Abstract
A commercial scale micropropagation technology was developed in Finland for the silver birch (Betula pendula), which is an increasingly important raw material source for the forest industry.
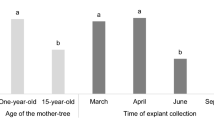
Genotype affected more the success of initiation and multiplication rate than e.g. age of the mother tree or season. The clonal fidelity of the in vitro propagation system based on axillary proliferation has been high. When producing plantlets using adventitious tissue culture system one distinct variant was discovered. The field performance of the micropropagated plantlets during the first season in the nursery was slightly better than that of conventional seedlings.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chu, I.Y.E., and Kurtz, S.L., 1990, Commercialization of plant tissue culture, in: “Handbook of Plant Cell Culture, Vol 5,” P.V. Ammirato, D.A. Evans, W.R. Sharp and Y.P.S. Bajaj, eds., McGraw Hill, New York.
George, E. F., and Sherrington, P. D., 1984, “Plant Propagation by Tissue Culture,” Exegetics Ltd. Hants.
McCown, B.H., 1985, From gene manipulation to forest establishment: shoot cultures of woody plants can be a central tool. Tappi J., 68:116.
Meier-Dinkel, A., 1990, Micropropagation of birches (Betula spp.). Manuscript for: “Biotechnology in Agriculture and Forestry. Trees III,” Y.P.S. Bajaj, ed.
Smith, M.A.L., and McCown, B.H., 1982/83, A comparison of source tissue for protoplast isolation from three woody plant species, Plant Sci. Lett. 28:149.
Särkilahti, E., 1988, Micropropagation of a mature colchicine-polyploid and irradiation-mutant of Betula pendula Roth. Tree Physiol., 4:173.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1991 Plenum Press, New York
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Jokinen, K., Törmälä, T. (1991). Micropropagation of Silver Birch (Betula pendula Roth.) and Clonal Fidelity of Mass Propagated Birch Plants. In: Ahuja, M.R. (eds) Woody Plant Biotechnology. NATO ASI Series, vol 210. Springer, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4684-7932-4_4
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4684-7932-4_4
Publisher Name: Springer, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-4684-7934-8
Online ISBN: 978-1-4684-7932-4
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive