Abstract
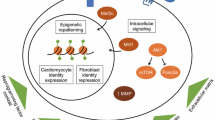
The therapeutic administration of microRNAs represents an innovative reprogramming strategy with which to advance cardiac regeneration and personalized medicine. Recently, a distinct set of microRNAs was found capable of converting murine fibroblasts to cardiomyocyte-like cells in vitro. Further treatment with JAK inhibitor I significantly enhanced the efficiency of the microRNA-mediated reprogramming (Jayawardena et al., Circ Res 110(11):1465–1473, 2012). This novel technique serves as an initial tool for switching the cell fate of cardiac fibroblasts toward the cardiomyocyte lineage using microRNAs. As the budding field of reprogramming biology develops, we hope that a thorough examination of the chemical, physical, and temporal parameters determining reprogramming efficiency and maturation will enable a better understanding of the mechanisms governing cardiac cell fate and provide new approaches for drug discovery and therapy for cardiovascular diseases.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yoshida Y, Yamanaka S (2012) An emerging strategy of gene therapy for cardiac disease. Circ Res 111(9):1108–1110
Takahashi K, Yamanaka S (2006) Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors. Cell 126(4):663–676
Jayawardena TM et al (2012) MicroRNA-mediated in vitro and in vivo direct reprogramming of cardiac fibroblasts to cardiomyocytes. Circ Res 110(11):1465–1473
Nam YJ et al (2013) Reprogramming of human fibroblasts toward a cardiac fate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110(14):5588–5593
Song K et al (2012) Heart repair by reprogramming non-myocytes with cardiac transcription factors. Nature 485(7400):599–604
Qian L et al (2012) In vivo reprogramming of murine cardiac fibroblasts into induced cardiomyocytes. Nature 485(7400):593–598
Mummery C (2011) Induced pluripotent stem cells—a cautionary note. N Engl J Med 364(22):2160–2162
Yamashita T et al (2011) Tumorigenic development of induced pluripotent stem cells in ischemic mouse brain. Cell Transplant 20(6):883–891
Christoforou N et al (2013) Induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiac progenitors differentiate to cardiomyocytes and form biosynthetic tissues. PLoS One 8(6):e65963
Protze S et al (2012) A new approach to transcription factor screening for reprogramming of fibroblasts to cardiomyocyte-like cells. J Mol Cell Cardiol 53(3):323–332
Stiber J et al (2008) STIM1 signalling controls store-operated calcium entry required for development and contractile function in skeletal muscle. Nat Cell Biol 10(6):688–697
Eckel J et al (2011) TRPC6 enhances angiotensin II-induced albuminuria. J Am Soc Nephrol 22(3):526–535
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2014 Springer Science+Business Media New York
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Jayawardena, T., Mirotsou, M., Dzau, V.J. (2014). Direct Reprogramming of Cardiac Fibroblasts to Cardiomyocytes Using MicroRNAs. In: Kidder, B. (eds) Stem Cell Transcriptional Networks. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 1150. Humana Press, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-0512-6_18
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-0512-6_18
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana Press, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-4939-0511-9
Online ISBN: 978-1-4939-0512-6
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols