Abstract
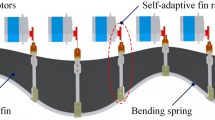
To improve the motion performance of the amphibious bionic robot, this paper combines the advantages of bionic propulsion mechanism and traditional p(ropulsion mechanism, and designs an amphibious robot with fast propulsion speed, strong environmental adaptability and high motion stability. It compounds with the wheel, undulatory fin, and propeller. Firstly, the present study analyses the kinetics of the undulatory fin propulsion and propeller propulsion based on the theory of fluid mechanics and flow resistance, and omnidirectional wheel steering characteristics. The mechanism of the robot’s thrust generation is known, which lays the foundation for the structural design. Then, through the analysis of the motion characteristics of the robot, the amphibious robot can realize turning in situ, ascending, descending and Land-Water transition by single or multiple propulsion. Finally, the experimental results show the robot has a maximum speed of 6.54 m/s on land and 1.1 m/s underwater and can pass through various scenarios such as vertical walls, sandy roads, gravel roads, grass, 25° ramps, and transitions between land and water. This type of robot has excellent performance and environmental adaptability, and can be used in the fields of resource detection and information collection in offshore areas, providing new ideas for the design of future amphibious robots.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wu, Z.Y., Qi, J., Zhang, S.: Amphibious robots: a review. Appl. Mech. Mater. 494–495, 1036–1041 (2014)
Kozlov, V., Seeman, M.: Outdoor navigation with a spherical amphibious robot. In: The 2010 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (2010)
Alvarez, J., Bertaska, I.R., Ellenrieder, K.V.: Nonlinear control of an unmanned amphibious vehicle. In: ASME Dynamic Systems & Control Conference (2013)
Rafeeq, M., Toha, S.F., Ahmad, S., Razib, M.A.: Locomotion strategies for amphibious robots-a review. IEEE Access 9, 26323–26342 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3057406
Zhang, S., Zhou, Y., Xu, M., Liang, X., Liu, J., Yang, J.: AmphiHex-I: locomotory performance in amphibious environments with specially designed transformable flipper legs. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 21(3), 1720–1731 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/TMECH.2015.2490074
Ohashi, T., Yamada, H., Hirose, S.: Loop forming snake-like robot ACM-R7 and its Serpenoid Oval control. In: 2010 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, pp. 413–418. Taipei, Taiwan (2010)
Wang, W., Yu, J., Ding, R., Tan, M.: Bio-inspired design and realization of a novel multimode amphibious robot. In: 2009 IEEE International Conference on Automation and Logistics, pp. 140–145. Shenyang, China (2009)
Bai, X.-J., Shang, J.-Z., Luo, Z.-R., Jiang, T., Yin, Q.: Development of amphibious biomimetic robots. J. Zhejiang Univ.-Sci. A 23(3), 157–187 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.A2100137
Wang, T., Wu, Y., Liang, J., Han, C., Chen, J., Zhao, Q.: Analysis and Experimental Kinematics of a Skid-Steering Wheeled Robot Based on a Laser Scanner Sensor. Sensors 15(5), 9681–9702 (2015)
Yin, S., Hu, Q., Zeng, Y., Wei, C., Chen, Z.: Kinetic analysis and design of a bio-inspired amphibious robot with two undulatory fins. In: 2021 IEEE International Conference on Real-time Computing and Robotics (RCAR), pp. 1368–1373. Xining, China (2021)
Ruoxin, L., et al.: A multi-body dynamics based numerical modeling tool for solving aquatic biomimetic problems. Bioinspir. Biomim. 13, 056001 (2018)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 Beijing HIWING Sci. and Tech. Info Inst
About this paper
Cite this paper
Tong, B., Hu, Q., Zeng, Y., Li, S., Zhang, T. (2023). Optimal Design and Motion Performance Analysis for the Novel Compound Amphibious Robot. In: Fu, W., Gu, M., Niu, Y. (eds) Proceedings of 2022 International Conference on Autonomous Unmanned Systems (ICAUS 2022). ICAUS 2022. Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering, vol 1010. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-0479-2_64
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-0479-2_64
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-99-0478-5
Online ISBN: 978-981-99-0479-2
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)