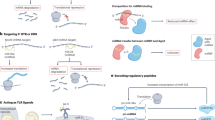
Abstract
Majority of the human genome is transcribed into RNAs with absent or limited protein-coding potential. microRNAs (miRNAs) and long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) are two major families of the non-protein-coding transcripts. miRNAs and lncRNAs can regulate fundamental cellular processes via diverse mechanisms. The expression and function of miRNAs and lncRNAs are tightly regulated in development and physiological homeostasis. Dysregulation of miRNAs and lncRNAs is critical to pathogenesis of human disease. Moreover, recent evidence indicates a cross talk between miRNAs and lncRNAs. Herein we review recent advances in the biology of miRNAs and lncRNAs with respect to the above aspects. We focus on their roles in cancer, respiratory disease, and neurodegenerative disease. The complexity, flexibility, and versatility of the structures and functions of miRNAs and lncRNAs demand integration of experimental and bioinformatics tools to acquire sufficient knowledge for applications of these noncoding RNAs in clinical care.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Derrien T, Johnson R, Bussotti G, Tanzer A, Djebali S et al (2012) The GENCODE v7 catalog of human long noncoding RNAs: analysis of their gene structure, evolution, and expression. Genome Res 22:1775–1789
Bartel DP (2004) MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116:281–297
Lee RC, Feinbaum RL, Ambros V (1993) The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell 75:843–854
Kozomara A, Griffiths-Jones S (2014) miRBase: annotating high confidence microRNAs using deep sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res 42:D68–D73
Lee Y, Kim M, Han J, Yeom KH, Lee S et al (2004) MicroRNA genes are transcribed by RNA polymerase II. EMBO J 23:4051–4060
Bortolin-Cavaille ML, Dance M, Weber M, Cavaille J (2009) C19MC microRNAs are processed from introns of large Pol-II, non-protein-coding transcripts. Nucleic Acids Res 37:3464–3473
Katahira J, Yoneda Y (2011) Nucleocytoplasmic transport of microRNAs and related small RNAs. Traffic 12:1468–1474
Bhayani MK, Calin GA, Lai SY (2012) Functional relevance of miRNA sequences in human disease. Mutat Res 731:14–19
Roberts TC (2014) The MicroRNA biology of the mammalian nucleus. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 3:e188
Hu G, Drescher KM, Chen XM (2012) Exosomal miRNAs: biological properties and therapeutic potential. Front Genet 3:56
Valadi H, Ekstrom K, Bossios A, Sjostrand M, Lee JJ et al (2007) Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat Cell Biol 9:654–659
Laulagnier K, Motta C, Hamdi S, Roy S, Fauvelle F et al (2004) Mast cell- and dendritic cell-derived exosomes display a specific lipid composition and an unusual membrane organization. Biochem J 380:161–171
Hogan MC, Manganelli L, Woollard JR, Masyuk AI, Masyuk TV et al (2009) Characterization of PKD protein-positive exosome-like vesicles. J Am Soc Nephrol 20:278–288
Zhou R, O'Hara SP, Chen XM (2011) MicroRNA regulation of innate immune responses in epithelial cells. Cell Mol Immunol 8:371–379
Vlassov AV, Magdaleno S, Setterquist R, Conrad R (2012) Exosomes: current knowledge of their composition, biological functions, and diagnostic and therapeutic potentials. Biochim Biophys Acta 1820:940–948
Mittelbrunn M, Gutierrez-Vazquez C, Villarroya-Beltri C, Gonzalez S, Sanchez-Cabo F et al (2011) Unidirectional transfer of microRNA-loaded exosomes from T cells to antigen-presenting cells. Nat Commun 2:282
McDonald MK, Tian Y, Qureshi RA, Gormley M, Ertel A et al (2014) Functional significance of macrophage-derived exosomes in inflammation and pain. Pain 155:1527–1539
Putz U, Howitt J, Doan A, Goh CP, Low LH et al (2012) The tumor suppressor PTEN is exported in exosomes and has phosphatase activity in recipient cells. Sci Signal 5:ra70
Bracken CP, Gregory PA, Kolesnikoff N, Bert AG, Wang J et al (2008) A double-negative feedback loop between ZEB1-SIP1 and the microRNA-200 family regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Cancer Res 68:7846–7854
Li C, Nguyen HT, Zhuang Y, Lin Y, Flemington EK et al (2011) Post-transcriptional up-regulation of miR-21 by type I collagen. Mol Carcinog 50:563–570
Olsen PH, Ambros V (1999) The lin-4 regulatory RNA controls developmental timing in Caenorhabditis elegans by blocking LIN-14 protein synthesis after the initiation of translation. Dev Biol 216:671–680
Friedman RC, Farh KK, Burge CB, Bartel DP (2009) Most mammalian mRNAs are conserved targets of microRNAs. Genome Res 19:92–105
Agarwal V, Bell GW, Nam JW, Bartel DP (2015) Predicting effective microRNA target sites in mammalian mRNAs. eLife 4:e05005
Maroney PA, Yu Y, Fisher J, Nilsen TW (2006) Evidence that microRNAs are associated with translating messenger RNAs in human cells. Nat Struct Mol Biol 13:1102–1107
Nottrott S, Simard MJ, Richter JD (2006) Human let-7a miRNA blocks protein production on actively translating polyribosomes. Nat Struct Mol Biol 13:1108–1114
Petersen CP, Bordeleau ME, Pelletier J, Sharp PA (2006) Short RNAs repress translation after initiation in mammalian cells. Mol Cell 21:533–542
Pillai RS, Bhattacharyya SN, Artus CG, Zoller T, Cougot N et al (2005) Inhibition of translational initiation by Let-7 MicroRNA in human cells. Science 309:1573–1576
Humphreys DT, Westman BJ, Martin DI, Preiss T (2005) MicroRNAs control translation initiation by inhibiting eukaryotic initiation factor 4E/cap and poly(A) tail function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:16961–16966
Rehwinkel J, Behm-Ansmant I, Gatfield D, Izaurralde E (2005) A crucial role for GW182 and the DCP1:DCP2 decapping complex in miRNA-mediated gene silencing. RNA 11:1640–1647
Behm-Ansmant I, Rehwinkel J, Doerks T, Stark A, Bork P et al (2006) mRNA degradation by miRNAs and GW182 requires both CCR4:NOT deadenylase and DCP1:DCP2 decapping complexes. Genes Dev 20:1885–1898
Wu L, Fan J, Belasco JG (2006) MicroRNAs direct rapid deadenylation of mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:4034–4039
Guo H, Ingolia NT, Weissman JS, Bartel DP (2010) Mammalian microRNAs predominantly act to decrease target mRNA levels. Nature 466:835–840
Liu Z, Liu H, Desai S, Schmitt DC, Zhou M et al (2013) miR-125b functions as a key mediator for snail-induced stem cell propagation and chemoresistance. J Biol Chem 288:4334–4345
Zhou M, Liu Z, Zhao Y, Ding Y, Liu H et al (2010) MicroRNA-125b confers the resistance of breast cancer cells to paclitaxel through suppression of pro-apoptotic Bcl-2 antagonist killer 1 (Bak1) expression. J Biol Chem 285:21496–21507
Kiriakidou M, Tan GS, Lamprinaki S, De Planell-Saguer M, Nelson PT et al (2007) An mRNA m7G cap binding-like motif within human Ago2 represses translation. Cell 129:1141–1151
Stefani G, Slack FJ (2008) Small non-coding RNAs in animal development. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 9:219–230
Kim DH, Saetrom P, Snove O Jr, Rossi JJ (2008) MicroRNA-directed transcriptional gene silencing in mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:16230–16235
Benhamed M, Herbig U, Ye T, Dejean A, Bischof O (2012) Senescence is an endogenous trigger for microRNA-directed transcriptional gene silencing in human cells. Nat Cell Biol 14:266–275
Zardo G, Ciolfi A, Vian L, Starnes LM, Billi M et al (2012) Polycombs and microRNA-223 regulate human granulopoiesis by transcriptional control of target gene expression. Blood 119:4034–4046
Adilakshmi T, Sudol I, Tapinos N (2012) Combinatorial action of miRNAs regulates transcriptional and post-transcriptional gene silencing following in vivo PNS injury. PLoS One 7:e39674
Place RF, Li LC, Pookot D, Noonan EJ, Dahiya R (2008) MicroRNA-373 induces expression of genes with complementary promoter sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:1608–1613
Shimakami T, Yamane D, Jangra RK, Kempf BJ, Spaniel C et al (2012) Stabilization of hepatitis C virus RNA by an Ago2-miR-122 complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109:941–946
Ha TY (2011) The role of MicroRNAs in regulatory T cells and in the immune response. Immune Netw 11:11–41
Calin GA, Dumitru CD, Shimizu M, Bichi R, Zupo S et al (2002) Frequent deletions and down-regulation of micro-RNA genes miR15 and miR16 at 13q14 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99:15524–15529
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA (2011) Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell 144:646–674
He L, Thomson JM, Hemann MT, Hernando-Monge E, Mu D et al (2005) A microRNA polycistron as a potential human oncogene. Nature 435:828–833
Hayashita Y, Osada H, Tatematsu Y, Yamada H, Yanagisawa K et al (2005) A polycistronic microRNA cluster, miR-17-92, is overexpressed in human lung cancers and enhances cell proliferation. Cancer Res 65:9628–9632
Takamizawa J, Konishi H, Yanagisawa K, Tomida S, Osada H et al (2004) Reduced expression of the let-7 microRNAs in human lung cancers in association with shortened postoperative survival. Cancer Res 64:3753–3756
Johnson SM, Grosshans H, Shingara J, Byrom M, Jarvis R et al (2005) RAS is regulated by the let-7 microRNA family. Cell 120:635–647
Tsang WP, Ng EK, Ng SS, Jin H, Yu J et al (2010) Oncofetal H19-derived miR-675 regulates tumor suppressor RB in human colorectal cancer. Carcinogenesis 31:350–358
Ueda R, Kohanbash G, Sasaki K, Fujita M, Zhu X et al (2009) Dicer-regulated microRNAs 222 and 339 promote resistance of cancer cells to cytotoxic T-lymphocytes by down-regulation of ICAM-1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:10746–10751
Tazawa H, Tsuchiya N, Izumiya M, Nakagama H (2007) Tumor-suppressive miR-34a induces senescence-like growth arrest through modulation of the E2F pathway in human colon cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:15472–15477
O'Connell RM, Taganov KD, Boldin MP, Cheng G, Baltimore D (2007) MicroRNA-155 is induced during the macrophage inflammatory response. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:1604–1609
Gironella M, Seux M, Xie MJ, Cano C, Tomasini R et al (2007) Tumor protein 53-induced nuclear protein 1 expression is repressed by miR-155, and its restoration inhibits pancreatic tumor development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:16170–16175
Gregory PA, Bert AG, Paterson EL, Barry SC, Tsykin A et al (2008) The miR-200 family and miR-205 regulate epithelial to mesenchymal transition by targeting ZEB1 and SIP1. Nat Cell Biol 10:593–601
Nguyen HT, Li C, Lin Z, Zhuang Y, Flemington EK et al (2012) The microRNA expression associated with morphogenesis of breast cancer cells in three-dimensional organotypic culture. Oncol Rep 28:117–126
Wurdinger T, Tannous BA, Saydam O, Skog J, Grau S et al (2008) miR-296 regulates growth factor receptor overexpression in angiogenic endothelial cells. Cancer Cell 14:382–393
Lal A, Pan Y, Navarro F, Dykxhoorn DM, Moreau L et al (2009) miR-24-mediated downregulation of H2AX suppresses DNA repair in terminally differentiated blood cells. Nat Struct Mol Biol 16:492–498
Calin GA, Liu CG, Sevignani C, Ferracin M, Felli N et al (2004) MicroRNA profiling reveals distinct signatures in B cell chronic lymphocytic leukemias. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:11755–11760
Chan JA, Krichevsky AM, Kosik KS (2005) MicroRNA-21 is an antiapoptotic factor in human glioblastoma cells. Cancer Res 65:6029–6033
Doghman M, El Wakil A, Cardinaud B, Thomas E, Wang J et al (2010) Regulation of insulin-like growth factor-mammalian target of rapamycin signaling by microRNA in childhood adrenocortical tumors. Cancer Res 70:4666–4675
Ma L, Teruya-Feldstein J, Weinberg RA (2007) Tumour invasion and metastasis initiated by microRNA-10b in breast cancer. Nature 449:682–688
Calin GA, Sevignani C, Dumitru CD, Hyslop T, Noch E et al (2004) Human microRNA genes are frequently located at fragile sites and genomic regions involved in cancers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:2999–3004
Jazdzewski K, Murray EL, Franssila K, Jarzab B, Schoenberg DR et al (2008) Common SNP in pre-miR-146a decreases mature miR expression and predisposes to papillary thyroid carcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:7269–7274
Lee YS, Dutta A (2007) The tumor suppressor microRNA let-7 represses the HMGA2 oncogene. Genes Dev 21:1025–1030
Mayr C, Hemann MT, Bartel DP (2007) Disrupting the pairing between let-7 and Hmga2 enhances oncogenic transformation. Science 315:1576–1579
Chin LJ, Ratner E, Leng S, Zhai R, Nallur S et al (2008) A SNP in a let-7 microRNA complementary site in the KRAS 3′ untranslated region increases non-small cell lung cancer risk. Cancer Res 68:8535–8540
Volinia S, Calin GA, Liu CG, Ambs S, Cimmino A et al (2006) A microRNA expression signature of human solid tumors defines cancer gene targets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:2257–2261
O'Donnell KA, Wentzel EA, Zeller KI, Dang CV, Mendell JT (2005) c-Myc-regulated microRNAs modulate E2F1 expression. Nature 435:839–843
Peter ME (2009) Let-7 and miR-200 microRNAs: guardians against pluripotency and cancer progression. Cell Cycle 8:843–852
Li C, Nguyen HT, Zhuang Y, Lin Z, Flemington EK et al (2012) Comparative profiling of miRNA expression of lung adenocarcinoma cells in two-dimensional and three-dimensional cultures. Gene 511:143–150
Mouw JK, Yui Y, Damiano L, Bainer RO, Lakins JN et al (2014) Tissue mechanics modulate microRNA-dependent PTEN expression to regulate malignant progression. Nat Med 20:360–367
Weber JA, Baxter DH, Zhang S, Huang DY, Huang KH et al (2010) The microRNA spectrum in 12 body fluids. Clin Chem 56:1733–1741
Taylor DD, Gercel-Taylor C (2008) MicroRNA signatures of tumor-derived exosomes as diagnostic biomarkers of ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol 110:13–21
Skog J, Wurdinger T, van Rijn S, Meijer DH, Gainche L et al (2008) Glioblastoma microvesicles transport RNA and proteins that promote tumour growth and provide diagnostic biomarkers. Nat Cell Biol 10:1470–1476
Ng EK, Chong WW, Jin H, Lam EK, Shin VY et al (2009) Differential expression of microRNAs in plasma of patients with colorectal cancer: a potential marker for colorectal cancer screening. Gut 58:1375–1381
Huang Z, Huang D, Ni S, Peng Z, Sheng W et al (2010) Plasma microRNAs are promising novel biomarkers for early detection of colorectal cancer. Int J Cancer 127:118–126
Pu XX, Huang GL, Guo HQ, Guo CC, Li H et al (2010) Circulating miR-221 directly amplified from plasma is a potential diagnostic and prognostic marker of colorectal cancer and is correlated with p53 expression. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 25:1674–1680
Cheng H, Zhang L, Cogdell DE, Zheng H, Schetter AJ et al (2011) Circulating plasma MiR-141 is a novel biomarker for metastatic colon cancer and predicts poor prognosis. PLoS One 6:e17745
Toiyama Y, Takahashi M, Hur K, Nagasaka T, Tanaka K et al (2013) Serum miR-21 as a diagnostic and prognostic biomarker in colorectal cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 105:849–859
Ogata-Kawata H, Izumiya M, Kurioka D, Honma Y, Yamada Y et al (2014) Circulating exosomal microRNAs as biomarkers of colon cancer. PLoS One 9:e92921
Lowery AJ, Miller N, Devaney A, McNeill RE, Davoren PA et al (2009) MicroRNA signatures predict oestrogen receptor, progesterone receptor and HER2/neu receptor status in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res 11:R27
Volinia S, Galasso M, Sana ME, Wise TF, Palatini J et al (2012) Breast cancer signatures for invasiveness and prognosis defined by deep sequencing of microRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109:3024–3029
Foekens JA, Sieuwerts AM, Smid M, Look MP, de Weerd V et al (2008) Four miRNAs associated with aggressiveness of lymph node-negative, estrogen receptor-positive human breast cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:13021–13026
Rodriguez-Gonzalez FG, Sieuwerts AM, Smid M, Look MP, Meijer-van Gelder ME et al (2011) MicroRNA-30c expression level is an independent predictor of clinical benefit of endocrine therapy in advanced estrogen receptor positive breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 127:43–51
Maillot G, Lacroix-Triki M, Pierredon S, Gratadou L, Schmidt S et al (2009) Widespread estrogen-dependent repression of microRNAs involved in breast tumor cell growth. Cancer Res 69:8332–8340
Ichikawa T, Sato F, Terasawa K, Tsuchiya S, Toi M et al (2012) Trastuzumab produces therapeutic actions by upregulating miR-26a and miR-30b in breast cancer cells. PLoS One 7:e31422
Ebert MS, Neilson JR, Sharp PA (2007) MicroRNA sponges: competitive inhibitors of small RNAs in mammalian cells. Nat Methods 4:721–726
Ma L, Young J, Prabhala H, Pan E, Mestdagh P et al (2010) miR-9, a MYC/MYCN-activated microRNA, regulates E-cadherin and cancer metastasis. Nat Cell Biol 12:247–256
Huang S, Chen Y, Wu W, Ouyang N, Chen J et al (2013) miR-150 promotes human breast cancer growth and malignant behavior by targeting the pro-apoptotic purinergic P2X7 receptor. PLoS One 8:e80707
Kuss AW, Chen W (2008) MicroRNAs in brain function and disease. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep 8:190–197
Kim J, Inoue K, Ishii J, Vanti WB, Voronov SV et al (2007) A MicroRNA feedback circuit in midbrain dopamine neurons. Science 317:1220–1224
Gehrke S, Imai Y, Sokol N, Lu B (2010) Pathogenic LRRK2 negatively regulates microRNA-mediated translational repression. Nature 466:637–641
Blennow K, de Leon MJ, Zetterberg H (2006) Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet 368:387–403
Cogswell JP, Ward J, Taylor IA, Waters M, Shi Y et al (2008) Identification of miRNA changes in Alzheimer's disease brain and CSF yields putative biomarkers and insights into disease pathways. J Alzheimers Dis 14:27–41
Maes OC, Chertkow HM, Wang E, Schipper HM (2009) MicroRNA: implications for Alzheimer disease and other human CNS disorders. Curr Genomics 10:154–168
Maes OC, Xu S, Yu B, Chertkow HM, Wang E et al (2007) Transcriptional profiling of Alzheimer blood mononuclear cells by microarray. Neurobiol Aging 28:1795–1809
Blalock EM, Chen KC, Stromberg AJ, Norris CM, Kadish I et al (2005) Harnessing the power of gene microarrays for the study of brain aging and Alzheimer’s disease: statistical reliability and functional correlation. Ageing Res Rev 4:481–512
Nunez-Iglesias J, Liu CC, Morgan TE, Finch CE, Zhou XJ (2010) Joint genome-wide profiling of miRNA and mRNA expression in Alzheimer's disease cortex reveals altered miRNA regulation. PLoS One 5:e8898
Hebert SS, Horre K, Nicolai L, Papadopoulou AS, Mandemakers W et al (2008) Loss of microRNA cluster miR-29a/b-1 in sporadic Alzheimer’s disease correlates with increased BACE1/beta-secretase expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:6415–6420
Hebert SS, Horre K, Nicolai L, Bergmans B, Papadopoulou AS et al (2009) MicroRNA regulation of Alzheimer’s Amyloid precursor protein expression. Neurobiol Dis 33:422–428
Booton R, Lindsay MA (2014) Emerging role of MicroRNAs and long noncoding RNAs in respiratory disease. Chest 146:193–204
Williams AE, Moschos SA, Perry MM, Barnes PJ, Lindsay MA (2007) Maternally imprinted microRNAs are differentially expressed during mouse and human lung development. Dev Dyn 236:572–580
Harris KS, Zhang Z, McManus MT, Harfe BD, Sun X (2006) Dicer function is essential for lung epithelium morphogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:2208–2213
Lu Y, Thomson JM, Wong HY, Hammond SM, Hogan BL (2007) Transgenic over-expression of the microRNA miR-17-92 cluster promotes proliferation and inhibits differentiation of lung epithelial progenitor cells. Dev Biol 310:442–453
Jardim MJ, Dailey L, Silbajoris R, Diaz-Sanchez D (2012) Distinct microRNA expression in human airway cells of asthmatic donors identifies a novel asthma-associated gene. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 47:536–542
Solberg OD, Ostrin EJ, Love MI, Peng JC, Bhakta NR et al (2012) Airway epithelial miRNA expression is altered in asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 186:965–974
Tsitsiou E, Williams AE, Moschos SA, Patel K, Rossios C et al (2012) Transcriptome analysis shows activation of circulating CD8+ T cells in patients with severe asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol 129:95–103
O'Connell RM, Rao DS, Baltimore D (2012) microRNA regulation of inflammatory responses. Annu Rev Immunol 30:295–312
Pandit KV, Corcoran D, Yousef H, Yarlagadda M, Tzouvelekis A et al (2010) Inhibition and role of let-7d in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 182:220–229
Dakhlallah D, Batte K, Wang Y, Cantemir-Stone CZ, Yan P et al (2013) Epigenetic regulation of miR-17~92 contributes to the pathogenesis of pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 187:397–405
Liu G, Friggeri A, Yang Y, Milosevic J, Ding Q et al (2010) miR-21 mediates fibrogenic activation of pulmonary fibroblasts and lung fibrosis. J Exp Med 207:1589–1597
Cushing L, Kuang PP, Qian J, Shao F, Wu J et al (2011) miR-29 is a major regulator of genes associated with pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 45:287–294
Yang S, Banerjee S, de Freitas A, Sanders YY, Ding Q et al (2012) Participation of miR-200 in pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Pathol 180:484–493
Jiang X, Tsitsiou E, Herrick SE, Lindsay MA (2010) MicroRNAs and the regulation of fibrosis. FEBS J 277:2015–2021
Ezzie ME, Crawford M, Cho JH, Orellana R, Zhang S et al (2012) Gene expression networks in COPD: microRNA and mRNA regulation. Thorax 67:122–131
Sato T, Liu X, Nelson A, Nakanishi M, Kanaji N et al (2010) Reduced miR-146a increases prostaglandin E(2)in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease fibroblasts. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 182:1020–1029
Lewis A, Riddoch-Contreras J, Natanek SA, Donaldson A, Man WD et al (2012) Downregulation of the serum response factor/miR-1 axis in the quadriceps of patients with COPD. Thorax 67:26–34
Cunningham F, Amode MR, Barrell D, Beal K, Billis K et al (2015) Ensembl 2015. Nucleic Acids Res 43:D662–D669
Lanz RB, McKenna NJ, Onate SA, Albrecht U, Wong J et al (1999) A steroid receptor coactivator, SRA, functions as an RNA and is present in an SRC-1 complex. Cell 97:17–27
Rinn JL, Chang HY (2012) Genome regulation by long noncoding RNAs. Annu Rev Biochem 81:145–166
Shibayama Y, Fanucchi S, Magagula L, Mhlanga MM (2014) lncRNA and gene looping: what’s the connection? Transcription 5:e28658
Shi X, Sun M, Liu H, Yao Y, Song Y (2013) Long non-coding RNAs: a new frontier in the study of human diseases. Cancer Lett 339:159–166
Zong X, Tripathi V, Prasanth KV (2011) RNA splicing control: yet another gene regulatory role for long nuclear noncoding RNAs. RNA Biol 8:968–977
Kretz M, Siprashvili Z, Chu C, Webster DE, Zehnder A et al (2013) Control of somatic tissue differentiation by the long non-coding RNA TINCR. Nature 493:231–235
Hacisuleyman E, Goff LA, Trapnell C, Williams A, Henao-Mejia J et al (2014) Topological organization of multichromosomal regions by the long intergenic noncoding RNA Firre. Nat Struct Mol Biol 21:198–206
Ponting CP, Oliver PL, Reik W (2009) Evolution and functions of long noncoding RNAs. Cell 136:629–641
Nagano T, Mitchell JA, Sanz LA, Pauler FM, Ferguson-Smith AC et al (2008) The Air noncoding RNA epigenetically silences transcription by targeting G9a to chromatin. Science 322:1717–1720
Rinn JL, Kertesz M, Wang JK, Squazzo SL, Xu X et al (2007) Functional demarcation of active and silent chromatin domains in human HOX loci by noncoding RNAs. Cell 129:1311–1323
Pandey RR, Mondal T, Mohammad F, Enroth S, Redrup L et al (2008) Kcnq1ot1 antisense noncoding RNA mediates lineage-specific transcriptional silencing through chromatin-level regulation. Mol Cell 32:232–246
Zhao J, Sun BK, Erwin JA, Song JJ, Lee JT (2008) Polycomb proteins targeted by a short repeat RNA to the mouse X chromosome. Science 322:750–756
Mohammad F, Mondal T, Guseva N, Pandey GK, Kanduri C (2010) Kcnq1ot1 noncoding RNA mediates transcriptional gene silencing by interacting with Dnmt1. Development 137:2493–2499
Wu Y, Zhang L, Wang Y, Li H, Ren X et al (2015) Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR promotes tumor cell invasion and metastasis by recruiting EZH2 and repressing E-cadherin in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Oncol 46:2586–2594
Khalil AM, Guttman M, Huarte M, Garber M, Raj A et al (2009) Many human large intergenic noncoding RNAs associate with chromatin-modifying complexes and affect gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:11667–11672
Zhao J, Ohsumi TK, Kung JT, Ogawa Y, Grau DJ et al (2010) Genome-wide identification of polycomb-associated RNAs by RIP-seq. Mol Cell 40:939–953
Brannan CI, Dees EC, Ingram RS, Tilghman SM (1990) The product of the H19 gene may function as an RNA. Mol Cell Biol 10:28–36
Brown CJ, Ballabio A, Rupert JL, Lafreniere RG, Grompe M et al (1991) A gene from the region of the human X inactivation centre is expressed exclusively from the inactive X chromosome. Nature 349:38–44
Simon MD, Pinter SF, Fang R, Sarma K, Rutenberg-Schoenberg M et al (2013) High-resolution Xist binding maps reveal two-step spreading during X-chromosome inactivation. Nature 504:465–469
Chu C, Qu K, Zhong FL, Artandi SE, Chang HY (2011) Genomic maps of long noncoding RNA occupancy reveal principles of RNA-chromatin interactions. Mol Cell 44:667–678
Arab K, Park YJ, Lindroth AM, Schafer A, Oakes C et al (2014) Long noncoding RNA TARID directs demethylation and activation of the tumor suppressor TCF21 via GADD45A. Mol Cell 55(4):604–614
Tripathi V, Ellis JD, Shen Z, Song DY, Pan Q et al (2010) The nuclear-retained noncoding RNA MALAT1 regulates alternative splicing by modulating SR splicing factor phosphorylation. Mol Cell 39:925–938
Bernard D, Prasanth KV, Tripathi V, Colasse S, Nakamura T et al (2010) A long nuclear-retained non-coding RNA regulates synaptogenesis by modulating gene expression. EMBO J 29:3082–3093
Gong C, Maquat LE (2011) lncRNAs transactivate STAU1-mediated mRNA decay by duplexing with 3′ UTRs via Alu elements. Nature 470:284–288
Yoon JH, Abdelmohsen K, Srikantan S, Yang X, Martindale JL et al (2012) LincRNA-p21 suppresses target mRNA translation. Mol Cell 47:648–655
Carrieri C, Cimatti L, Biagioli M, Beugnet A, Zucchelli S et al (2012) Long non-coding antisense RNA controls Uchl1 translation through an embedded SINEB2 repeat. Nature 491:454–457
Zappulla DC, Cech TR (2006) RNA as a flexible scaffold for proteins: yeast telomerase and beyond. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol 71:217–224
Koziol MJ, Rinn JL (2010) RNA traffic control of chromatin complexes. Curr Opin Genet Dev 20:142–148
Tsai MC, Manor O, Wan Y, Mosammaparast N, Wang JK et al (2010) Long noncoding RNA as modular scaffold of histone modification complexes. Science 329:689–693
Faghihi MA, Modarresi F, Khalil AM, Wood DE, Sahagan BG et al (2008) Expression of a noncoding RNA is elevated in Alzheimer’s disease and drives rapid feed-forward regulation of beta-secretase. Nat Med 14:723–730
Carrieri C, Forrest AR, Santoro C, Persichetti F, Carninci P et al (2015) Expression analysis of the long non-coding RNA antisense to Uchl1 (AS Uchl1) during dopaminergic cells’ differentiation in vitro and in neurochemical models of Parkinson’s disease. Front Cell Neurosci 9:114
Ishii N, Ozaki K, Sato H, Mizuno H, Saito S et al (2006) Identification of a novel non-coding RNA, MIAT, that confers risk of myocardial infarction. J Hum Genet 51:1087–1099
Pasmant E, Laurendeau I, Heron D, Vidaud M, Vidaud D et al (2007) Characterization of a germ-line deletion, including the entire INK4/ARF locus, in a melanoma-neural system tumor family: identification of ANRIL, an antisense noncoding RNA whose expression coclusters with ARF. Cancer Res 67:3963–3969
Daughters RS, Tuttle DL, Gao W, Ikeda Y, Moseley ML et al (2009) RNA gain-of-function in spinocerebellar ataxia type 8. PLoS Genet 5:e1000600
Khalil AM, Faghihi MA, Modarresi F, Brothers SP, Wahlestedt C (2008) A novel RNA transcript with antiapoptotic function is silenced in fragile X syndrome. PLoS One 3:e1486
Prensner JR, Chinnaiyan AM (2011) The emergence of lncRNAs in cancer biology. Cancer Discov 1:391–407
Naemura M, Murasaki C, Inoue Y, Okamoto H, Kotake Y (2015) Long noncoding RNA ANRIL regulates proliferation of non-small cell lung cancer and cervical cancer cells. Anticancer Res 35:5377–5382
Cai Y, He J, Zhang D (2015) Long noncoding RNA CCAT2 promotes breast tumor growth by regulating the Wnt signaling pathway. Onco Targets Ther 8:2657–2664
Zhuang Y, Nguyen HT, Burow ME, Zhuo Y, El-Dahr SS et al (2014) Elevated expression of long intergenic non-coding RNA HOTAIR in a basal-like variant of MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Mol Carcinog. 54(12):1656–1667
Gupta RA, Shah N, Wang KC, Kim J, Horlings HM et al (2010) Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR reprograms chromatin state to promote cancer metastasis. Nature 464:1071–1076
Kogo R, Shimamura T, Mimori K, Kawahara K, Imoto S et al (2011) Long noncoding RNA HOTAIR regulates polycomb-dependent chromatin modification and is associated with poor prognosis in colorectal cancers. Cancer Res 71:6320–6326
Chung S, Nakagawa H, Uemura M, Piao L, Ashikawa K et al (2011) Association of a novel long non-coding RNA in 8q24 with prostate cancer susceptibility. Cancer Sci 102:245–252
Calin GA, Pekarsky Y, Croce CM (2007) The role of microRNA and other non-coding RNA in the pathogenesis of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Best Pract Res Clin Haematol 20:425–437
Calin GA, Liu CG, Ferracin M, Hyslop T, Spizzo R et al (2007) Ultraconserved regions encoding ncRNAs are altered in human leukemias and carcinomas. Cancer Cell 12:215–229
Khaitan D, Dinger ME, Mazar J, Crawford J, Smith MA et al (2011) The melanoma-upregulated long noncoding RNA SPRY4-IT1 modulates apoptosis and invasion. Cancer Res 71:3852–3862
Li L, Feng T, Lian Y, Zhang G, Garen A et al (2009) Role of human noncoding RNAs in the control of tumorigenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:12956–12961
Huarte M, Guttman M, Feldser D, Garber M, Koziol MJ et al (2010) A large intergenic noncoding RNA induced by p53 mediates global gene repression in the p53 response. Cell 142:409–419
Yu W, Gius D, Onyango P, Muldoon-Jacobs K, Karp J et al (2008) Epigenetic silencing of tumour suppressor gene p15 by its antisense RNA. Nature 451:202–206
Gutschner T, Hammerle M, Eissmann M, Hsu J, Kim Y et al (2013) The noncoding RNA MALAT1 is a critical regulator of the metastasis phenotype of lung cancer cells. Cancer Res 73:1180–1189
Tano K, Mizuno R, Okada T, Rakwal R, Shibato J et al (2010) MALAT-1 enhances cell motility of lung adenocarcinoma cells by influencing the expression of motility-related genes. FEBS Lett 584:4575–4580
Lopez-Ayllon BD, Moncho-Amor V, Abarrategi A, Ibanez de Caceres I, Castro-Carpeno J et al (2014) Cancer stem cells and cisplatin-resistant cells isolated from non-small-lung cancer cell lines constitute related cell populations. Cancer Med 3:1099–1111
Weber DG, Johnen G, Casjens S, Bryk O, Pesch B et al (2013) Evaluation of long noncoding RNA MALAT1 as a candidate blood-based biomarker for the diagnosis of non-small cell lung cancer. BMC Res Notes 6:518
Yao Y, Fan Y, Wu J, Wan H, Wang J et al (2012) Potential application of non-small cell lung cancer-associated autoantibodies to early cancer diagnosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 423:613–619
Guffanti A, Iacono M, Pelucchi P, Kim N, Solda G et al (2009) A transcriptional sketch of a primary human breast cancer by 454 deep sequencing. BMC Genomics 10:163
Kan JY, Wu DC, Yu FJ, Wu CY, Ho YW et al (2015) Chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 5 is involved in tumor-associated dendritic cell-mediated colon cancer progression through non-coding RNA MALAT-1. J Cell Physiol 230:1883–1894
Fan Y, Shen B, Tan M, Mu X, Qin Y et al (2014) TGF-beta-induced upregulation of malat1 promotes bladder cancer metastasis by associating with suz12. Clin Cancer Res 20:1531–1541
Okugawa Y, Toiyama Y, Hur K, Toden S, Saigusa S et al (2014) Metastasis-associated long non-coding RNA drives gastric cancer development and promotes peritoneal metastasis. Carcinogenesis 35:2731–2739
Hu L, Wu Y, Tan D, Meng H, Wang K et al (2015) Up-regulation of long noncoding RNA MALAT1 contributes to proliferation and metastasis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 34:7
Kuo IY, Wu CC, Chang JM, Huang YL, Lin CH et al (2014) Low SOX17 expression is a prognostic factor and drives transcriptional dysregulation and esophageal cancer progression. Int J Cancer 135:563–573
Wang X, Li M, Wang Z, Han S, Tang X et al (2015) Silencing of long noncoding RNA MALAT1 by miR-101 and miR-217 inhibits proliferation, migration, and invasion of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells. J Biol Chem 290:3925–3935
Mohamadkhani A (2014) Long noncoding RNAs in interaction with RNA binding proteins in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepat Mon 14:e18794
Liu SP, Yang JX, Cao DY, Shen K (2013) Identification of differentially expressed long non-coding RNAs in human ovarian cancer cells with different metastatic potentials. Cancer Biol Med 10:138–141
Ren S, Liu Y, Xu W, Sun Y, Lu J et al (2013) Long noncoding RNA MALAT-1 is a new potential therapeutic target for castration resistant prostate cancer. J Urol 190:2278–2287
Sowalsky AG, Xia Z, Wang L, Zhao H, Chen S et al (2015) Whole transcriptome sequencing reveals extensive unspliced mRNA in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. Mol Cancer Res 13:98–106
Wang F, Ren S, Chen R, Lu J, Shi X et al (2014) Development and prospective multicenter evaluation of the long noncoding RNA MALAT-1 as a diagnostic urinary biomarker for prostate cancer. Oncotarget 5:11091–11102
Ellis MJ, Ding L, Shen D, Luo J, Suman VJ et al (2012) Whole-genome analysis informs breast cancer response to aromatase inhibition. Nature 486:353–360
Ji Q, Zhang L, Liu X, Zhou L, Wang W et al (2014) Long non-coding RNA MALAT1 promotes tumour growth and metastasis in colorectal cancer through binding to SFPQ and releasing oncogene PTBP2 from SFPQ/PTBP2 complex. Br J Cancer 111:736–748
Xu C, Yang M, Tian J, Wang X, Li Z (2011) MALAT-1: a long non-coding RNA and its important 3′ end functional motif in colorectal cancer metastasis. Int J Oncol 39:169–175
Lin R, Roychowdhury-Saha M, Black C, Watt AT, Marcusson EG et al (2011) Control of RNA processing by a large non-coding RNA over-expressed in carcinomas. FEBS Lett 585:671–676
Yang L, Lin C, Liu W, Zhang J, Ohgi KA et al (2011) ncRNA- and Pc2 methylation-dependent gene relocation between nuclear structures mediates gene activation programs. Cell 147:773–788
Loewen G, Jayawickramarajah J, Zhuo Y, Shan B (2014) Functions of lncRNA HOTAIR in lung cancer. J Hematol Oncol 7:90
Loewen G, Zhuo Y, Zhuang Y, Jayawickramarajah J, Shan B (2014) lincRNA HOTAIR as a novel promoter of cancer progression. J Can Res Updates 3:7
Zhuang Y, Wang X, Nguyen HT, Zhuo Y, Cui X et al (2013) Induction of long intergenic non-coding RNA HOTAIR in lung cancer cells by type I collagen. J Hematol Oncol 6:35
Svoboda M, Slyskova J, Schneiderova M, Makovicky P, Bielik L et al (2014) HOTAIR long non-coding RNA is a negative prognostic factor not only in primary tumors, but also in the blood of colorectal cancer patients. Carcinogenesis 35:1510–1515
Chiyomaru T, Yamamura S, Fukuhara S, Yoshino H, Kinoshita T et al (2013) Genistein inhibits prostate cancer cell growth by targeting miR-34a and oncogenic HOTAIR. PLoS One 8:e70372
Xue X, Yang YA, Zhang A, Fong KW, Kim J et al (2016) LncRNA HOTAIR enhances ER signaling and confers tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer. Oncogene 35(21):2746–2755
Mourtada-Maarabouni M, Pickard MR, Hedge VL, Farzaneh F, Williams GT (2009) GAS5, a non-protein-coding RNA, controls apoptosis and is downregulated in breast cancer. Oncogene 28:195–208
Dimitrova N, Zamudio JR, Jong RM, Soukup D, Resnick R et al (2014) LincRNA-p21 activates p21 in cis to promote Polycomb target gene expression and to enforce the G1/S checkpoint. Mol Cell 54:777–790
Cai B, Wu Z, Liao K, Zhang S (2014) Long noncoding RNA HOTAIR can serve as a common molecular marker for lymph node metastasis: a meta-analysis. Tumour Biol 35(9):8445–8450
Zheng HT, Shi DB, Wang YW, Li XX, Xu Y et al (2014) High expression of lncRNA MALAT1 suggests a biomarker of poor prognosis in colorectal cancer. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 7:3174–3181
de Kok JB, Verhaegh GW, Roelofs RW, Hessels D, Kiemeney LA et al (2002) DD3(PCA3), a very sensitive and specific marker to detect prostate tumors. Cancer Res 62:2695–2698
Bussemakers MJ, van Bokhoven A, Verhaegh GW, Smit FP, Karthaus HF et al (1999) DD3: a new prostate-specific gene, highly overexpressed in prostate cancer. Cancer Res 59:5975–5979
Nilsson J, Skog J, Nordstrand A, Baranov V, Mincheva-Nilsson L et al (2009) Prostate cancer-derived urine exosomes: a novel approach to biomarkers for prostate cancer. Br J Cancer 100:1603–1607
Kogure T, Yan IK, Lin WL, Patel T (2013) Extracellular vesicle-mediated transfer of a novel long noncoding RNA TUC339: a mechanism of intercellular signaling in human hepatocellular cancer. Genes Cancer 4:261–272
Zhuang Y, Nguyen HT, Burow ME, Zhuo Y, El-Dahr SS et al (2015) Elevated expression of long intergenic non-coding RNA HOTAIR in a basal-like variant of MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Mol Carcinog 54:1656–1667
Pedram Fatemi R, Salah-Uddin S, Modarresi F, Khoury N, Wahlestedt C et al (2015) Screening for small-molecule modulators of long noncoding RNA-protein interactions using AlphaScreen. J Biomol Screen 20:1132–1141
Ng SY, Lin L, Soh BS, Stanton LW (2013) Long noncoding RNAs in development and disease of the central nervous system. Trends Genet 29:461–468
Ng SY, Johnson R, Stanton LW (2012) Human long non-coding RNAs promote pluripotency and neuronal differentiation by association with chromatin modifiers and transcription factors. EMBO J 31:522–533
Modarresi F, Faghihi MA, Patel NS, Sahagan BG, Wahlestedt C et al (2011) Knockdown of BACE1-AS Nonprotein-coding transcript modulates beta-amyloid-related hippocampal neurogenesis. Int J Alzheimers Dis 2011:929042
Muddashetty R, Khanam T, Kondrashov A, Bundman M, Iacoangeli A et al (2002) Poly(A)-binding protein is associated with neuronal BC1 and BC200 ribonucleoprotein particles. J Mol Biol 321:433–445
Mus E, Hof PR, Tiedge H (2007) Dendritic BC200 RNA in aging and in Alzheimer’s disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:10679–10684
Morais VA, Verstreken P, Roethig A, Smet J, Snellinx A et al (2009) Parkinson's disease mutations in PINK1 result in decreased Complex I activity and deficient synaptic function. EMBO Mol Med 1:99–111
Scheele C, Petrovic N, Faghihi MA, Lassmann T, Fredriksson K et al (2007) The human PINK1 locus is regulated in vivo by a non-coding natural antisense RNA during modulation of mitochondrial function. BMC Genomics 8:74
Herriges MJ, Swarr DT, Morley MP, Rathi KS, Peng T et al (2014) Long noncoding RNAs are spatially correlated with transcription factors and regulate lung development. Genes Dev 28:1363–1379
Szafranski P, Dharmadhikari AV, Brosens E, Gurha P, Kolodziejska KE et al (2013) Small noncoding differentially methylated copy-number variants, including lncRNA genes, cause a lethal lung developmental disorder. Genome Res 23:23–33
Michalik KM, You X, Manavski Y, Doddaballapur A, Zornig M et al (2014) Long noncoding RNA MALAT1 regulates endothelial cell function and vessel growth. Circ Res 114:1389–1397
Yoon JH, Abdelmohsen K, Gorospe M (2014) Functional interactions among microRNAs and long noncoding RNAs. Semin Cell Dev Biol 34C:9–14
de Giorgio A, Krell J, Harding V, Stebbing J, Castellano L (2013) Emerging roles of competing endogenous RNAs in cancer: insights from the regulation of PTEN. Mol Cell Biol 33:3976–3982
Wang Y, Xu Z, Jiang J, Xu C, Kang J et al (2013) Endogenous miRNA sponge lincRNA-RoR regulates Oct4, Nanog, and Sox2 in human embryonic stem cell self-renewal. Dev Cell 25:69–80
Liu XH, Sun M, Nie FQ, Ge YB, Zhang EB et al (2014) Lnc RNA HOTAIR functions as a competing endogenous RNA to regulate HER2 expression by sponging miR-331-3p in gastric cancer. Mol Cancer 13:92
Ma MZ, Li CX, Zhang Y, Weng MZ, Zhang MD et al (2014) Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR, a c-Myc activated driver of malignancy, negatively regulates miRNA-130a in gallbladder cancer. Mol Cancer 13:156
Zhou X, Ye F, Yin C, Zhuang Y, Yue G et al (2015) The interaction between MiR-141 and lncRNA-H19 in regulating cell proliferation and migration in gastric cancer. Cell Physiol Biochem 36:1440–1452
Kallen AN, Zhou XB, Xu J, Qiao C, Ma J et al (2013) The imprinted H19 lncRNA antagonizes let-7 microRNAs. Mol Cell 52:101–112
Cesana M, Cacchiarelli D, Legnini I, Santini T, Sthandier O et al (2011) A long noncoding RNA controls muscle differentiation by functioning as a competing endogenous RNA. Cell 147:358–369
Jeck WR, Sharpless NE (2014) Detecting and characterizing circular RNAs. Nat Biotechnol 32:453–461
Hansen TB, Jensen TI, Clausen BH, Bramsen JB, Finsen B et al (2013) Natural RNA circles function as efficient microRNA sponges. Nature 495:384–388
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2017 Springer Science+Business Media LLC
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Xue, M., Zhuo, Y., Shan, B. (2017). MicroRNAs, Long Noncoding RNAs, and Their Functions in Human Disease. In: Huang, J., et al. Bioinformatics in MicroRNA Research. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 1617. Humana Press, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-7046-9_1
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-7046-9_1
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana Press, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-4939-7044-5
Online ISBN: 978-1-4939-7046-9
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols