Abstract
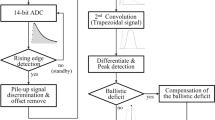
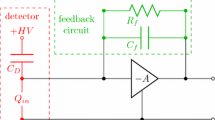
Direct digitization of the preamplifier output of a Si(Li) detector, with all subsequent pulse processing performed digitally, enhances throughput versus resolution performance Sensitivity, resolution, and especially pileup rejection for photons below 1 keV are also improved. Adaptive pulse shaping allows both low dead time operation with minimal loss of resolution and automatic adjustment to a wide range of beam current without requiring manual selection of processing time.
An overview of the operating principles of a digital pulse processor will be presented and compared with conventional approaches. Examples of spectra taken with the same spectrometer under the same conditions, changing only the pulse processors, will illustrate the advantages of adaptive digital processing.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Koeman, Nucl. Instrum. Methods 123,161 (1975).
H. Koeman, Nucl. Instrum. Methods 123,169 (1975).
H. Koeman, Nucl. Instrum. Methods 123,181(1975)
E. Lifshin, and M. F. Ciccarelli, in:Scanning Electron Microscopy 1973, IITRI Chicago, pp. 89–96 (1973).
T. Lakatos, Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. B47, 307 (1990).
A. Georgiev and W. Gast, IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 40, 772 (1993).
P. L. Ryder, NBS Special Publication 604 (K. F. J. Heinrich, D. E. Newbury, and R. L. Myklebust, eds). National Bureau of Standards, Washington, DC, pp. 177–192 (1981).
E. H. Schamber, NBS Special Publication 604 (K. F. J. Heinrich, D. E. Newbury, and R. L. Myklebust, eds.) National Bureau of Standards, Washington, DC, pp. 193–232 (1981).
C. E. Fiori et. al, NBS Special Publication 604 (K.E J. Heinrich, D. E. Newbury, and R. L. Myklebust, eds.)National Bureau of Standards, Washington, DC, pp. 233–272 (1981).
J. J. McCarthy and E H. Schamber, NBS Special Publication 604 (K. F. J. Heinrich, D. E. Newbury, and R. L. Myklebust, eds.) National Bureau of Standards, Washington, DC, pp. 273–296 (1981).
J. C. Russ, NBS Special Publication 604 (K. E J. Heinrich, D. E. Newbury, and R. L. Myklebust, eds.) National Bureau of Standards, Washington, DC., pp. 297–314 (1981).
C. E. Fiori and C. R. Swyt, Microbeam Anal. 1,89 (1992).
S. J. B. Reed, Microbeam Analysis-1990 (J. R. Michael and Peter Ingram, eds.) San Francisco Press, San Francisco, 181–184 (1990).
P. J. Statham and T. Nashashibi, in: Microbeam Analysis-1988 (D. E. Newbury, ed.) San Francisco Press, San Francisco, pp. 50–54 (1988).
P. J. Statham, Inst. Phys. Conf. Ser. 119, 425 (1991).
J. I. Goldstein, D. E. Newbury, P. Echlin, D. C. Joy, A. D. Romig, Jr.C.E.Lyman, C. Fiori, and E. Lifshin, in: Scanning Electron Microscopy and X-Ray Microanalysis, Second Ed., Plenum Press, New York, pp. 296–298 (1992).
G. E Knoll, Radiation Detection and Measurement,Second Ed., John Wiley and Sons, New York, pp. 575–577 (1989).
C. Cottini, E. Gatti, and V. Svelto, Nucl. Instrum. Methods 24, 241 (1963).
T. L. Mayhugh and J. E Pierce, IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. NS-29, 587 (1982).
D. C. Joy, Rev. Sci. Instrum. 56, 1772 (1985).
F. S. Goulding and D. A. Landis, IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. NS-29, 1125 (1982).
K. Kandiah, A. J. Smith, and G. White, IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. NS-22, 2058 (1975).
V. Jordanov and G. F. Knoll, IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 40, 764 (1993).
F. S. Goulding, Nucl. Instrum. Methods 100,493 (1972).
J. Llacer, Nucl. Instrum. Methods 130, 565 (1975).
E. Gatti and M. Sampietro, Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A287, 513 (1990).
C. E. Fiori and C. R. Swyt, in: Proceedings of the 50th Annual Meeting of the Electron Microscopy Society of America (G. W. Bailey, J. Bentley, and J. A. Small, eds.) pp. 1770–1771 (1992).
V. D. Scot and G. Love, Quantitative Electron-Probe Microanalysis, Ellis Horwood Ltd., Chichester, United Kingdom, pp. 95–96 (1983).
R. A. Sareen, personal communication (1993).
J. I. Goldstein, D. E. Newbury, P. Echlin, D. C. Joy, A. D. Romig, Jr.,C.E.Lyman, C.Fiori, and E. Lifshin, Scanning Electron Microscopy and X-Ray Microanalysis, Second ed., Plenum Press, New York, pp. 59–60 (1992).
Ibid.,pp. 514–515.
P. J. Statham, NBS Special Publication 604 (K. E J. Heinrich, D. E. Newbury, and R. L. Myklebust, eds.) National Bureau of Standards, Washington, DC, pp. 127–139 (1981).
S. A. S. Audet, personal communication (1993).
J. J. McCarthy and M. Misenheimer, Microbeam Anal. 2, S178 (1993).
J. I. Goldstein, D. E. Newbury, R Echlin, D. C. Joy, A. D. Roming, Jr.,C. E. Lyman, C. Fiori, and E. Lifshin, in: Scanning Electron Microscopy and X-Ray Microanalysis, Second Ed., Plenum Press, New York, p. 337 (1992).
J. J. McCarthy, M. W. Ales, and D. J. McMillan, in: Microbeam Analysis-1990, (J. R. Michael and Peter Ingram, eds.), San Francisco Press, San Francisco, pp. 79–84 (1990).
C. E. Cox, B. G. Lowe, and R. A. Sareen, IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 35, 28 (1988).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1995 Springer Science+Business Media New York
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Mott, R.B., Friel, J.J. (1995). Improving EDS Performance with Digital Pulse Processing. In: Williams, D.B., Goldstein, J.I., Newbury, D.E. (eds) X-Ray Spectrometry in Electron Beam Instruments. Springer, Boston, MA. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4615-1825-9_9
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4615-1825-9_9
Publisher Name: Springer, Boston, MA
Print ISBN: 978-1-4613-5738-4
Online ISBN: 978-1-4615-1825-9
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive