Abstract
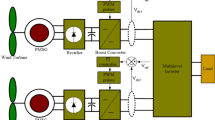
It uses a boost converter configuration, a multilevel converter, and a PI controller for a turbine related to the permanent magnet synchronous generator (PMSG) for coordinated network operation. In wind turbine generators, voltage and frequency are variable due to erratic wind flow. An inverter, a rectifier, and a boost converter are all part of a power converter. Here, we present a simple AC/DC conversion of a PM synchronous machine (PMSM) with maximum power point tracking (MPPT). The proposed topology makes use of five level of multilevel converters to transform the three-phase AC voltage generated by the PMSG into a set of DC hyperlink voltage. During this PI controller, variations within the obligation ratio and ceaselessly various output voltage are used to take care of the DC hyperlink voltage at fixed ranges. A multilevel converter offers direct power angle management attributable to its voltage-controlled rectifier. In this paper, we present a control technique for wind power conversion programs with no different energy storage units (ESS), which depends on the wind turbines’ management to easy the output power. Matlab/Simulink is used to create the model of the direct-drive PMSG-based wind power generation, together with simulation outcomes to validate the effectiveness of the power smoothing algorithm. The experiment within the laboratory shall be continued in future analysis.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aigner T, Jaehnert S, Doormain GL, Gjengedal T (2012) The effect of large-scale wind power on system balancing in Northern Europe. IEEE Trans Sustain Energy 3(4):751–759
Howlader AM, Senjyu T, Saber AY (2015) An integrated power smoothing control for a grid-interactive wind farm considering wake effects. IEEE Syst J 9(3):954–965
Howlader AM, Urasaki N, Yona A, Senjyu T, Saber AY (2013) A review of output power smoothing methods for wind energy conversion systems. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 26:135–146
Tasneem Z, Noman AA, Das SK, Saha DK, Islam MR, Ali1 MF, Badal MFR, Ahamed H, Moyeen SI, Alam F (2020) An analytical review on the evaluation of wind resource and wind turbine for urban application: prospect and challenges. ELSEVIER Dev Built Environ 4
Cardenas R, Pena R, Alepuz S, Asher G (2013) Overview of control systems for the operation of DFIGs in wind energy applications. IEEE Trans Industr Electron 60(9):2776–2798
Zhang Y-N, Cao H-J, Zhang M-M (2021) Investigation of leading-edge protuberances for the performance improvement of thick wind turbine airfoil1. J Wind Eng Industr Aerodyn 217:1–12
Shariatpanah H, Fadaeinedjad R, Rashidinejad M (2013) A new model for PMSG-based wind turbine with yaw control. IEEE Trans Energy Convers 28(4):929–937
Dey P, Datta M, Fernando N, Senjyu T (2018) Fault-ride-through performance improvement of a PMSG based wind energy systems via coordinated control of STATCOM. In: Conference 2018. IEEE, Lyon, pp 1236–1241
Skander-Mustapha S, Ghodbane-Cherif M, Slama-Belkhodja I (2020) Performance improvement of start-up system for small scale autonomous wind system. In: Conference 2020, IEEE, Hammamet
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Aarif, M., Joshi, D., Jangid, R., Sharma, S.S. (2023). Grid Power Smoothing Management for Direct-Drive PMSG Variable-Speed Wind Energy Conversion System with Multilevel Converter. In: Tuba, M., Akashe, S., Joshi, A. (eds) ICT Infrastructure and Computing. Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems, vol 520. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-5331-6_3
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-5331-6_3
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-19-5330-9
Online ISBN: 978-981-19-5331-6
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)