Abstract
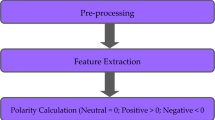
Many innovations are frequently rejected by the general public owing to controversies, which has a detrimental impact on their acceptance and their commercialization. Recently, there is an increase in the use of microblogging sites such as Twitter, Instagram, and Reddit, and thanks to these, the general public may convey their views and thoughts on any issue more easily than ever before. We aim to explore unlabelled Twitter data and use the sentiment analysis tool VADER on it to determine the general public’s perception of autonomous vehicles. The data from Twitter is pre-processed using the tools provided by the NLTK library, and then a sentiment intensity value is calculated for each tweet using VADER’s sentiment intensity analyser. We count the number of tweets that have positive, negative, or neutral impressions and identify why. We collected a total of 35,476 tweets and finally analysed 32,976 tweets after pre-processing.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gupta N, Fischer ARH, Frewer LJ (2012) Socio-psychological determinants of public acceptance of technologies: a review. Public Underst. Sci. 21(7):782–795
Hohenberger C, Spörrle M, Welpe IM (2017) Not fearless, but self-enhanced: the effects of anxiety on the willingness to use autonomous cars depend on individual levels of self-enhancement. Technol Forecast Soc Chang 116:40–52
Schoettle B, Sivak M (2014) A survey of public opinion about autonomous and self-driving vehicles in the US, the UK, and Australia. University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Transportation Research Institute
Fraedrich E et al. (2016) User perspectives on autonomous driving: a use-case-driven study in Germany
Penmetsa P, et al. (2021) Effects of the autonomous vehicle crashes on public perception of the technology. IATSS Res
Kohl C et al (2018) Anticipating acceptance of emerging technologies using twitter: the case of self-driving cars. J Bus Econ 88(5):617–642
National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (2013) Preliminary statement of policy concerning automated vehicles. Washington, DC 1:14
Hutto C, Gilbert E (2014) Vader: a parsimonious rule-based model for sentiment analysis of social media text. In: Proceedings of the international AAAI conference on web and social media, vol 8, no 1
Putra IAGS, Putri DR (2022) Analysis of public opinion sentiment on covid-19 vaccine based on social media. In: International conference on government education management and tourism, vol 1, no 1
Shelar A, Huang C-Y (2018) Sentiment analysis of twitter data. In: 2018 international conference on computational science and computational intelligence (CSCI). IEEE
Bird S, Klein E, Loper E (2009) Natural language processing with Python: analyzing text with the natural language toolkit. O’Reilly Media, Inc.
Sachdeva N, Sharma A, Sharma S (2021) Advertising and spams: how to recognize the lie and reality in social media. In: Data driven approach towards disruptive technologies. Springer, Singapore, pp 179–190
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Gupta, A.S., Sharma, S. (2023). Analysis of Public Perception of Autonomous Vehicles Based on Unlabelled Data from Twitter. In: Tuba, M., Akashe, S., Joshi, A. (eds) ICT Infrastructure and Computing. Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems, vol 520. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-5331-6_7
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-5331-6_7
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-19-5330-9
Online ISBN: 978-981-19-5331-6
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)