Huppertz, B. and Kingdom, J. C. (2004) Apoptosis in the trophoblast–role of apoptosis in placental morphogenesis. J. Soc. Gynecol. Invest. 11, 353–362.
Bevers, E. M., Comfurius, P., and Zwaal, R. F. (1996) Regulatory mechanisms in maintenance and modulation of transmembrane lipid asymmetry: pathophysiological implications. Lupus 5, 480–487.
Lyden, T. W., Ng, A. K., and Rote, N. (1993) Modulation of phosphatidylserine epitope expression by BeWo cells during forskolin treatment. Placenta 14, 177–186.
Savill, J. (1998) Apoptosis. Phagocytic docking without shocking. Nature 392, 442–443.
Huppertz, B., Frank, H. G., Kingdom, J. C. P., Reister, F., and Kaufmann, P. (1998) Villous cytotrophoblast regulation of the syncytial apoptotic cascade in the human placenta. Histochem. Cell Biol. 110, 495–508.
van den Eijnde, S. M., van den Hoff, M. J., Reutelingsperger, C. P. , van Heerde, W. L., Henfling, M. E., Vermeij-Keers, C., Schutte, B., Borgers, M., and Ramaekers, F. C. (2001) Transient expression of phosphatidylserine at cell-cell contact areas is required for myotube formation. J. Cell Sci. 114, 3631–3642.
Adler, R. R., Ng, A. K., and Rote, N. (1995) Monoclonal antiphosphatidylserine antibody inhibits intercellular fusion of the choriocarcinoma line JAR. Biol. Reprod. 53, 905–910.
Martin, I., Pecheur, E. I., Ruysschaert, J. M., and Hoekstra, D. (1999) Membrane fusion induced by a short fusogenic peptide is assessed by its insertion and orientation into target bilayers. Biochemistry 38, 9337–9347.
Decout, A., Labeur, C., Goethals, M., Brasseur, R., Vandekerckhove, J., and Rosseneu, M. (1998) Enhanced efficiency of a targeted fusogenic peptide. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1372, 102–116.
Leventis, R., Gagne, J., Fuller, N., Rand, R. P., and Silvius, J. R. (1986) Divalent cation induced fusion and lipid lateral segregation in phosphatidylcholine-phosphatidic acid vesicles. Biochemistry 25, 6978–6987.
Faraudo, J. and Travesset, A. (2007) Phosphatidic acid domains in membranes: effect of divalent counterions. Biophys. J. 92, 2806–2818.
Bartoli, M. and Richard, I. (2005) Calpains in muscle wasting. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 37, 2115–2133.
Barnoy, S., Glaser, T. and Kosower, N.S. (1998) The calpain–calpastatin system and protein degradation in fusing myoblasts. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1402, 52–60.
Barnoy, S., Maki, M., and Kosower, N.S. (2005) Overexpression of calpastatin inhibits L8 myoblast fusion. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 332, 697–701.
Black, S., Kadyrov, M., Kaufmann, P., Ugele, B., Emans, N., and Huppertz, B. (2004) Syncytial fusion of human trophoblast depends on caspase 8. Cell Death Differ. 11, 90–98.
Das, M., Xu, B., Lin, L., Chakrabarti, S., Shivaswamy, V. , and Rote, N. S. (2004) Phosphatidylserine efflux and intercellular fusion in a BeWo model of human villous cytotrophoblast. Placenta 25, 396–407.
Drewlo, S., Leyting, S., Kokozidou, M., Mallet, F. and Potgens, A.J. (2006) C-Terminal truncations of syncytin-1 (ERVWE1 envelope) that increase its fusogenicity. Biol. Chem. 387, 1113–20.
Frendo, J.L., Cronier, L., Bertin, G., Guibourdenche, J., Vidaud, M., Evain- Brion, D., Malassine, A. (2003) Involvement of connexin 43 in human trophoblast cell fusion and differentiation. J. Cell Sci. 116, 3413–3421.
Cronier, L., Defamie, N., Dupays, L., Theveniau-Ruissy, M., Goffin, F., Pointis, G., and Malassine, A. (2002) Connexin expression and gap junctional communication in human first trimester trophoblast. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 8, 1005–1013.
Getsios, S. and MacCalman, C. D. (2003) Cadherin-11 modulates the terminal differentiation and fusion of human trophoblastic cells in vitro. Dev. Biol. 257, 41–54.
Kudo, Y. and Boyd, C. A. (2004) RNA interference-induced reduction in CD98 expression suppresses cell fusion during syncytialization of human placental BeWo cells. FEBS Lett. 577, 473–477.
de Parseval, N., Lazar, V., Casella, J. F., Benit, L., and Heidmann, T. (2003) Survey of human genes of retroviral origin: identification and transcriptome of the genes with coding capacity for complete envelope proteins. J. Virol. 77, 10414–10422.
Rote, N. S., Chakrabarti, S., and Stetzer, B. P. (2004) The role of human endogenous retroviruses in trophoblast differentiation and placental development. Placenta 25, 673–683.
Mi, S., Lee, X., Li, X.-P., Veldman, G. M., Finnerty, H., Racie, L., LaVallie, E., Tang, X.-Y., Edouard, P., Howes, S., Keth, J. C., and McCoy, J. M. (2000) Syncytin is a captive retroviral envelope protein involved in human placental morphogenesis. Nature 403, 785–789.
Blond, J. L., Lavillete, D., Cheynet, V., Bouton, O., Oriol, G., Chapel-Fernandes, S., Mandrand, B., Mallet, F., and Cosset, F. L. (2000) An envelope glycoprotein of the human endogenous retrovirus HERV-W is expressed in the human placenta and fuses cells expressing the type D mammalian retrovirus receptor. J. Virol. 74, 3321–3329.
Lavillette, D., Marin, M., Ruggieri, A., Mallet, F., Cosset, F. L., and Kabat, D. (2002) The envelope glycoprotein of human endogenous retrovirus type W uses a divergent family of amino acid transporters/cell surface receptors. J. Virol. 76, 6442–6452.
Frendo, J. L., Olivier, D., Cheynet, V., Blond, J. L., Bouton, O., Vidaud, M., Rabreau, M., Evain-Brion, D., and Mallet, F. (2003) Direct involvement of HERV-W Env glycoprotein in human trophoblast cell fusion and differentiation. Mol. Cell Biol. 23, 3566–3574.
Yu, C., Shen, K., Lin, M., Chen, P., Lin, C., Chang, G. D., and Chen, H. (2002) GCMa regulates the syncytin-mediated trophoblast fusion. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 50062–50068.
Smallwood, A., Papageorgiou, A., Nicolaides, K., Alley, M. K, Alice, J., Nargund, G., Ojha, K., Campbell, S., and Banerjee, S. (2003) Temporal regulation of syncytin (HERV-W), maternally imprinted PEG10, and SGCE in human placenta. Biol. Reprod. 69, 286–293.
Cariappa, R., Heath-Monnig, E., and Smith, C. H. (2003) Isoforms of amino acid transporters in placental syncytiotrophoblast: plasma membrane localization and potential role in maternal/fetal transport. Placenta 24, 713–726.
Baczyk, D., Satkunaratnam, A., Nait-Oumesmar, B., Huppertz, B., Cross, J. C., and Kingdom, J. C. P. (2004) Complex patterns of GCM1 mRNA and protein in villous and extravillous trophoblast cells of the human placenta. Placenta 25, 553–559.
Blaise, S., de Parseval, N., Bénit, L., and Heidmann, T. (2003) Genomewide screening for fusogenic human endogenous envelopes identifies syncytin 2, a gene conserved on primate evolution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 100, 13013–13018.
Huppertz, B., Frank, H. G., Reister, F., Kingdom, J., Korr, H., and Kaufmann P. (1999) Apoptosis cascade progresses during turnover of human trophoblast: Analysis of human cytotrophoblast and syncytial fragments in vitro. Lab. Invest. 12, 1–16.
Kliman, H. J., Nestler, J. E., Sermasi, E., Sanger, J. M., and Strauss, J. F. 3rd. (1986) Purification, characterization, and in vitro differentiation of cytotrophoblasts from human term placentae. Endocrinology 118, 1567–1582.
Guilbert, L. J., Winkler-Lowen, B., Sherburne, R., Rote, N. S., Li, H., and Morrish, D. W. (2002) Preparation and functional characterization of villous cytotropho-blasts free of syncytial fragments. Placenta 23, 175–183.
Cronier, L., Guibourdenche, J., Niger, C., and Malassine, A. (1999) Oestradiol stimulates morphological and functional differentiation of human villous cytotro-phoblast. Placenta 20, 669–676.
Alsat, E., Haziza, J., and Evain-Brion, D. (1993) Increase in epidermal growth factor receptor and its messenger ribonucleic acid levels with differentiation of human trophoblast cells in culture. J. Cell Physiol. 154, 122–128.
Morrish, D., Linetsky, E., Bhardwaj, D., Li, H., Dakour, J., Marsh, R., Paterson, M., and Godbout, R. (1996) Identification by subtractive hybridization of a spectrum of novel and unexpected genes associated with in vitro differentiation of human cytotrophoblast cells. Placenta 17, 431–441.
Garcia-Lloret, M., Morrish, D., Wegmann, T., Honore, L., Turner, A., and Guilbert, L. (1994) Demonstration of functional cytokine-placental interactions: CSF-1 and GM-CSF stimulate human cytotrophoblast differentiation and peptide hormone secretion. Exp. Cell Res. 214, 46–54.
Cronier, L., Alsat, E., Hervé, J.C., Delèze, J., and Malassiné, A. (1998) Dexamethasone stimulates Gap junctional communication peptide hormone production and differentiation in human term trophoblast. Trophoblast Res. 11, 35–49.
Cronier, L., Bastide, B., Hervé, J. C., Delèze, J., and Malassiné, A. (1994) Gap junctional communication during human trophoblast differentiation: influence of human chorionic gonadotropin. Endocrinology 135, 402–408.
Shi, Q., Lei, Z., Rao, C., and Lin, J. (1993) Novel role of human chorionic gonadotropin in differentiation of human cytotrophoblasts. Endocrinology 132, 1387–1395.
Keryer, G., Alsat, E., Tasken, K., and Evain-Brion, D. (1998) Cyclic AMP–dependent protein kinases and human trophoblast cell differentiation in vitro. J. Cell Sci. 111, 995–1004.
Frendo, J.L., Thérond, P., Bird, T., Massin, N., Muller, F., Guibourdenche, J., Luton, D., Vidaud, M., Anderson, W., and Evain-Brion, D. (2001) Overexpression of copper zinc superoxide dismutase impairs human trophoblast cell fusion and differentiation. Endocrinology 142, 3638–3648.
Frendo, J. L., Thérond, P., Guibourdenche, J., Bidart, J. M., Vidaud, M., and Evain-Brion, D. (2000) Modulation of copper/zinc superoxide dismutase expression and activity with in vitro differentiation of human villous cytotrophoblast. Placenta 21, 773–781.
Insel, P. A. and Ostrom, R. S. (2003) Forskolin as a tool for examining adenylyl cyclase expression, regulation, and G protein signaling. Cell Mol. Neurobiol. 23, 305–14.
Kudo, Y., Boyd, C. A., Kimura, H., Cook, P. R., Redman, C. W., and Sargent, I. L. (2003) Quantifying the syncytialisation of human placental trophoblast BeWo cells grown in vitro. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1640, 25–31.
Borges, M., Bose, P., Frank, H. G., Kaufmann, P., and Pötgens, A. J. G. (2003) A two colour fluorescence assay for the measurement of syncytial fusion between trophoblast-derived cell lines. Placenta 24, 959–964.
Alsat, E., Wyplosz, P., Malassine, A., Guibourdenche, J., Porquet, D., Nessmann, C., and Evain-Brion, D. (1996) Hypoxia impairs cell fusion and differentiation process in human cytotrophoblast, in vitro. J. Cell Physiol. 168, 346–353.
Saleh, L., Prast, J., Haslinger, P., Husslein, P., Helmer, H., and Knofler, M. (2007) Effects of different human chorionic gonadotrophin preparations on trophoblast differentiation. Placenta 28, 199–203.
Handwerger, S. (1991) The physiology of placental lactogen in human pregnancy. Endocrinology 12, 329–336.
Gauster, M., Siwetz, M., and Huppertz, B. (2007) Is upregulation of hCG expression a marker of syncytialization of BeWo cells?Placenta 28, A71.
Chang, C., Chen, P. T., Chang, G. D., Huang, C. J., and Chen, H. (2004) Functional characterization of the placental fusogenic membrane protein syncytin. Biol. Reprod. 71, 1956–1962.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2008 Humana Press, a part of Springer Science + Business Media, LLC
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Huppertz, B., Borges, M. (2008). Placenta Trophoblast Fusion. In: Chen, E.H. (eds) Cell Fusion. Methods in Molecular Biology™, vol 475. Humana Press. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-59745-250-2_8
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-59745-250-2_8
Publisher Name: Humana Press
Print ISBN: 978-1-58829-911-6
Online ISBN: 978-1-59745-250-2
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols