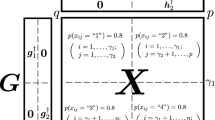Abstract
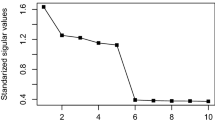
When I subjects answer questions regarding J variables K times, the data can be stored in a three-mode data set of size \(I \times J \times K\). Among the various component analysis approaches to summarize such data, Three-mode Principal Component Analysis (3MPCA) is often used. 3MPCA expresses a three-mode data set by means of A-, B-, and C-mode components and a core array, but this approach is not suitable for predicting data at unobserved time points. To handle this issue, the current study suggests a fixed orthonormal polynomial basis for the 3MPCA model. Briefly, we fix the C-mode component matrix with an orthonormal polynomial basis. More specifically, i) measurement time points, and ii) log transformation of the measurement time points were used as an orthonormal polynomial basis. The use of our proposed methods was demonstrated by applying them to a longitudinal data set collected from patients with depression.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersson, C.A., Bro, R: Improving the speed of multi-way algorithms: Part I. Tucker 3. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 42, 93–103 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0169-7439(98)00010-0
Hastie, T., Tibshirani, R.: Varying-coefficient models. J. Roy. Stat. Soc. Ser. B 55, 757–796 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.2517-6161.1993.tb01939.x
Kiers, H.A.: Joint orthomax rotation of the core and component matrices resulting from three-mode principal components analysis. J. Classif. 15(2), 245–63 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003579900033
Kiers, H.A., van Mechelen, I.: Three-way component analysis: principles and illustrative application. Psychol. Methods 6, 84–110 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1037/1082-989x.6.1.84
Kroonenberg, P.M., de Leeuw, J.: Principal component analysis of three-mode data by means of alternating least squares algorithms. Psychometrika 45, 69–97 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02293599
Kroonenberg, P.M.: Three-Mode Principal Component Analysis: Theory and Applications. DSWO Press, Leiden (1983)
Kroonenberg, P.M., Murakami, T., Coebergh, J.W.: Added value of three-way methods for the analysis of mortality trends illustrated with worldwide female cancer mortality (1968–1985). Stat. Methods Med. Res. 11, 275–92 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1191/0962280202sm287ra
Monden, R., Wardenaar, K.J., Stegeman, A., Conradi, H.J., de Jonge, P.: Simultaneous decomposition of depression heterogeneity on the person-, symptom-and time-level: the use of three-mode principal component analysis. PLoS ONE 10, e0132765 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0132765
Timmerman, M.E., Kiers, H.A.L.: Three-mode principal components analysis: Choosing the numbers of components and sensitivity to local optima. Br. J. Math. Stat. Psychol. 53, 1–16 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1348/000711000159132
Tucker, L.R.: Some mathematical notes on three-mode factor analysis. Psychometrika 31, 279–311 (1966). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02289464
Acknowledgments
The second and last authors’ research was partially supported by JSPS Bilateral Program Grant Number JPJSBP 120219927, and the last author’s research was partially supported by JSPS KAKENHI Grant Number 20H04151.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Monden, R., Nagai, I., Yanagihara, H. (2023). Implications of the Usage of Three-Mode Principal Component Analysis with a Fixed Polynomial Basis. In: Czarnowski, I., Howlett, R., Jain, L.C. (eds) Intelligent Decision Technologies. KESIDT 2023. Smart Innovation, Systems and Technologies, vol 352. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-2969-6_19
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-2969-6_19
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-99-2968-9
Online ISBN: 978-981-99-2969-6
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)