Abstract
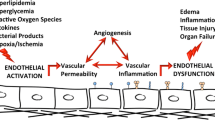
Circulatory homeostasis is usually maintained by quiescent endothelial cells that possess highly effective anticoagulant and platelet thromboregulatory mechanisms. Following injury, the vascular endothelium is considered to undergo a process of activation where cells are exposed to oxidative stress, lose intrinsic antithrombotic properties and become procoagulant and facilitative for platelet aggregation. Endothelial cells express an ATPDase that hydrolyzes extracellular adenosine nucleotides and can inhibit stimulated human platelet aggregation in vitro. Loss of this ectoenzyme activity with reduced membrane protein expression occurs shortly following TNFα stimulation or perturbation of endothelial cells by reactive oxygen species in vitro. Comparable events follow reperfusion injury and xenograft rejection in vivo. Additionally, the administration of antioxidants and purified apyrases ameliorate rat renal reperfusion injury and discordant xenograft rejection, respectively.
Following our identification of the gene encoding vascular ATPDase as CD39, we are now examining the pathophysiological significance of the expression of CD39/ATPDase by the vasculature and how this enzymatic function is modulated by inflammatory processes. This work will be facilitated by the generation of knock-out and CD39 transgenic mice. Our approach should provide a closer understanding of thrombosis and vascular disruption in the context of transplant vascular pathobiology and other inflammatory diseases characterized by vascular thrombosis and platelet activation.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cotran RS, Pober JS. Endothelial activation and inflammation. Progress in Immunology 1989; 8: 747.
Cotran RS, Pober, J.S. Cytokine-endothelial interactions in inflammation, immunity, and vascular injury. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 1990; 1: 225–235.
Vercellotti GM, Platt JL, Bach FH, Dalmasso AP. Neutrophil adhesion to xenogeneic endothelium via iC3b. Journal of Immunology 1991; 146: 730–734.
Dalmasso AP. The complement system in xenotransplantation. Immunopharmacology 1992; 24: 149–160.
Albelda SM, Smith CW, Ward PA. Adhesion molecules and inflammatory injury. FASEB Journal 1994; 8: 504–512.
Esmon CT. Cell mediated events that control blood coagulation and vascular injury. [Review]. Annual Review of Cell Biology 1993; 9: 1–26.
Brooks CJ Stackpoole A, Savage C. Synergistic interactions of CD4+ and CD8+ T-cell subsets with human vascular endothelial cells in primary proliferative allogeneic responses. Int Immunology 1993; 5: 1041–1048.
Murray AG, Khodadoust MM, Pober JS, Bothwell ALM. Porcine aortic endothelial cells activate human T cells: Direct presentation of MHC antigens and co-stimulation by ligands for human CD2 and CD28. Immunity 1994; 1: 57–63.
Robson SC, Candinas D, Hancock WW, Wrighton C, Winkler H, Bach FH. Role of endothelial cells in transplantation. [Review]. International Archives of Allergy & Immunology 1995; 106: 305–322.
Bach FH, Robson SC, Winkler H, Ferran C, Stuhlmeier KM, Wrighton CJ, Hancock WW. Barriers to xenotransplantation. Nature Medicine 1995; 1: 869–873.
Platt JL, Bach FH. The barrier to xenotransplantation. Transplantation 1991; 52: 937–947.
Platt JL, Vercellotti GM, Dalmasso AP, Matas AJ, Bolman RM, Najarian JS, Bach FH. Transplantation of discordant xenografts: a review of progress. [Review]. Immunology Today 1990; 11: 450–456.
Hancock WW, Blakely ML, Van der Werf W, Bach FH. Rejection of guinea pig cardiac xenografts post-cobra venom factor therapy is associated with infiltration by mononuclear cells secreting interferon-gamma and diffuse endothelial activation. Transplantation Proceedings 1993; 25: 2932.
Manner M, Shult W, Senninger N, Machens G, Otto G. Evaluation of preservation damage after porcine liver transplantation by assessment of hepatic microcirculation. Transplantation 1990; 50: 940–943.
Michel A, Vons C, Icard P, Hillaire S, Hazebroucq G, Franco D, Houssin D. Efficacy of a modified University of Wisconsin solution in rat liver preservation: its prevailing role on vascular endothelium rather than hepatocyte protection. Transplantation Proceedings 1990; 22: 2291–2292.
Jacobson J, Odlind B, Tufveson G, Wahlberg J. Effects of cold ischemia and reperfusion on trapping of erythrocytes in the rat kidney. Transplantation International 1988; 1: 75–79.
Cywes R, Packham MA, Tietze L, Sanabria JR, Harvey R, Phillips MJ, Strasberg SM. Role of platelets in hepatic allograft preservation injury in the rat. Hepatology 1993; 18: 635–647.
Cywes R, Mullen JB, Stratis MA, Greig PD, Levy GA, Harvey PR, Strasberg SM. Prediction of the outcome of transplantation in man by platelet adherence in donor liver allografts. Evidence of the importance of preservation injury. Transplantation 1993; 56: 316–323.
Ogawa S, Gerlach H, Esposito C, Pasagian MA, Brett J, Stern D. Hypoxia modulates the barrier and coagulant function of cultured bovine endothelium. Increased monolayer permeability and induction of procoagulant properties. Journal of Clinical Investigation 1990; 85: 1090–1098.
Ambrosio G, Oriente A, Napoli C, Palumbo G, Chiariello P, Marone G, Condorelli M, Chiariello M, Triggiani M. Oxygen radicals inhibit human plasma acetylhydrolase, the enzyme that catabolizes platelet-activating factor. Journal of Clinical Investigation 1994; 93: 2408–2416.
Broekman MJ, Eiroa AM, Marcus AJ. Inhibition of human platelet reactivity by endothelium-derived relaxing factor from human umbilical vein endothelial cells in suspension: blockade of aggregation and secretion by an aspirin-insensitive mechanism. Blood 1991; 78: 1033–1040.
Marcus AJ, Safier LB. Thromboregulation: multicellular modulation of platelet reactivity in hemostasis and thrombosis. [Review]. FASEB Journal 1993; 7: 516–522.
Schmidt HHHW, Walter U. NO at work. Cell 1994; 78: 919–925.
Pinsky DJ, Mehmet CO, Koga S, Taha Z, Broekman MJ, Marcus AJ, Liao H, Naka Y, Brett J, Cannon PJ, Novigrod R, Malinski T, Stern DM. Cardiac preservation is enhanced in a heterotopic rat transplant model by supplementing the nitric oxide pathway. Journal of Clinical Investigation 1994; 93: 2291–2297.
Saran M, Michel C, Bors W. Reaction of NO with O2-: implications for the action of endothelium-derived relaxing factor. Free Radical Research Communications. 1990; 10: 221–226.
Land W, Schneeberger H, Schleibner S, Illner WD, Abendroth D, Rutili G, Arfors KE, Messmer K. The beneficial effect of human recombinant superoxide dismutase on acute and chronic rejection events in recipients of cadaveric renal transplants. Transplantation 1994; 57: 211–217.
Celi A, Pellegrini G, Lorenzet R, De Blasi A, Ready N, Furie BC, Furie B. P-selectin induces the expression of tissue factor on monocytes. Proceedings National Academy Sciences USA. 1994; 91: 8767–8771.
Faint RW. Platelet-neutrophil interactions: their significance. [Review]. Blood Reviews 1992; 6: 83–91.
Tsuji T, Nagata K, Koike J, Todorki N, Irimura T. Induction of superoxide anion production from monocytes and neutrophils by activated platelets through the P-selectin-sialyl Lewis X interaction. Journal of Leukocyte Biology 1994; 56: 583–587.
Topol EJ, Plow EF. Clinical trials of platelet receptor inhibitors. Thrombosis and Haemostasis 1993; 70: 94–98.
Marcus AJ, Safier LB, Hajjar KA, Ullman HL, Islam N, Broekman MJ, Eiroa AM. Inhibition of platelet function by an aspirin-insensitive endothelial cell ADPase. Thromboregulation by endothelial cells. Journal of Clinical Investigation 1991; 88: 1690–1696.
Ihrcke NS, Wrenshall LE, Lindman BJ, Platt JL. Role of heparan sulfate in immune system-blood vessel interactions. Immunology Today 1993; 14: 500–505.
Magee JC, Platt JL, Oldham KT, Guice KS. Oxidant stress increases susceptibility of porcine endothelial cells to injury by xenoreactive antibody and complement. Transplantation Proceedings 1994; 26: 1170.
Taparelli C, Metternich R, Ehrhardt C, Cook N. Synthetic low-molecular weight thrombin inhibitors: molecular design and pharmacolgical profile. Trends in Pharmacological Sciences 1993; 14: 366–376.
Calne RY. Organ transplantation between widely disparate species. Transplantation Proceedings 1970; 2: 550–556.
Bach FH. Reconsideration of the mechanism of first-set vascularized allograft rejection: some concluding remarks. [Review]. Human Immunology 1990; 28: 263–269.
Dalmasso AP, Vercellotti GM, Fischel RJ, Bolman RM, Bach FH, Platt JL, Mechanism of complement activation in the hyperacute rejection of porcine organs transplanted into primate recipients. American Journal of Pathology 1992; 140: 1157–1166.
Platt JL, Lindman BJ, Geller RL, Noreen HJ, Swanson JL, Dalmasso AP, Bach FH. The role of natural antibodies in the activation of xenogenic endothelial cells. Transplantation 1991; 52: 1037–1043.
Galili U. Interaction of the natural anti-gal antibody with alpha-galactosyl epitopes — a major obstacle for xenotransplantation in humans. Immunology Today 1993; 14: 480–482.
Bach FH, Robson SC, Ferran C, Winkler H, Millan MT, Stuhlmeier KM, Vanhove B, Blakely ML, van der Werf W, Hofer E, et at. Endothelial cell activation and thromboregulation during xenograft rejection. [Review]. Immunological Reviews 1994; 141: 5–30.
Bach FH, Robson SC, Ferran C, Millan M, Anrather J, Kopp C, Lesnikoski B, Goodman DJ, Hancock WW, Wrighton C, et al. Xenotransplantation: endothelial cell activation and beyond. Transplantation Proceedings 1995; 27: 77–79.
Robson SC, Candinas D, Hancock WW, Siegel JB, Millan M, Bach FH. Loss of ATP diphosphohydrolase activity following endothelial cell activation. Transplantation Proceedings 1996; 28(2). 536–7.
Goodman DG, Von Alberini M, Bach FH. Interaction of human NK cells and porcine endothelial cells. Transplantation. 1996; 61:763–771.
Lu CY, Khair-el-din TA, Dawidson IA, Butler TM, Brasky KM, Vazquez MA, Sicher SC. Xenotransplantation. FASEB Journal 1994; 8: 1122–1130.
Makowka L, Chapman FA, Cramer DV, Qian SG, Sun H, Starzl TE. Platelet-activating factor and hyperacute rejection. The effect of a platelet-activating factor antagonist, SRI 63–441, on rejection of xenografts and allografts in sensitized hosts. Transplantation 1990; 50: 359–365.
Coughlan AF, Berndt MC, Dunlop LC, Hancock WW. In vivo studies of P-selectin and platelet activating factor during endotoxemia, accelerated allograft rejection, and discordant xenograft rejection. Transplantation Proceedings 1993; 25: 2930–2931.
Robson SC, Young VK, Cook NS, Metternich R, Kasper-Konig W, Lesnikoski BA, Candinas D, Pierson RN, Hancock WW, White DJ, Bach FH. Thrombin inhibition in an ex vivo model of hyperacute xenograft rejection. Transplantation 1996; 61: 862–868.
BA Lesnikoski, DR Candinas, WW Hancock, Grey S, I Otsu, FH Bach, SC Robson. Inhibition of platelet GPIIbIlla receptors prolongs discordant xenograft survival. Transplantation Proceedings 1996; 28(2). 581.
Sims PJ, Wiedmer T. The response of human platelets to activated components of the complement system. [Review]. Immunology Today 1991; 12: 338–342.
Hamilton KK, Hattori R, Esmon CT, Sims PJ. Complement proteins C5b-9 induce vesiculation of the endothelial plasma membrane and expose catalytic surface for assembly of the prothrombinase enzyme complex. Journal of Biological Chemistry 1990; 265: 3809–3814.
Esmon CT, Taylor FB, Snow TR. Inflammation and Coagulation — Linked Processes Potentially Regulated Through a Common Pathway Mediated by Protein-C. Thrombosis Haemostasis 1991; 66: 160–165.
Palabrica T, Lobb R, Furie BC, Aronovitz M, Benjamin C, Hsu YM, Sajer SA, Furie B. Leukocyte accumulation promoting fibrin deposition is mediated in vivo by P-Selectin on adherent platelets. Nature 1992; 359:848–851.
Furie B, Furie BC. Molecular and cellular biology of blood coagulation. New England Journal of Medicine 1992; 326: 800–806.
Saadi S, Holzknecht RA, Patte CP, Stern DM, Platt JL. Complement mediated regulation of tissue factor activity in endothelium. Journal of Experimental Medicine 1995; 182: 1807–1814.
Preissner KT. Anticoagulant potential of endothelial cell membrane components. Haemostasis 1988: 18: 271–306.
Conway EM, Rosenberg RD. Tumour necrosis factor suppresses transcription of the thrombomodulin gene in endothelial cells. Molecular & Cellular Biology. 1988; 8: 5588–5592.
Conway EM, Bach R, Rosenberg RD, Königsberg WH. Tumor necrosis factor enhances expression of tissue factor mRNA in endothelial cells. Thrombosis Research 1989; 53: 231–241.
Bakker WW, Poelstra K, Barradas MA, Mikhailidis DP. Platelets and ectonucleotidases. Platelets 1994; 5: 121–129.
Plesner L. Ecto-ATPases: identities and functions. International Review of Cytology. 1995; 158: 141–214.
LeBel D, Poirier GG, Phaneuf S, St JP, Laliberte JF, Beaudoin AR. Characterization and purification of a calcium-sensitive ATP diphosphohydrolase from pig pancreas. Journal of Biological Chemistry 1980; 255: 1227–1233.
Laliberte JF, Beaudoin AR. Sequential hydrolysis of the gamma-and beta-phosphate groups of ATP by the ATP diphosphohydrolase from pig pancreas. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta 1983; 742: 9–15.
Cote YP, Picher M, St JP, Beliveau R, Potier M, Beaudoin AR. Identification and localization of ATP-diphosphohydrolase (apyrase) in bovine aorta: relevance to vascular tone and platelet aggregation. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta 1991; 1078: 187–191.
Cote YP, Ouellet S, Beaudoin AR. Kinetic properties of type-II ATP diphosphohydrolase from the tunica media of the bovine aorta. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta 1992; 1160: 246–250.
Cote YP, Filep JG, Battistini B, Gauvreau J, Sirois P, Beaudoin AR. Characterization of ATP-diphosphohy-drolase activities in the intima and media of the bovine aorta: evidence for a regulatory role in platelet activation in vitro. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta 1992; 1139: 133–142.
Picher M, Beliveau R, Potier M, Savaria D, Rousseau E, Beaudoin AR. Demonstration of an ecto-ATP-diphosphohydrolase (E.C.3.6.1.5.) in non-vascular smooth muscles of the bovine trachea. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta 1994; 1200: 167–174.
Picher M, Cote YP, Beliveau R, Potier M, Beaudoin AR. Demonstration of a novel type of ATP-diphospho-hydrolase (EC 3.6.1.5) in the bovine lung. Journal of Biological Chemistry 1993; 268: 4699–4703.
Stout JG, Kirley TL. Purification and characterization of the ecto-Mg-ATPase of chicken gizzard smooth muscle. Journal of Biochemical & Biophysical Methods 1994; 29: 61–75.
Christoforidis S, Papamarcaki T, Galaris D, Kellner R, Tsolas O. Purification and properties of human placental ATP diphosphohydrolase. European Journal of Biochemistry 1995; 234: 66–74.
Papamarcaki T, Tsolas O. Identification of ATP diphosphohydrolase activity in human term placenta using a novel assay for AMP. Molecular & Cellular Biochemistry 1990; 97: 1–8.
Handa M, Guidotti G. Purification and cloning of a soluble ATP-diphosphohydrolase (apyrase) from potato tubers (Solanum tuberosum). Biochemical & Biophysical Research Communications 1996; 218: 916–923.
Wang T-F, Guidotti G. CD39 is an ecto-(Ca2+, Mg 2+)-apyrase. Journal of Biological Chemistiy 1996; 271:9898–9901
Knowles AF, Isler RE, Reece JF. The common occurrence of ATP diphosphohydrolase in mammalian plasma membranes. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta 1983; 731: 88–96.
Lieberman GE, Lewis GP. Properties of vascular ADPase. Artery 1980; 8: 374–380.
Yagi K, Nishino I, Eguchi M, Kitagawa M, Miura Y, Mizoguchi T. Involvement of ecto-ATPase as an ATP receptor in the stimulatory effect of extracellular ATP on NO release in bovine aorta endothelial cells. Biochemical & Biophysical Research Communications 1994.; 203: 1237–1243.
Lin S-H, Guidotti G. Cloning and expression of a cDNA coding for a rat liver plasma membrane ecto-ATPase. Journal of Biological Chemistry 1989; 264: 14408–14414.
Lüthje J. Origin, metabolism and function of extracellular adenine nucleotides in the blood [published erratum appears in Klin Wochenschr 1989 May 15;67(10):558]. [Review]. Klinische Wochenschrift 1989; 67: 317–327.
McClure MO, Kakkar A, Cusack NJ, Born GV. Evidence for the dependence of arterial haemostasis on ADR Proceedings of the Royal Society of London Series B: Biological Sciences 1988; 234: 255–262.
Herbert JM, Bernat A, Maffrand JR. Importance of platelets in experimental venous thrombosis in the rat. Blood 1992; 80: 2281–2286.
Nabel EG. Biology of the impaired endothelium. American Journal Cardiology 1991; 6:(pt. 12) 6C–8C.
Sakon M, Hawiger J. Mechanism triggering platelet hemostatic plug formation in vivo. Transactions of the Association of American Physicians 1984; 97: 311–318.
Harker LA, Ross R. Vessel injury, thrombosis, and platelet survival. [Review]. Advances in Experimental Medicine & Biology 1978; 102: 197–210.
Hourani SMO, Hall DA. Receptors for platelets on human blood platelets. TIPS 1994; 15: 103–107.
Cronstein BN, Levin RI, Belanoff J, Weissmann G, Hirschorn R. Adenosine: an endogenous inhibitor of neutrophil mediated injury to endothelial cells. Journal of Clinical Investigation 1986; 78: 760–770.
Khimenko PL, Moore TM, Hill LW, Wilson PS, Coleman S, Rizzo A, Taylor AE. Adenosine A2 receptors reverse ischemia-reperfusion lung injury independent of beta-receptors. Journal of Applied Physiology 1995;78:990–996.
Cronstein BN. A novel approach to the development of anti-inflammatory agents: adenosine release at inflamed sites. Journal Investigative Medicine 1995; 43: 50–57.
Antonysamy MA, Moticka EJ, Ramkumar V. Adenosine acts as an endogenous modulator of IL-2 dependent proliferation of cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Journal of Immunology 1995; 155: 2813–2821.
Di Virgilio F. The P2z purinoreceptor: an intriguing role in immunity, inflammation and cell death. Immunology Today 1995; 16: 524–528.
Apasov S, Redegeld F, Sitkovsky M. Cell mediated cytotoxicity: Contact and secreted factors. Current Opinion in Immunology 1993; 5: 404–410.
Aalto TK, Raivio KO. Metabolism of extracellular adenine nucleotides by human endothelial cells exposed to reactive oxygen metabolites. American Journal of Physiology 1993; 264: C282–C286.
Brisseau GF, Dackiw AP, Cheung PY, Christie N, Rotstein OD. Posttranscriptional regulation of macrophage tissue factor expression by antioxidants. Blood 1995; 85: 1025–1035.
Stout JG, Kirley TL. Tissue distribution of ecto-Mg-ATPase in adult and embryonic chicken. Biochemical & Molecular Biology International 1994; 32: 745–753.
Sevigny J, Cote YP, Beaudoin AR. Purification of pancreas type I ecto-ATP diphosphohydrolase and identification by affinity labelling with the 5′-p-fluorosulfonylbenzoyladenosine ATP analogue. Biochemistry Journal 1995; 312: 351–356.
Maliszewski CR, Delespesse GJ, Schoenborn MA, Armitage RJ, Fanslow WC, Nakajima T, Baker E, Sutherland GR, Poindexter K, Birks C, et al. The CD39 lymphoid cell activation antigen; molecular cloning and structural characterization. Journal of Immunology 1994; 153: 3574–3583.
Kansas GS, Wood GS, Tedder TF. Expression, distribution, and biochemistry of human CD39. Role in activation-associated homotypic adhesion of lymphocytes. Journal of Immunology 1991; 146: 2235–2244.
Favaloro EJ. Differential expression of surface antigens on activated endothelium. Immunology Cellular Biology 1993; 71: 571–581.
Wrighton C, Kopp CW, McShea A, Vetr H, Bach FH. High level of functional human thrombomodulin in cultured porcine aortic endothelial cells. Transplantation Proceedings 1995; 27: 288–289.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1997 Springer Science+Business Media New York
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Kaczmarek, E. et al. (1997). Vascular ATP Diphosphohydrolase (CD39/ATPDase). In: Plesner, L., Kirley, T.L., Knowles, A.F. (eds) Ecto-ATPases. Springer, Boston, MA. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4615-5955-9_22
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4615-5955-9_22
Publisher Name: Springer, Boston, MA
Print ISBN: 978-1-4613-7729-0
Online ISBN: 978-1-4615-5955-9
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive